A Robust and Portable Protocol for RNA Isolation from Urinary Cells for Noninvasive Monitoring of Kidney Allograft Recipients
Weill Cornell, New York, NY
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B33
Keywords: Gene expression, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Monitoring and Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Urinary cell mRNA abundance, assessed by RT-qPCR assay, is a robust monitoring tool. In the CTOT-04 study, urine processed by 5 transplant sites were shipped to Gene core and 741 (17%) of 4300 urine pellets did not pass quality control [QC] parameters (N Engl J Med 2013;369:20-3). We aimed to optimize urine processing protocol.
*Methods: In our Gene Expression Monitoring (GEM) research laboratory, we incorporated a customized lysis buffer step in the RNA isolation protocol (lysate-enhanced RNA isolation protocol). RNA quantity (nanogram) and purity (OD 260/280) of samples stored at -80C were assessed by NanoDrop spectrophotometer. A sample was considered to have passed the QC parameters if the 18S rRNA was >5x10E7 copies and TGFb1 mRNA was >100 copies in one microgram of total RNA obtained from urinary cells.
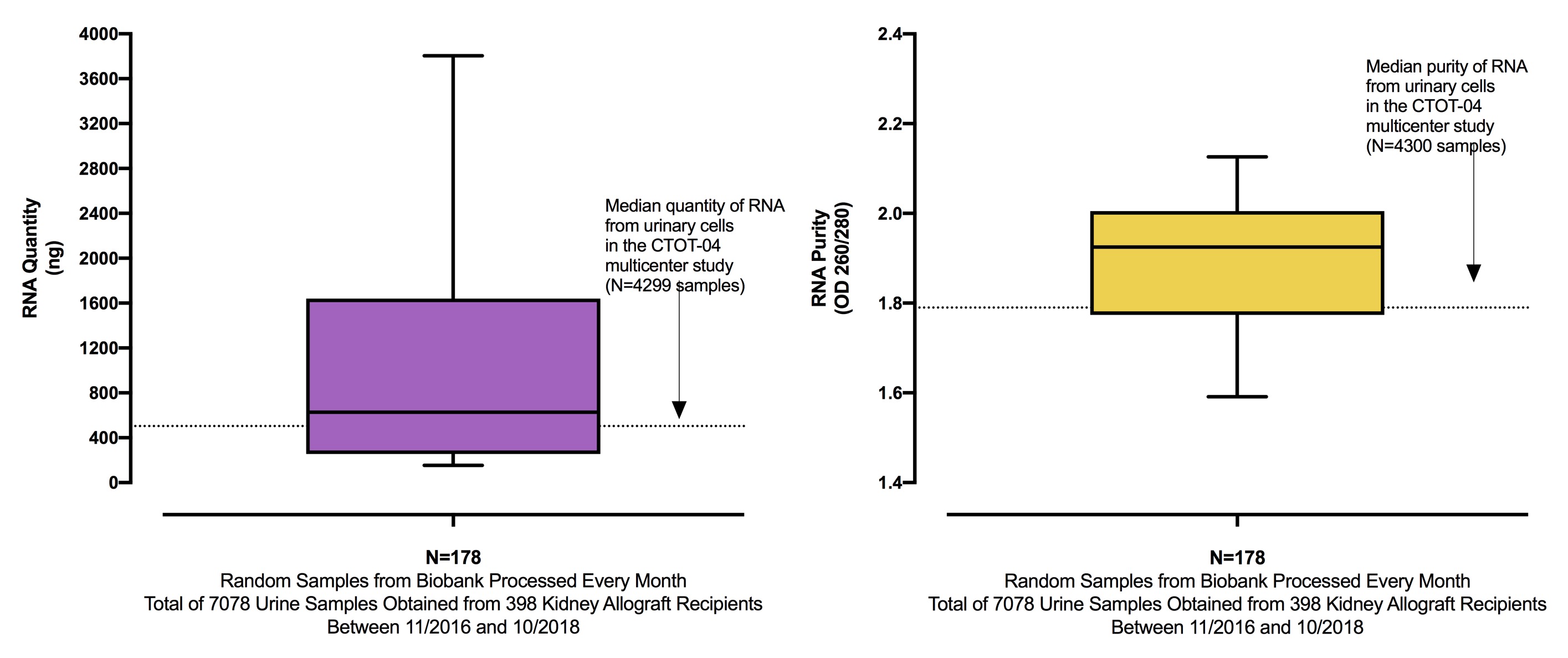
*Results: From a total of 7078 urine specimens systematically collected from 398 kidney allograft recipients enrolled in an NIH sponsored study and stored in our Biobank, 178 were randomly selected and processed using the lysate-enhanced RNA isolation protocol. The median (IQR) quantity of RNA isolated using this protocol was 627 ng (255-1641) and higher than that from the CTOT-04 study (504 ng [283-894]; purity was also higher 1.93 (1.77-2.01) vs. 1.79 (1.64-1.89) (Figure 1).
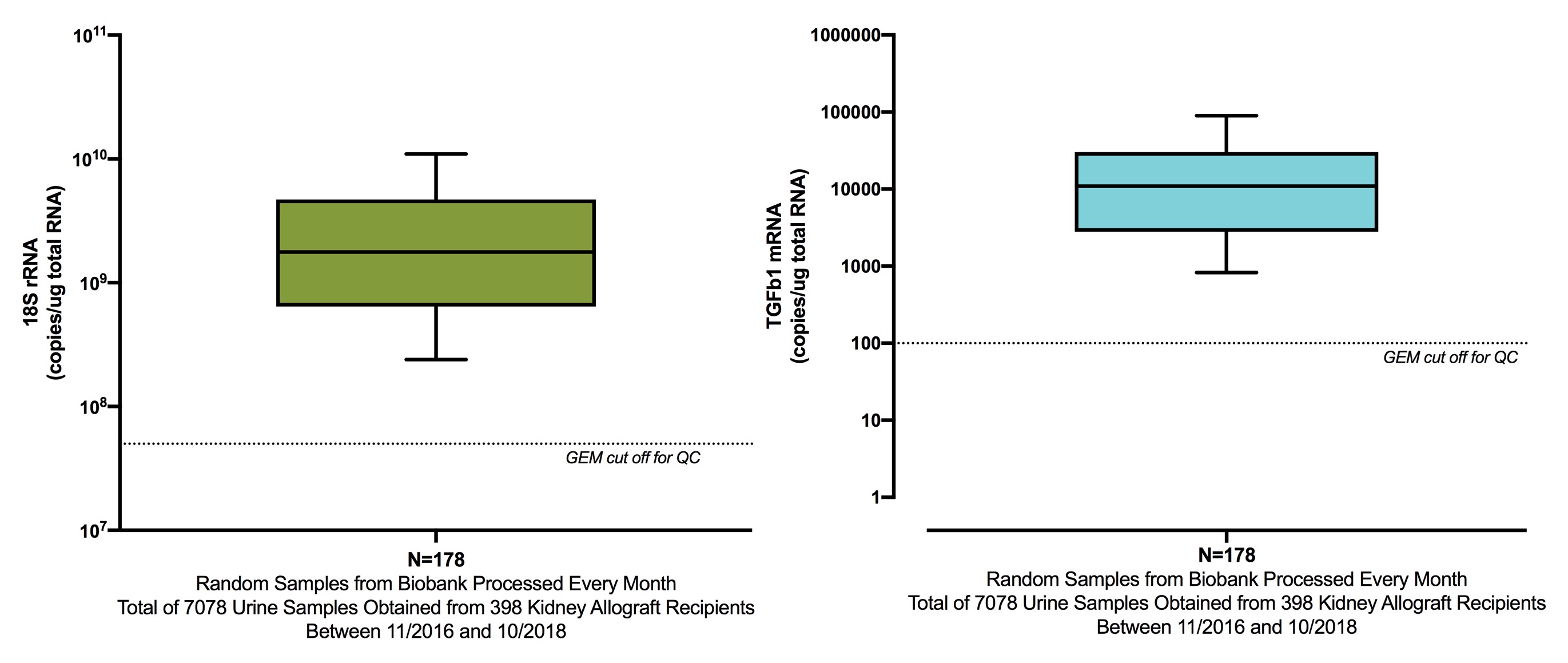
Figure 2 shows the abundance of 18S rRNA and TGFb1 mRNA processed with the lysate-enhanced protocol.
Importantly, of the 178 samples, 168 passed the pre-specified QC parameters (94.4% current study vs. 82.8% in CTOT-04 study, P<0.0001 Fisher's exact test).
*Conclusions: RNA isolation from urinary cells is challenging and requires considerable expertise. We report here further refinement of the RNA isolation protocol that ensures high quality RNA retrieval from urinary cell pellets. The versatile procedure is portable to other laboratories. a useful feature for wide spread adoption of urinary cell monitoring of human kidney allograft recipients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Botticelli B, Albakry S, Edusei E, Yang H, Cassidy M, Li C, Snopkowski C, Lubetzky M, Lee J, Dadhania D, Muthukumar T, Suthanthiran M. A Robust and Portable Protocol for RNA Isolation from Urinary Cells for Noninvasive Monitoring of Kidney Allograft Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-robust-and-portable-protocol-for-rna-isolation-from-urinary-cells-for-noninvasive-monitoring-of-kidney-allograft-recipients/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress