Risk Factors for Chronic Opioid Use after Liver Transplantation
J. Fleming, D. Taber, B. O'Brien, N. Patel, N. Pilch, R. Gilbert, L. Wilson, Z. Elmaasarani, S. Ball, P. Mauldin, P. Baliga.
MUSC, Charleston, SC.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 379
Keywords: Liver transplantation, Psychosocial, Risk factors
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Psychosocial and Treatment Adherence
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Presentation Time: 4:42pm-4:54pm
Location: Room 3AB
Opioid use is associated with increased readmissions and mortality in the liver transplant (OLTx) population. The aim of our study was to identify risk factors for chronic opioid use in OLTx.
METHODS: Single-center, retrospective cohort study of OLTx between 1/10-12/16. Data was collected via manual chart abstraction and use of a pharmaceutical claims database. Patients that filled an opioid prescription in more than 3 months in the year after transplant (excluding the month of transplant) were identified as chronic opioid users (COU). Multivariable logistic regression with backward elimination was performed to identify risk factors for COU in the overall OLTx population, as well as the opioid naïve and experienced subpopulations.
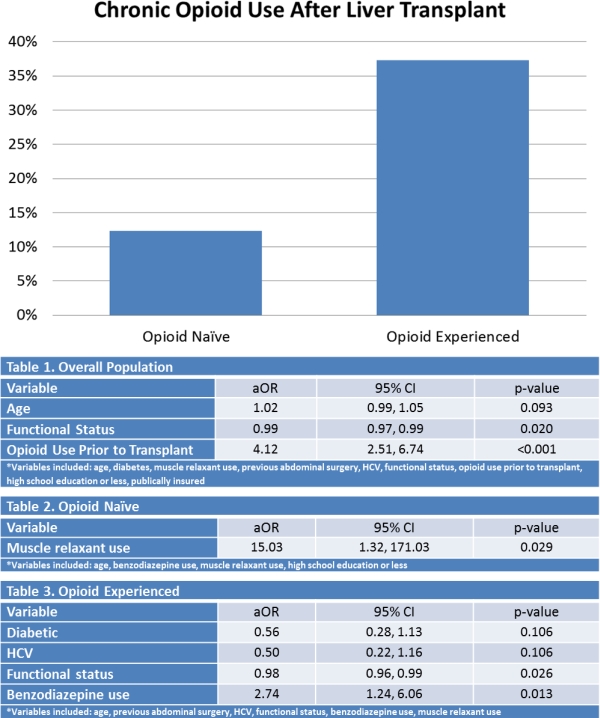
RESULTS: 446 patients were included in the analysis, 101 (23%) of whom were COU after transplant. Significantly more opioid experienced patients were COU after OLTx compared to opioid naïve patients (69 (37.3% vs 32 (12.3%), p<0.001) (figure 1). In the overall OLTx cohort, risk factors for COU included lower functional status and opioid use prior to transplant (table 1). In the opioid naïve cohort, the only risk factor for COU was muscle relaxant use (table 2). In the opioid experienced cohort, risk factors for COU included lower functional status and benzodiazepine use at the time of transplant (Table 3).
CONCLUSIONS: The strongest risk factor for COU after OLTx is pre-transplant opioid use. Within the opioid experienced subpopulation, lower functional status and concomitant benzodiazepine use independently impact the risk of COU. Muscle relaxant use was the only independent risk factor for opioid naïve patients.
CITATION INFORMATION: Fleming J., Taber D., O'Brien B., Patel N., Pilch N., Gilbert R., Wilson L., Elmaasarani Z., Ball S., Mauldin P., Baliga P. Risk Factors for Chronic Opioid Use after Liver Transplantation Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleming J, Taber D, O'Brien B, Patel N, Pilch N, Gilbert R, Wilson L, Elmaasarani Z, Ball S, Mauldin P, Baliga P. Risk Factors for Chronic Opioid Use after Liver Transplantation [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/risk-factors-for-chronic-opioid-use-after-liver-transplantation/. Accessed January 24, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress