Alemtuzumab is Associated with Higher Rates of De Novo Donor Specific Antibody (DSA) in Patients with No Pre-Transplant DSA
Surgery, University of Wisconsin, Madison, WI.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 211
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Induction therapy, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: Room 6C
Introduction: Basiliximab, alemtuzumab, and thymoglobulin are the most commonly used induction agents in the US. While many centers use depleting antibody induction therapy in patients with DSA, the optimal induction for patients without pre-transplant DSA is not completely understood. The goal of this study is to compare the incidence of de novo DSA (dnDSA) and outcomes between induction therapies in patients with no pre-transplant DSA.
Methods: 1,147 adult patients undergoing kidney transplantation at a single high-volume institution between January 2013 and May 2017 were identified. Patients receiving multiple or no induction agents were excluded. 782 patients were identified as having a negative virtual cross match (VXM) (absence of DSA) and were included in this study. Kaplan-Meier analysis was used to assess the incidence of dnDSA and allograft survival between induction therapies in this group. DnDSA is defined as the development of new post-transplant DSA, at any MFI level.
Results: Of 782 included patients, the majority received basiliximab at 66.8%; 11.1% received alemtuzumab and 22.1% received thymoglobulin. Patients receiving alemtuzumab were less sensitized, more likely to be white, and younger (p<0.01). The overall incidence of dnDSA at 1 year in patients with a negative VXM was 7.2%. Patients who received alemtuzumab had the highest rate of dnDSA at 14.5% compared to 5.4% and 8.9% in the basiliximab and thymoglobulin groups, respectively (p=0.009). 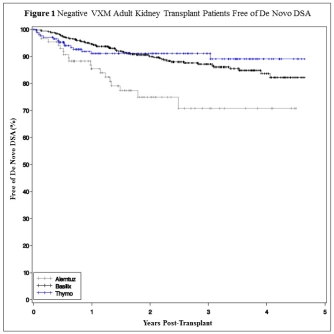 Importantly, there was no association between induction agent and overall actuarial graft survival (alemtuzumab 100%, basiliximab 98.2%, thymoglobulin 98.8%). There was no difference in graft survival for patients that developed dnDSA within 1 year after transplant compared to those that did not develop dnDSA.
Importantly, there was no association between induction agent and overall actuarial graft survival (alemtuzumab 100%, basiliximab 98.2%, thymoglobulin 98.8%). There was no difference in graft survival for patients that developed dnDSA within 1 year after transplant compared to those that did not develop dnDSA.
Conclusion: Alemtuzumab is associated with significantly higher rates of dnDSA in patients with no pre-transplant DSA when compared to basiliximab and thymoglobulin but had no impact on kidney allograft outcomes. Additional controlled analyses and long-term follow up are needed to more completely understand this finding.
CITATION INFORMATION: Bath N., Parajuli S., Leverson G., Jorgenson M., Fose J., Ellis T., Kaufman D., Djamali A., Redfield R. Alemtuzumab is Associated with Higher Rates of De Novo Donor Specific Antibody (DSA) in Patients with No Pre-Transplant DSA Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bath N, Parajuli S, Leverson G, Jorgenson M, Fose J, Ellis T, Kaufman D, Djamali A, Redfield R. Alemtuzumab is Associated with Higher Rates of De Novo Donor Specific Antibody (DSA) in Patients with No Pre-Transplant DSA [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/alemtuzumab-is-associated-with-higher-rates-of-de-novo-donor-specific-antibody-dsa-in-patients-with-no-pre-transplant-dsa/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
