A Hybrid Data Envelopment Analysis-Artificial Neural Network (DEANN) Technique for Extrapolating the Evolution of Kidney Transplant Patients
1Faculty of Economics and Management, Free University of Bolzano, Bolzano, Italy, 2Department of Economics and Management, University of Trento, Trento, Italy, 3Renal Transplant Unit, Department of Nephrology and Kidney Transplant, Hospital Clinic, Barcelona, Spain
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-089
Keywords: Graft function, Kidney transplantation, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Complications: Non-Immune Mediated Late Graft Failure
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The current study introduces a hybrid Data Envelopment Analysis (DEA) – Artificial Neural Network (ANN) technique to extrapolate the evolution of transplant patients based on the variables defining their pre-transplant profiles
*Methods: We focus on Living Donor Kidney Transplant (LDKT). Twelve input variables are used to generate the transplant profiles of the patients. Their post-transplant evolution is evaluated through six negative outputs, including rejection and death. The categorization of patients according to their relative performance is defined through two stages. The first one identifies the variables on which each patient underperforms and generates an evaluation index used as a reference training set for the two-layer feed-forward ANN implemented in the second stage.
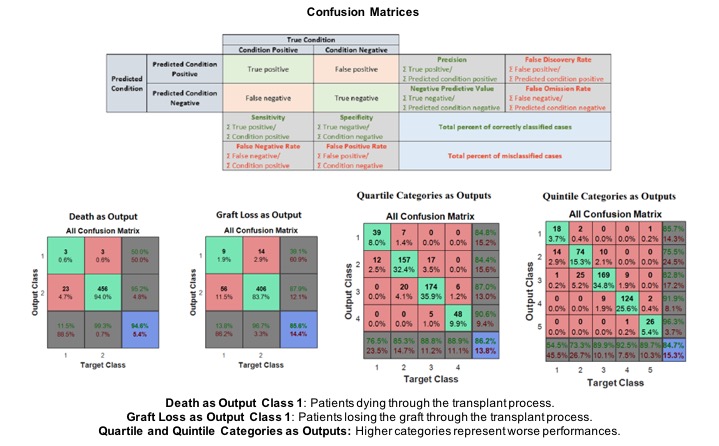
*Results: Data from 485 LDKT patients was retrieved through the 2006-2015 period. Given the profiles of the patients, DEA identifies each characteristic where an inefficiency occurs on a per patient basis as well as its magnitude relative to the reference benchmark defined by the best performing patients. Patients were then divided in quartile and quintile categories used to train the corresponding ANN. For comparison purposes, we illustrate the considerably poorer performance of the ANN when a unique variable such as graft loss or death is used as the reference output to train the algorithm.
*Conclusions: DEANN builds on the efficiency matrix derived from the DEA stage, which allows to train the ANN so as to extrapolate the behavior of patients based on their transplant profiles. Note that DEA can be used to incorporate fuzzy and uncertain variables to the analysis, which could not be otherwise evaluated through an ANN.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Santos-Arteaga F, Caprio DDi, Cucchiari D, Campistol JM, Oppenheimer F, Diekmann F, Revuelta I. A Hybrid Data Envelopment Analysis-Artificial Neural Network (DEANN) Technique for Extrapolating the Evolution of Kidney Transplant Patients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-hybrid-data-envelopment-analysis-artificial-neural-network-deann-technique-for-extrapolating-the-evolution-of-kidney-transplant-patients/. Accessed March 1, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress