6-Minute Walk Testing in Patients on the Kidney Transplant Waitlist
X. S. Cheng1, J. Lee2, K. V. Discipulo1, J. Myers3, J. C. Tan1
1Nephrology, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 2Kidney Transplant, Stanford Hospital, Palo Alto, CA, 3Cardiology, Veterans Affairs Palo Alto Health Care System, Palo Alto, CA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 323
Keywords: Age factors, Kidney transplantation, Waiting lists
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Ballroom C
*Purpose: Poor physical function in kidney transplant candidates is associated with frailty, sub-optimal transplant outcomes, and higher health care utilization. We need an instrument to objectively assess physical function in patients on the kidney waitlist. Our center began in-person re-evaluations of waitlisted patients with high allocation priority based on the new Kidney Allocation System. We used the 6-minute walk (6MWT) as a measure of cardiorespiratory fitness and 1-minute sit-to-stand tests (STS) as a measure of lower extremity strength. We hypothesize that 6MWT result is strongly correlated with STS result and incorporates information beyond co-morbidities.
*Methods: Nurse coordinators invited waitlisted patients with high allocation priority for evaluation at our Transplant Readiness Assessment Clinic (TRAC). We performed a retrospective chart review and data extraction of patients evaluated in TRAC from May 2017 through August 2018. A generalized estimating equation with clustering to account for multiple tests in the same patient was used to estimate the association between the covariates and 6MWT.
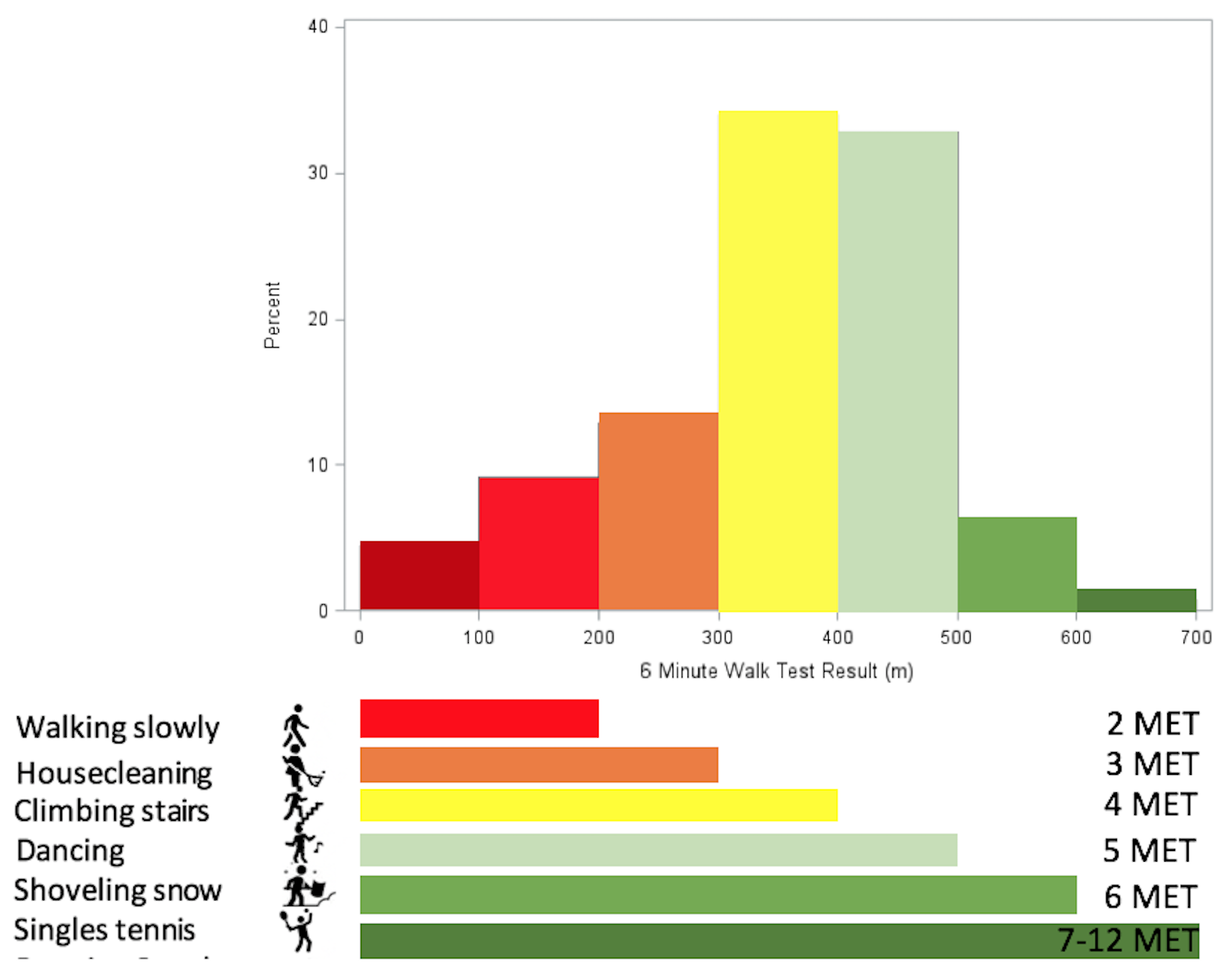
*Results: Over the study period, we evaluated 252 patients (Table 1). Mean 6MWT and STS results were 349±124 meters and 16±8 repetitions, respectively. 6MWT results were normally distributed over the range of common physical activities (Figure 1) and closely correlated with STS results (r=0.66). STS results were not normally distributed. In univariate regression, patient age, sex, dialysis duration, comorbidities, and STS were all associated with 6MWT performance. In multivariate regression, only age (p<0.0097), sex (p=0.0049) and STS result (p=0.005) were independently associated with 6MWT results.
*Conclusions: In waitlisted kidney transplant candidates, 6MWT is normally distributed and associated with lower extremity strength, age and sex but not other comorbidities. These findings suggest that the 6MWT is a promising metric to quantify cardiorespiratory fitness in kidney transplant candidates beyond traditional comorbidities.
| Variable |
Mean ± STD N (%) |
| Age (yr) | 56±12 |
| Sex (Male) | 134 (53%) |
| Dialysis duration (yr) | 7±3 |
| DM | 131 (52%) |
| CAD or equivalent | 98 (39%) |
| Prior coronary revascularization | 45 (18%) |
| LVH | 144 (57%) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheng XS, Lee J, Discipulo KV, Myers J, Tan JC. 6-Minute Walk Testing in Patients on the Kidney Transplant Waitlist [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/6-minute-walk-testing-in-patients-on-the-kidney-transplant-waitlist/. Accessed March 10, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress