Cardiac Troponin T (cTNT) in the Assessment of Kidney Transplant (KTx) Benefit and Risk
F. Cosio,1 A. Grupper,1 P. Dean,2 H. Amer.1
1Nephrology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
2Surgery, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 380
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, May 5, 2015
Session Time: 2:15pm-3:45pm
 Presentation Time: 2:51pm-3:03pm
Presentation Time: 2:51pm-3:03pm
Location: Terrace I-III
Introduction. Compared to waiting list (WL) KTx improves patient survival. However, mortality may increase early post-KTx. cTNT level at candidate evaluation is a strong, independent predictor of WL and KTx mortality. We used cTNT to better define the risk/benefit related to KTx versus WL.
Methods. Included are 2059 adults approved for KTx 2000-2011, 57% male, age 52+13, 34% diabetes (DM), 23% ischemic heart disease (IHD) and 43% not on dialysis at evaluation. All patients had cTNT measured at evaluation. During 63+30 months 1430 candidates (69%) received a KTx 77% from living donor. 436 (21%) died. Low risk candidates were defined as having no DM, no IHD and age<55. High risk as having DM or IHD or age>55.
Results. Mortality was greatly reduced after KTx (time dependent, HR=0.19 (0.15-0.24), p<0.0001) independent of factors related to high mortality: DM (HR=1.48, p<0.0001), dialysis (HR=1.63, p<0.0001), older (HR=1.43 x10y, p<0.0001), IHD (HR=1.39, p<0.0001) and higher cTNT (HR=2.79, p<0.0001) (multivariate Cox). cTNT was normal in 48% or mildly elevated (<0.03 ng/ml) in 21%. Mortality did not differ in these 2 groups. Mortality was increased in candidates with moderate (0.04-0.1) or high (>0.1) cTNT (HR=1.56 and 2.22, p<0.0001). 741 candidates (36%) were low risk (Figure, 1/2) but 114 (15%) had high cTNT and high WL mortality (HR=2.65, p=0.001). In low risk, KTx reduced mortality (HR=0.153, p<0.0001) particularly in those with high cTNT. 1318 candidates (64%) were high risk (Figure, 3/4). High cTNT (512, 36%) related with high WL (HR=2.30, p<0.0001) and KTx mortality (HR=1.34, p=0.001). In all high risk, KTx reduced mortality (HR=0.190, p<0.0001). Compared to WL, KTx was not associated with higher early mortality.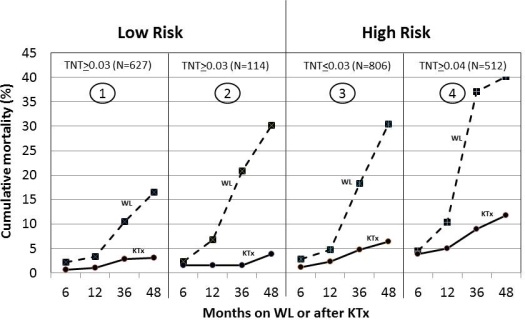
Discussion. KTx is associated with reduced mortality in all candidates. 15% presumed of low risk candidates have high cTNT and high risk. However, KTx rapidly reverses risk. In contrast, 64% of high risk candidates have low cTNT and mortality comparable to low risk. KTx benefit was variable and best estimated by cTNT and clinical parameters. Neither parameter alone is sufficient to estimate benefit
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Cosio F, Grupper A, Dean P, Amer H. Cardiac Troponin T (cTNT) in the Assessment of Kidney Transplant (KTx) Benefit and Risk [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/cardiac-troponin-t-ctnt-in-the-assessment-of-kidney-transplant-ktx-benefit-and-risk/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
