Impact of ATG Dose Reduction on Kidney Transplant Outcomes During the Covid-19 Pandemic
1Transplant Surgery, UC Davis, Sacramento, CA, 2Pathology, UC Davis, Sacramento, CA, 3Transplant Nephrology, UC Davis, Sacramento, CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1379
Keywords: Antilymphocyte antibodies, COVID-19, Kidney, Rejection
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » 37 - Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Immunosuppression: Induction Therapy
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Monday, June 6, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: During the COVID-19 pandemic, many transplant centers modified induction immunosuppression regimens. Beginning December 2020, our center reduced anti-thymocyte globulin (ATG) protocol dosing by up to 33% compared to the pre-pandemic doses (7.5, 4.5, and 3mg/kg, per immunologic risk) for all recipients, with no change in maintenance immunosuppression. We examined the impact of reduced ATG dose on kidney allograft and transplant recipient outcomes.
*Methods: We retrospectively reviewed adult recipients who received a kidney transplant between December 2020 and March 2021 (pandemic) with a minimum of 6 months follow up post-transplant, and recipients who received a transplant between January 2019 and December 2019 (pre-pandemic). We chose 2019 as a comparable pre-pandemic cohort as they were treated without influence from the COVID-19 pandemic. We abstracted patient demographic and laboratory data from electronic health records. We excluded multi-organ transplant recipients.
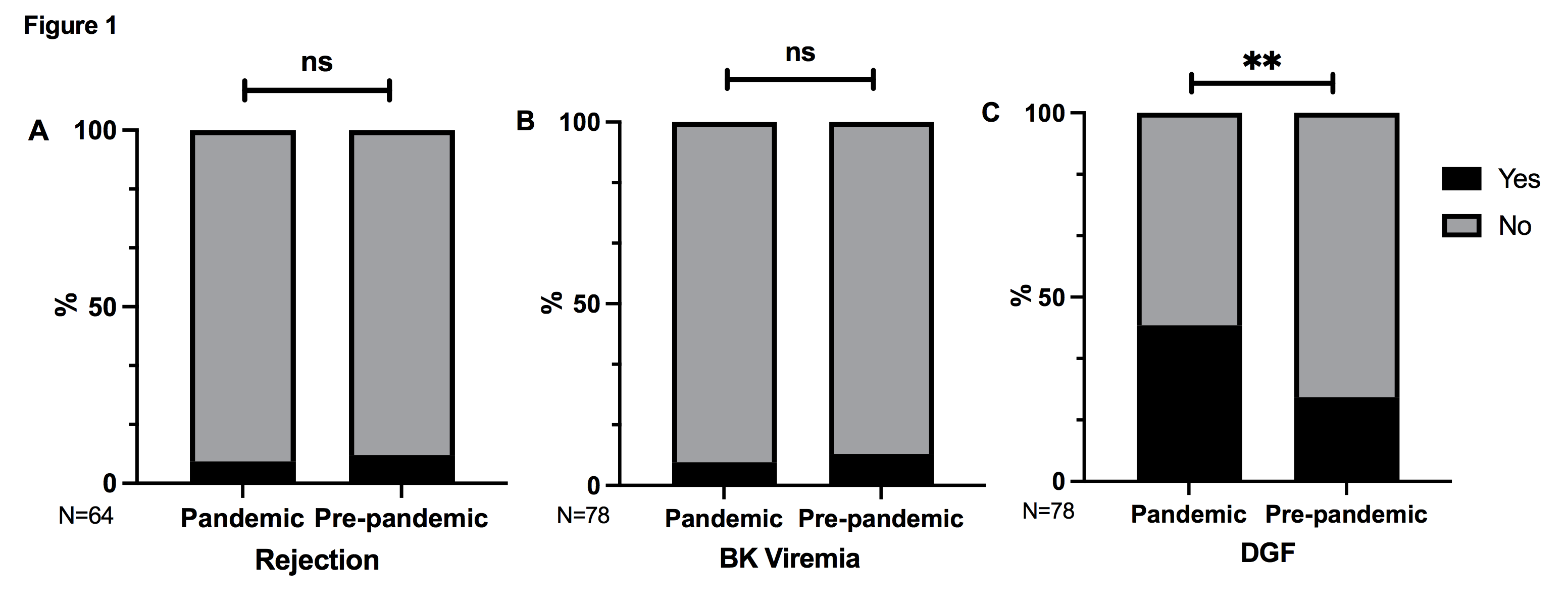
*Results: 78 adult kidney transplants were performed during the pandemic era and 211 were performed during the pre-pandemic era. The characteristics of the two cohorts are illustrated in Table 1. The primary outcomes are illustrated in Figure 1. The rate of biopsy proven rejection (including surveillance and for-cause biopsies) did not increase during the pandemic as compared to pre-pandemic era (6.3% vs 8.0%, respectively, p=0.8). The rate of BK viremia (>1000 copies/mL) at 3 months was lower in the pandemic era, but not statistically significant (6.4% vs 8.7%, respectively, p=0.6). The rate of delayed graft function (DGF) was significantly higher in the pandemic era compared to pre-pandemic (42.3% vs 22.9%, respectively, p=0.002). No recipients tested positive for COVID-19 within 1-month of transplant.
*Conclusions: Despite the reduction in ATG dose, we found no significant change in the rate of rejection or infection. We did however find a significant increase in the rate of DGF during the pandemic era. Further studies are needed to assess the long-term effects of reduced induction immunosuppression regimen on kidney transplant recipients.
| Pre-pandemic (N=211) | Pandemic (N=78) | |
| cPRA >= 40 (%) | 84 (39.8) | 17 (21.8) |
| Type of Transplant (%) | ||
| Deceased Donor | 144 (68.2) | 74 (94.9) |
| Donation After Circulatory Death | 43 (20.4) | 32 (41.0) |
| Kidney Donor Profile Index (%) (IQR) | 46 (23-65) | 61 (41-83) |
| Cold Ischemia Time (hours)+/- SD | 16.0 (13.0) | 19.2 (9.6) |
| Time to Biopsy (days) (IQR) | 90 (90-105) | 92 (87-96) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Than PA, Leon FDe, Jen K, Goussous N, Perez RV, Wang AX. Impact of ATG Dose Reduction on Kidney Transplant Outcomes During the Covid-19 Pandemic [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/impact-of-atg-dose-reduction-on-kidney-transplant-outcomes-during-the-covid-19-pandemic/. Accessed February 17, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress