130 Totally Robotic Donor Hepatectomy: Reproducibility Of A Standardized Technique Across 2 Specialized Centers
1Roger L Jenkins Transplant Institute, Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington, MA, 2Division of HPB Surgery, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea, Republic of, 3Lahey Hospital & Medical Center, Burlington, MA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 9020
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Living donor, Surgery
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 57 - Liver: Surgery Innovative Techniques*
Session Information
Session Name: Late Breaking: Clinical
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 3:30pm-5:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:40pm-4:50pm
Presentation Time: 4:40pm-4:50pm
Location: Hynes Room 313
*Purpose: Robotic surgery is emerging as a feasible though complex technique to enable minimally-invasive donor hepatectomy.
*Methods: First multicenter prospective study on 130 consecutive totally robotic donor hepatectomies (2016-2021) using a standardized technique in 2 liver transplantation centers with experience and expertise in both living donor and robotic surgery. Donor demographic, operative and outcome data were collected. Standardization of surgical technique were ensured with initial in-person training and proctoring, followed by regular video analysis.
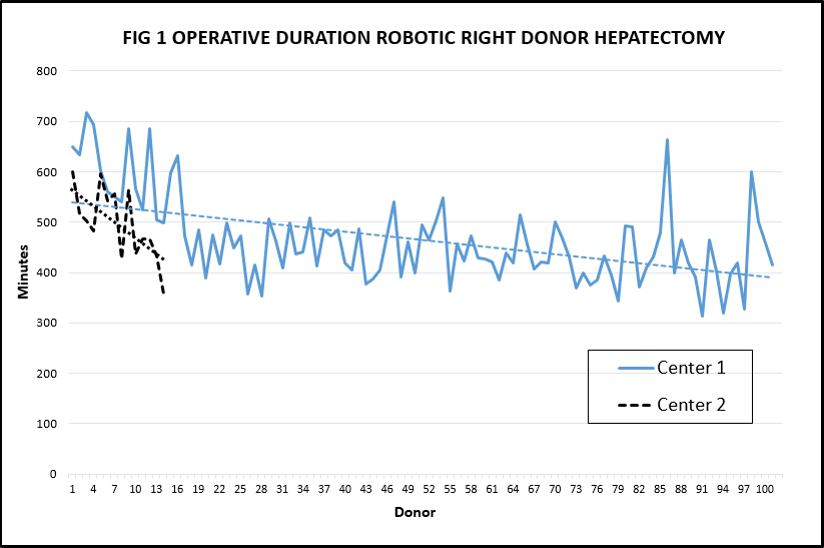
*Results: We performed 115 right (RH), 7 left and 8 left lateral segment robotic donor hepatectomy procedures. Average donor age 33, and weight 64.8kg. Majority of RH grafts had a single artery (99.1%), portal vein (89.6%) and bile duct (69.6%) for anastomoses. Most common arterial and bile duct anatomies were standard (88.7%) and Type 1 (74.8%; Korean classification) respectively. Average RH operative duration was 468mins; both centers showed improvement in this metric with experience (Fig1).
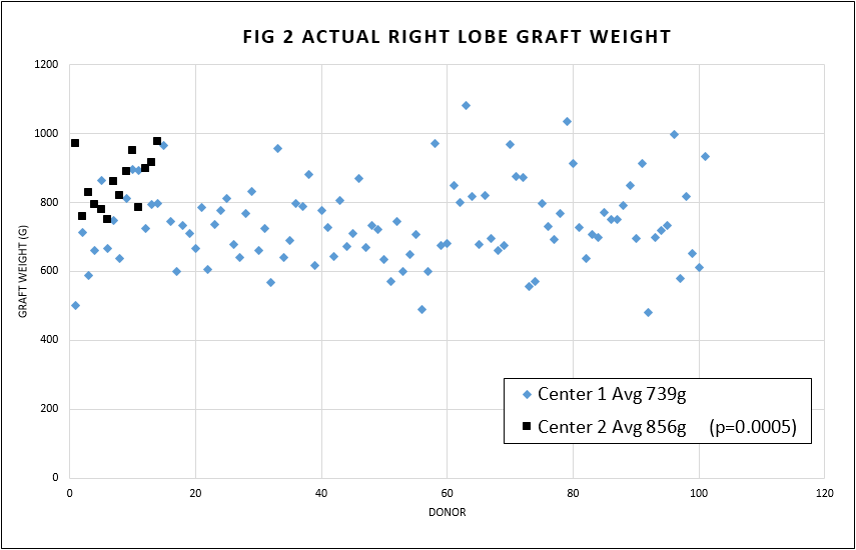
Average RH EBL was 127mls; 3 donors were transfused. No cases were converted to open or laparoscopic approach. There was significant difference in RH graft weights between the 2 centers (Fig2).
Majority of donors were started on solid diet on POD#1. Average highest recorded post-RH total bilirubin and INR were 2.6mg/dL and 1.4 respectively. Most common RH complications were bile leak (4.3%) and bleeding (2.6%). Rate of serious complications (Clavien ≥3) was 7.0% with zero mortality. There was no difference in overall or serious complication rates between the 2 centers.
*Conclusions: Our standardized technique for totally robotic donor hepatectomy, though complex and relatively novel, can be reproduced in another specialized robotic transplantation center with appropriate training, regular evaluation of surgical technique, prospective monitoring of outcomes and utmost attention to donor safety.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cheah Y, Yang H, Simon CJ, Kim J, Akoad M, Choi G. 130 Totally Robotic Donor Hepatectomy: Reproducibility Of A Standardized Technique Across 2 Specialized Centers [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/130-totally-robotic-donor-hepatectomy-reproducibility-of-a-standardized-technique-across-2-specialized-centers/. Accessed February 18, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress