Acute Renal Replacement Therapy in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: A Predictor of Increased Risk.
1Surgery, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
2Pediatric Gastroenterology, UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B273
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Outcome, Pediatric, Renal failure
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Pediatric Liver Transplant - Clinical
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background
Among pediatric patients (≤18 yrs) awaiting liver transplantation (LT), limited data exist on the prognostic significance of acute (<90d) renal replacement therapy (RRT) prior to LT.
Methods
Retrospective case-matched analysis (1 pre-LT RRT : 3 non-RRT) reviewed pediatric LTs performed at a university transplant center (136 pediatric LTs in 125 patients, 2008-2015). Factors affecting patient and graft survival were analyzed.
Results
Ten patients (12 LTs) received preoperative RRT, and were more often in the ICU, on vasopressors, and on mechanical ventilation (MV) pre-LT (p<0.05). Mean follow-up and post-LT length of stay (LOS) were similar between RRT and non-RRT groups. RRT patients had lower survival at hospital discharge and 30-days, 58% and 67%, respectively (p<0.05). Kaplan-Meier patient and graft survival were inferior in the RRT group (log-rank test p=0.046 & p=0.079) [Fig. 1]. A survival probability model using penalized regression predicted 30-day patient survival with 4 pre-LT variables: RRT duration, vasopressor need, MV, and LOS [Fig. 2].
Conclusion
In this largest series of acute RRT in pediatric LT, pre-LT RRT was associated with higher acuity and inferior short-term survival. Our model accurately differentiated survival probabilities, suggesting that recipients expected to have better post-LT outcomes can be identified even among the sickest patients.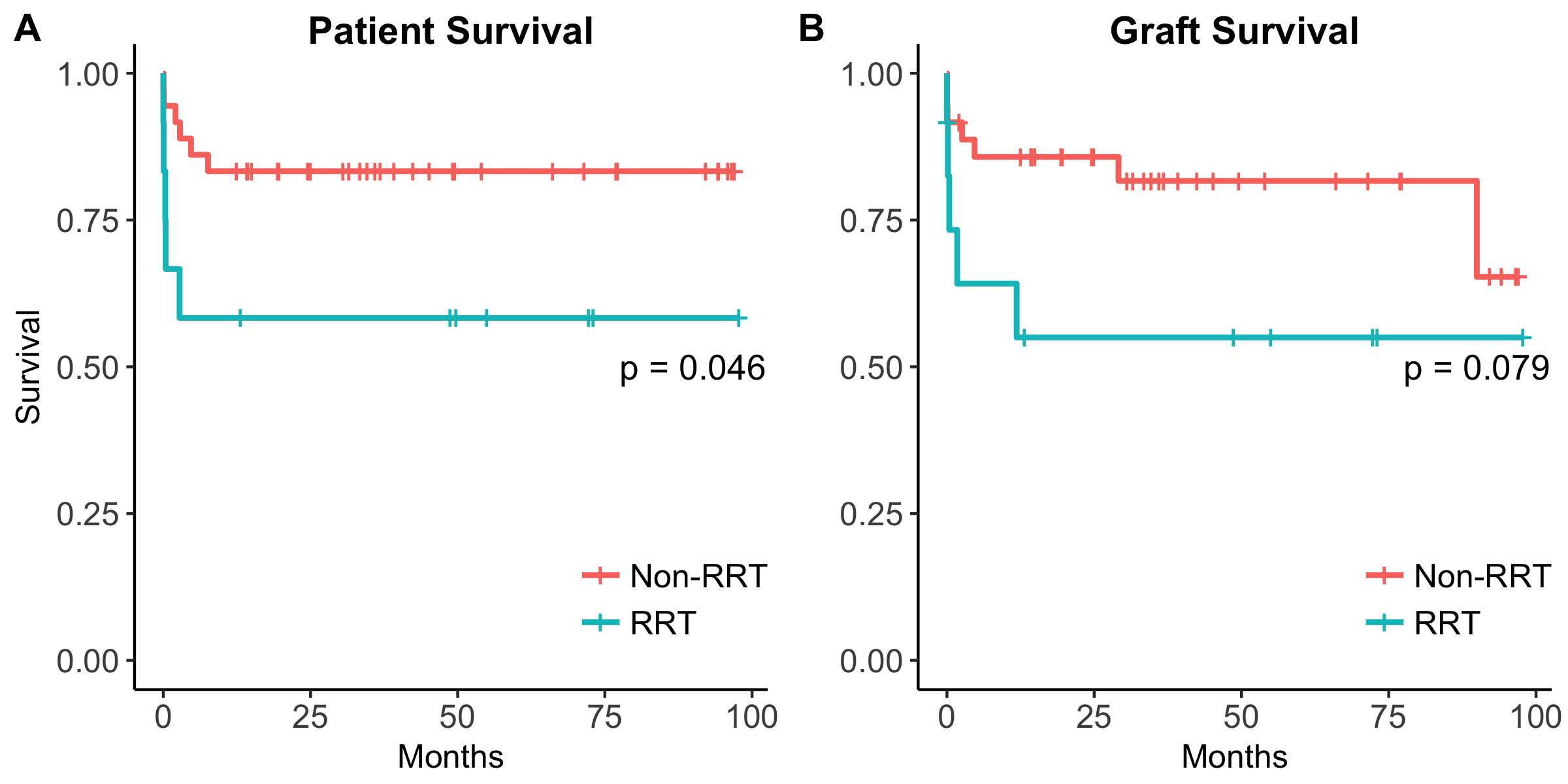 Fig. 1: Kaplan-Meier survival curves comparing (A) patient and (B) graft survival among RRT and non-RRT.
Fig. 1: Kaplan-Meier survival curves comparing (A) patient and (B) graft survival among RRT and non-RRT.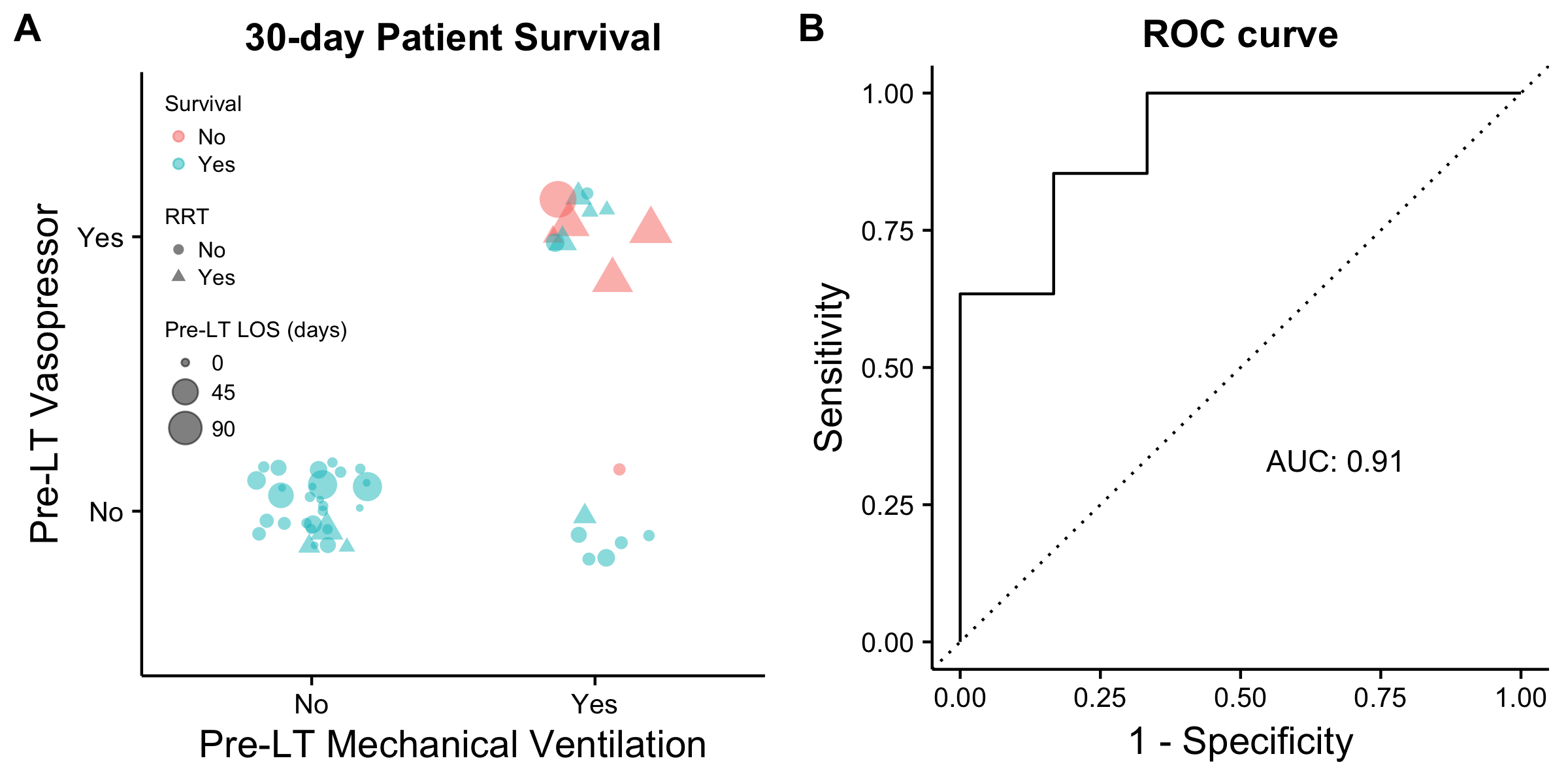 Fig. 2: Penalized regression model predicts 30-day patient survival using 4 pre-LT variables: RRT duration, vasopressor need, MV, and LOS (A). ROC curve of the model, concordance-statistic= 0.91 (B). ROC, receiver operator characteristic.
Fig. 2: Penalized regression model predicts 30-day patient survival using 4 pre-LT variables: RRT duration, vasopressor need, MV, and LOS (A). ROC curve of the model, concordance-statistic= 0.91 (B). ROC, receiver operator characteristic.
CITATION INFORMATION: Wong M, Venick R, Agopian V, Ebaid S, McDiarmid S, Zarrinpar A, Farmer D, Busuttil R, Kaldas F. Acute Renal Replacement Therapy in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: A Predictor of Increased Risk. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wong M, Venick R, Agopian V, Ebaid S, McDiarmid S, Zarrinpar A, Farmer D, Busuttil R, Kaldas F. Acute Renal Replacement Therapy in Pediatric Liver Transplantation: A Predictor of Increased Risk. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/acute-renal-replacement-therapy-in-pediatric-liver-transplantation-a-predictor-of-increased-risk/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
