5-Year Post-Transplant Outcomes with Bortezomib-Based Desensitization in Renal Transplant Recipients
1U of Cincinnati, Cincinnati, OH, 2Christ Hospital, Cincinnati, OH
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B174
Keywords: Antibodies, Highly-sensitized, HLA antibodies, Rejection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Kidney Immunosuppression: Desensitization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Renal transplant (RT) after desensitization (DS) has been associated with increased rejection rates. Proteasome inhibitor(PI)-based DS yields significant reductions in HLA Ab among sensitized RT candidates. Long-term post-RT outcomes following PI-based desensitization have not been reported. The purpose of this study was to assess: (1) overall patient survival, (2) rejection rate, and (3) death-censored graft survival up to 5-years post-RT following bortezomib-based DS (BBD).
*Methods: This was a retrospective matched case-control study of 140 adults who underwent RT between 11/2001-08/2013 who had 5-year follow-up data available. 20 BBD patients from a prior study were matched 1:3 to sensitized patients (African-American race, age, HLA mismatches, PRA) and unsensitized controls matched on identical factors except for PRA.
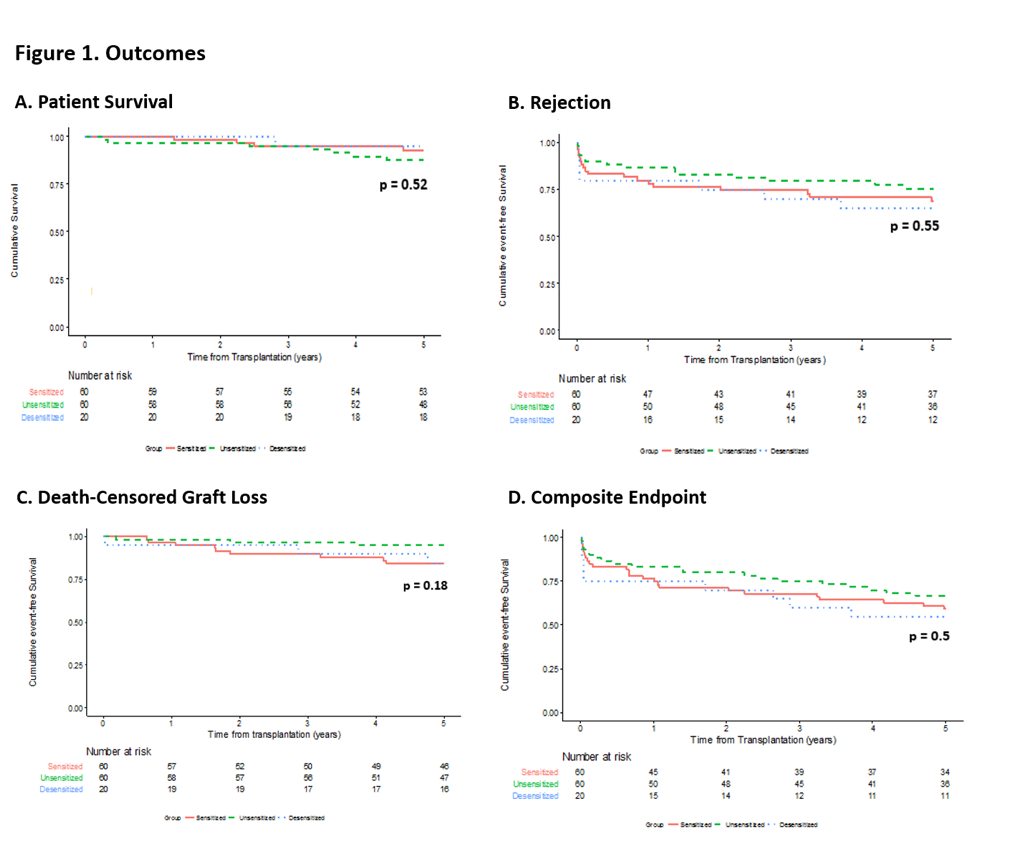
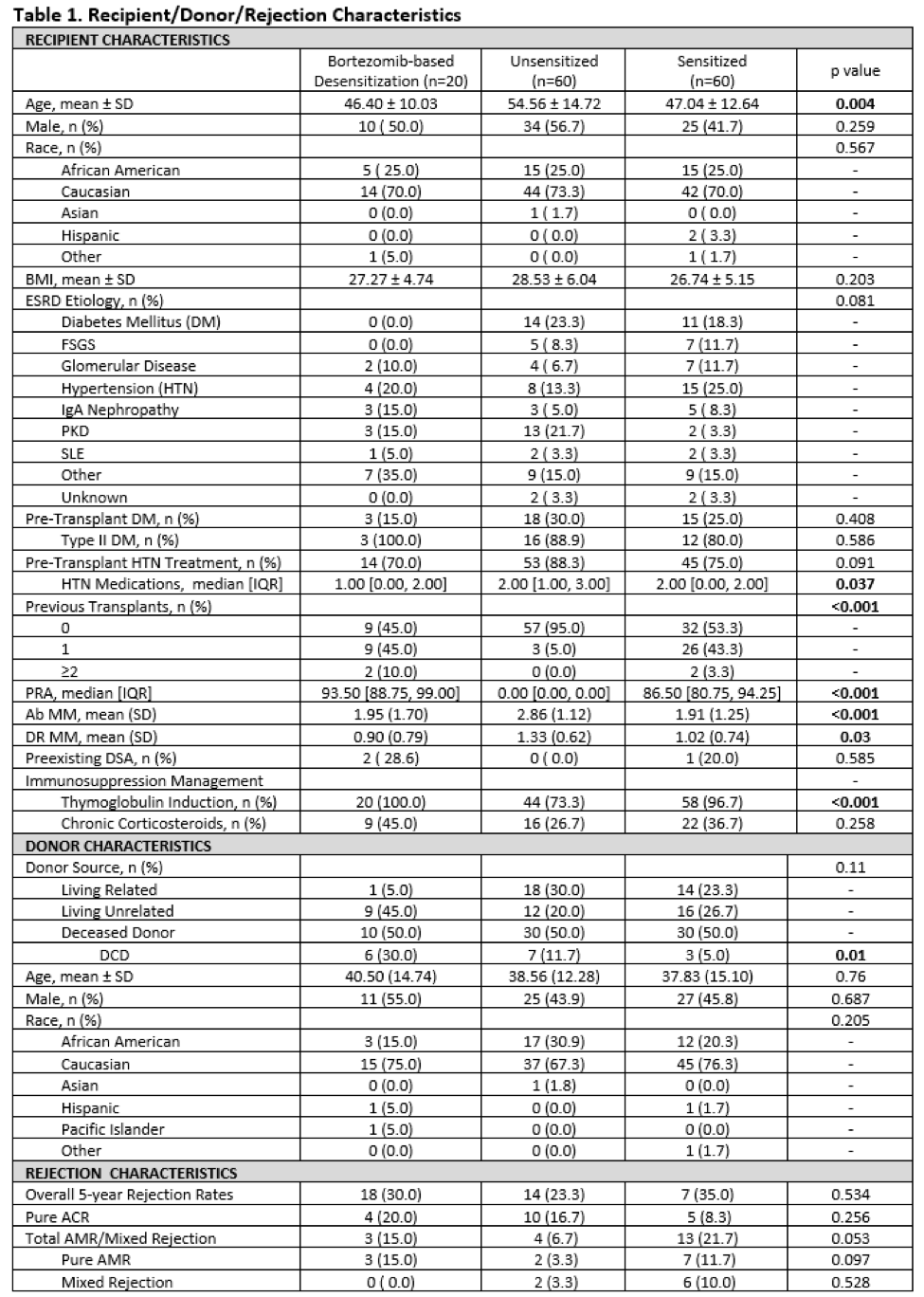
*Results: 5-year outcomes were compared for RT recipients from 3 groups: sensitized patients who received BBD (n=20), sensitized patients without desensitization (n=60), and unsensitized patients (n=60). Table 1 includes demographics. Figure 1 summarizes outcomes. No significant differences existed between the 3 cohorts in patient & death censored graft survival at 5-years post-RT. Regarding rejection(Table 1), numerical differences were observed between groups that approached statistical significance, most notable of which was a shift away from humoral to cellular rejection in the BBD group. This, along with absence of mixed acute rejection in the BBD group, suggests that prior BBD may modulate alloresponses following RT. Amongst rejecters, there was a higher proportion of humoral rejections in the sensitized group when compared to the other groups (p=0.044).
*Conclusions: Excellent patient & graft survival was observed in desensitized & sensitized patient groups. The primary long term effect of BBD appears to be a shift in the rejection type from humoral to cellular, with notable absence of late mixed rejection (which connotes the worst prognosis of all rejection subtypes). The observation of a potential immunomodulatory response by BBD to the renal allograft requires confirmation in a larger experience.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zheng K, Tremblay S, Shields AR, Cardi MA, Kremer J, Alloway RR, Woodle ES. 5-Year Post-Transplant Outcomes with Bortezomib-Based Desensitization in Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/5-year-post-transplant-outcomes-with-bortezomib-based-desensitization-in-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 19, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress