A New Reality: Virtual Crossmatch Can Be Used Successfully as Pre-Transplant Compatibility Testing for Most Deceased Donor Transplants at a High Volume Center
1Immunogenetics and Transplantation Laboratory, Dept. of Surgery, UCSF, San Francisco
2Dept. of Pathology, UCSF, San Francisco
3Dept. of Surgery, UCSF, San Francisco
4Dept. of Medicine, UCSF, San Francisco.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B93
Keywords: Alloantibodies, Allocation, Histocompatibility, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Aim: We developed a reliable virtual crossmatch (VXM) method for use as pre-transplant XM for deceased donor (DD) kidney transplantation (KTx). Here we report the biopsy results of 248 KTx performed based on neg-VXM.
Methods: Our VXM method includes 3 integral processes: accurate identification of HLA antibodies (Ab) using right tools and scientific principles, assessment of correlation between the strength of donor specific HLA Ab (DSA) and the level of T/B cell bindings by flow XM (FXM), and listing of clinically relevant unacceptable antigens that will not impact donor offers or graft survival. From the start of the new KAS through Dec. 2016, 434 DD-KTx were performed at UCSF, of which 375 (86%) were performed based on VXM (350 were VXM-ve with DSA+/- and 25 were VXM+ve with DP/DQα DSA). 59/434 (14%) of the KTxs were performed based on pre-tx FXM (54 were FXM-ve with DSA+/- and 5 were FXM+ve with DP DSA). Six month protocol/cause biopsies were evaluated for C4d and rejection.
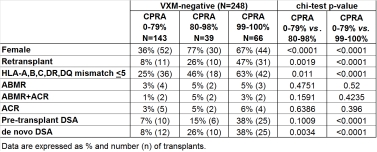
Results: All 350 pre-tx VXM-ve assessments were negative by retrospective FXM. There were no hyper acute rejections in these 350 Ktx. Biopsies of 273 neg-VXM-based KTx revealed no significant difference in the rate of antibody-mediated rejection (ABMR) or in acute cellular rejection (ACR) between 3 distinct CPRA groups. Females, re-KTx, well-matched KTx, and de nova DSA producers were more frequent in both 80-98% and 99-100% CPRA groups compared to 0-79% CPRA group. Pre-tx DSA was more common in 99-100% CPRA group compared to other groups.
Conclusions: Our VXM protocol is reliable, has excellent graft survival, and works even for those with 100% CPRA. Accurate VXM method improves organ allocation for broadly sensitized patients, increases the efficiency of regional/national sharing, and avoids reallocation into unintended recipients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Rajalingam R., Gae D., Laszik Z., Roll G., Tavakol M., Freise C., Adey D., Webber A., Dobi D., Cunniffe K., da Gente G., Ascher N., Stock P., Roberts J. A New Reality: Virtual Crossmatch Can Be Used Successfully as Pre-Transplant Compatibility Testing for Most Deceased Donor Transplants at a High Volume Center Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Rajalingam R, Gae D, Laszik Z, Roll G, Tavakol M, Freise C, Adey D, Webber A, Dobi D, Cunniffe K, Gente Gda, Ascher N, Stock P, Roberts J. A New Reality: Virtual Crossmatch Can Be Used Successfully as Pre-Transplant Compatibility Testing for Most Deceased Donor Transplants at a High Volume Center [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-new-reality-virtual-crossmatch-can-be-used-successfully-as-pre-transplant-compatibility-testing-for-most-deceased-donor-transplants-at-a-high-volume-center/. Accessed February 25, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress