ABO‐incompatible Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation
Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C242
Keywords: Graft failure, Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver grafts
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Liver: Recipient Selection
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
ABO-incompatible liver transplantation (ILT) has increased over the past decade despite reports suggesting that adult ILT recipient have worse outcomes than ABO-compatible liver transplant (CLT) recipients. We sought to determine if certain ILT recipient characteristics were associated with comparable outcomes to CLT.
Methods: We identified 730 ILT and 56822 CLT recipients from SRTR 2007-2016. We matched 3 CLTs for each ILT based on patient/donor characteristics. We compared all-cause graft failure using Kaplan-Meier estimators and Cox regression, stratified by age (pediatric, adult), HCC, Status-1, and MELD score.
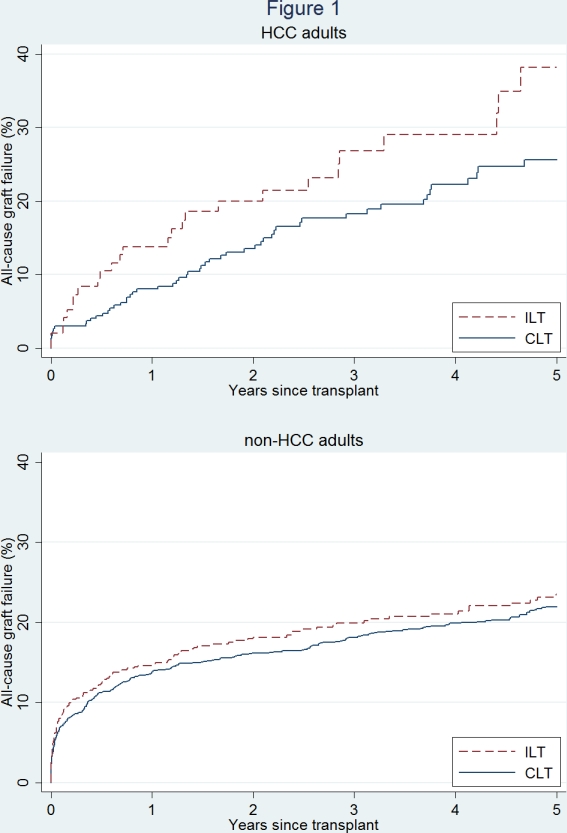
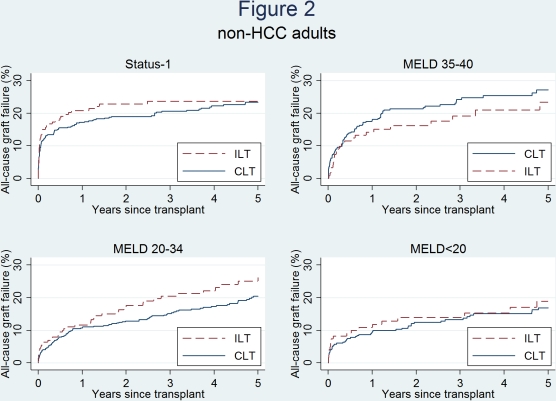
Results: Compared to CLTs (Table 1), ILTs were more likely to have higher MELD (26 vs 20), be Status-1 (24.7% vs 6.3%), and had previous liver transplants (8.2% vs 5.8%), but less likely to have HCC (20.5% vs 33.2%). ILT had similar 5-year graft failure with CLT among pediatric recipients (14.4% vs 17.1%, p=0.5), but higher graft failure among adult recipients (29.4% vs 24.4%, p=0.03). Among adult recipients (Figure 1), ILT was associated with significantly higher graft failure for recipients with HCC (HR=1.0011.602.56, p=0.0499), but similar graft failure rates for non-HCC recipients (HR=0.901.101.35, p=0.3). Further stratifying non-HCC recipients (Figure 2), ILT conferred comparable risk of graft failure among Status-1 (HR=0.781.121.60, p=0.5), MELD 35-40 (HR=0.500.791.25, p=0.3), MELD 20-34 (0.931.331.90, p=0.1), and MELD<20 (0.681.151.95, p=0.6).
Conclusions: ILT was associated with higher risk of graft failure among HCC adult recipients. However, the graft failure risk of ILT and CLT was comparable regardless of MELD, and ILT is acceptable for appropriate non-HCC patients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Luo X., Haugen C., Thomas A., Garonzik-Wang J., Segev D. ABO‐incompatible Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Luo X, Haugen C, Thomas A, Garonzik-Wang J, Segev D. ABO‐incompatible Deceased Donor Liver Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/aboincompatible-deceased-donor-liver-transplantation/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress