Repeat Liver Transplantation after Failed First Transplant in Childhood: Development of a Retransplant Risk Index
1University of Kentucky, Lexington, KY, 2University of California, San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 3University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C312
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Pediatric, Retransplantation, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Liver: Pediatrics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall C & D
*Purpose: Most morbidity and mortality after pediatric liver retransplantation (LRTx) occurs in the first 100 days. We studied factors associated with mortality and graft failure within the first 100 days after pediatric LRTx.
*Methods: Second liver transplant data after a first failed pediatric liver transplant were obtained from the Organ Procurement Transplant Network (OPTN). A multivariable Cox Regression analysis and retransplant risk index (RtRI) were generated to determine factors associated with early failure (graft failure or death) among recipients of pediatric first liver transplant.
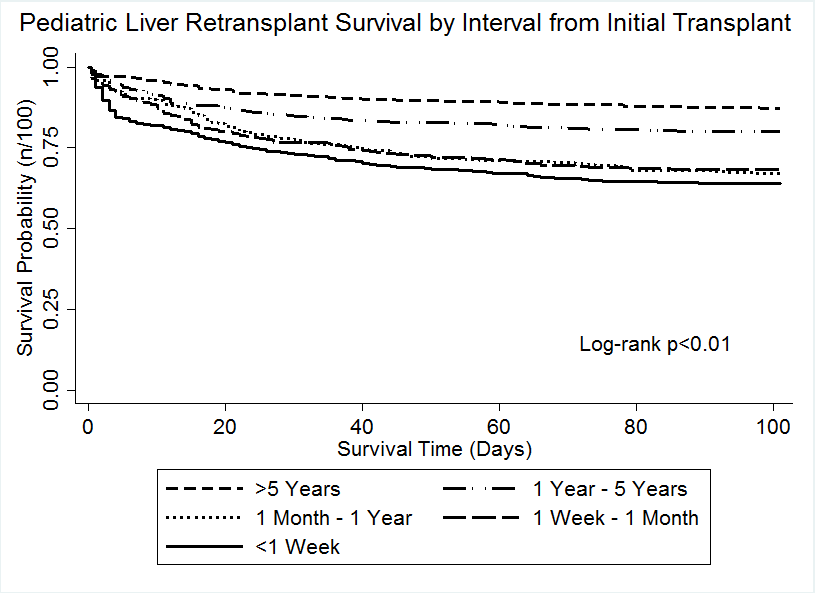
*Results: Of 1,822 recipients, 467 (25.6%) experienced failure within 100 days after LRtx. Inferior pediatric first transplant survival of <1 year conferred poor survival after LRTx. (Figure 1); 1 month-1 year [HR=1.86(1.21-2.84)] and 1 week-1 month [HR=1.56(1.01-2.41)]. Additional pre-transplant factors significantly associated with outcomes include, ventilator dependence [HR=2.56(1.90-3.46)], total bilirubin of >12.0 [HR=1.63(1.14-2.35)], dialysis status [HR=1.52(1.12-2.06)], and year of transplant prior to 1995 [HR=2.18(1.38-3.44)] and between 1995-2001 [HR=1.77(1.30-2.42)] . RtRI values above 2.0 revealed significant decline in three-month outcomes. (Table 1) Those without exception had higher RtRIs. (*Data for recipients in the era of transplant exception access). We provide an adjusted RtRI calculator based on combinations of factors.
*Conclusions: Pediatric first transplant survival predicts early LRTx outcomes. The RtRI may be used to identify individuals at high risk for inferior outcomes, and thus justify more urgent transplant and/or exception score for patients awaiting pediatric liver retransplantation.
| RtRI | N(%) | 3 Month Survival (%) | Exception* N=158 | No Exception* N=63 | Never Applied* N=656 |
| 0.00-1.00 | 221(12.1) | 89.0(84.0-92.5) | 96(60.8%) | 18(28.6%) | 107(6.7%) |
| 1.01-2.00 | 444(24.4) | 89.5(86.3-92.1) | 53(33.5%) | 24(38.1%) | 367(22.9%) |
| 2.01-3.00 | 253(13.9) | 79.4(73.8-83.9) | 2(1.3%) | 5(7.9%) | 246(15.4%) |
| 3.01-4.00 | 206(11.3) | 75.1(68.6-80.5) | 4(2.5%) | 6(9.5%) | 196(12.2%) |
| 4.01-5.00 | 148(8.1) | 66.2(58.0-73.2) | 3(1.9%) | 3(4.8%) | 142(8.9%) |
| >5.00 | 550(30.2) | 54.7(50.4-58.8) | 0(0.0%) | 7(11.1%) | 543(33.9%) |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Gupta M, Barry M, Levine M, Olthoff K, Shaked A, Abt P. Repeat Liver Transplantation after Failed First Transplant in Childhood: Development of a Retransplant Risk Index [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/repeat-liver-transplantation-after-failed-first-transplant-in-childhood-development-of-a-retransplant-risk-index/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress