Clinical Utility of CMV-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Immune Competence Score in Lung and Heart-Lung Transplant Recipients at Risk of Cytomegalovirus Infection
1Division of Infectious Diseases, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN
2Laboratory Medicine and Pathology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, MN.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C251
Keywords: Cytomeglovirus, Infection
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Lung: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Cytomegalovirus (CMV) is a common infection that causes significant morbidity among lung and heart-lung (LHL) transplant recipients. We determined the clinical utility of global CD8+ T cell and CMV-specific CD8+ T cell assay as predictor of CMV infection after LHL transplantation.
Methods: During a 10-year period, selected LHL transplant recipients underwent analysis of CMV-specific CD8+ T cells (CMV-CD8+; quantitatively and functionally) using MHC class I tetramers with CMV peptides (n=5). Functional assessment included measurement of interferon-gamma (IFNg) production and CD107a/b degranulation after stimulation with either CMV peptides (antigen-specific) or PMA/ionomycin (global CD8+ T cell). A T cell immune competence (TIC) score was derived from the CMV-CD8+ quantitative and functional data. CMV infection was diagnosed by PCR in blood and other clinical samples or histopathology. Per protocol, valganciclovir prophylaxis was given for 6 months (CMV R+) or at least one year (CMV D+/R-).
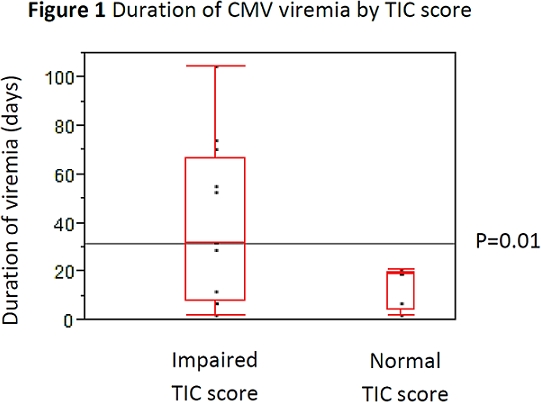
Results: Sixty-four LHL transplant patients positive for MHC Class I alleles HLA A1, A2, B7, B8, and/or B35 were tested for TIC score. The median age is 60 years (IQR: 42-64), and most (56%) were male. The majority was CMV R+ (60%); 30% were CMV D+/R-. CMV infection occurred in 27 patients (42.2%) at a median of 15.9 months (IQR: 10-6-22.6) post-transplant. CMV infection developed in 41% of patients with impaired TIC score or global CD8+ T cell function. Normal TIC score was associated with shorter duration of CMV viremia compared to impaired TIC score (18.7 vs. 31.6 days, p=0.01) (Figure 1). Likewise, normal TIC score and global CD8+ T cell function was associated with a lower rate of CMV relapse (13 vs. 75%, p=0.03).
Conclusion: Monitoring for TIC score and global CD8+ T cell function can be useful clinical guide in managing LHL transplant patients at risk of CMV infection. An impaired TIC score and global CD8+ T cell function is associated with a high rate of CMV infection, longer duration of viremia, and high rate of relapse.
CITATION INFORMATION: Meesing A., Abraham R., Razonable R. Clinical Utility of CMV-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Immune Competence Score in Lung and Heart-Lung Transplant Recipients at Risk of Cytomegalovirus Infection Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Meesing A, Abraham R, Razonable R. Clinical Utility of CMV-Specific CD8+ T-Cell Immune Competence Score in Lung and Heart-Lung Transplant Recipients at Risk of Cytomegalovirus Infection [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/clinical-utility-of-cmv-specific-cd8-t-cell-immune-competence-score-in-lung-and-heart-lung-transplant-recipients-at-risk-of-cytomegalovirus-infection/. Accessed February 20, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress