Alcohol Renal Syndrome: Alcohol Related Liver Disease for Liver Transplant is Associated with Renal Dysfunction
Westchester Medical Center / New York Medical College, Valhalla, NY
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1071
Keywords: Alcohol, Kidney, Liver transplantation, Renal dysfunction
Topic: Clinical Science » Liver » 52 - Liver: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Liver: Kidney Issues in Liver Transplantation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Date: Sunday, June 5, 2022
Session Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
 Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Presentation Time: 7:00pm-8:00pm
Location: Hynes Halls C & D
*Purpose: Liver transplantation (LT) due to alcohol related liver disease (ALD) has been increasing in the US. Alcohol has been known to increase the risk of renal dysfunction, and advanced liver disease has been known to impair kidney function in the form of hepatorenal syndrome. However, there is limited understanding of the combined effect of alcohol and liver disease on kidney function. The aim of this study is to investigate the effect of ALD compared to non-ALD on renal dysfunction.
*Methods: We performed a retrospective analysis of adult patients (Age>=18) who underwent LT between January 2002 and June 2021 at our institution. We compared the outcomes of LT and renal dysfunction for LT in patients with ALD and non-ALD.
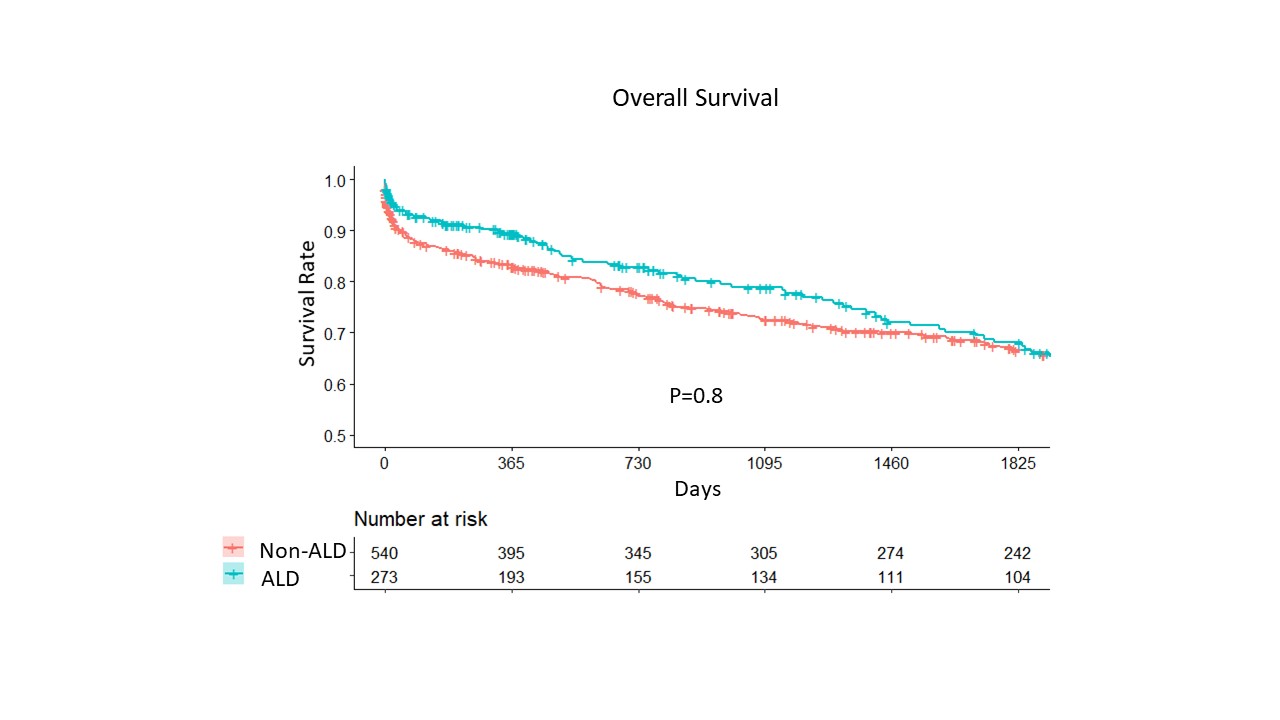
*Results: A total of 840 patients had liver transplant during the study period. Two hundred eighty four patients (34%) were transplanted for ALD. The median age (IQR) was younger in patients with ALD than non-ALD [54 (48-60) vs 56 (49-63), p<0.001]. The median MELD score in LT patients with ALD was significantly higher than that of patients with non-ALD [26 (16-35) vs 20 (13-31), p <0.001]. Although there were no significant differences in sodium or creatinine levels at the time of transplant, patients with ALD were more likely to be on dialysis than non-ALD patients [76 (26.8%) vs 69 (12.4), p<0.001]. On multivariate logistic regression analyses for renal dysfunction, ALD was significantly associated with renal dysfunction [Odds Ratio (95% CI) = 2.06 (1.48-2.87) p<0.001]. The overall 5-year survival rate was similar for both groups (68.1% vs 66.5%, p=0.82).
*Conclusions: The current study suggests that ALD is significantly associated with renal dysfunction in LT patients, providing evidence for an “Alcohol Renal Syndrome.” Further investigation is warranted to evaluate the effect of alcohol and liver disease on kidney function.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lee J, Okumura K, Misawa R, Sogawa H, Veillette G, John D, Partiula B, Bodin R, Wolf DC, Diflo T, Nishida S. Alcohol Renal Syndrome: Alcohol Related Liver Disease for Liver Transplant is Associated with Renal Dysfunction [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/alcohol-renal-syndrome-alcohol-related-liver-disease-for-liver-transplant-is-associated-with-renal-dysfunction/. Accessed February 15, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress