Optimizing Survival Outcomes for Advanced Age Patients Undergoing Liver Transplant.
Houston Methodist Hospital, Houston, TX
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B201
Keywords: Elderly patients, Liver transplantation, Outcome, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Liver Retransplantation and Other Complications
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Objectives
Age at liver transplant (LT) is progressively increasing and is a known risk factor for mortality. We sought to evaluate preTx predictors for mortality among advanced age pts (AAP, age>65).
Methods
Retrospective analysis of 394 primary deceased donor LTs performed from 2008-14 at a single center.
Results
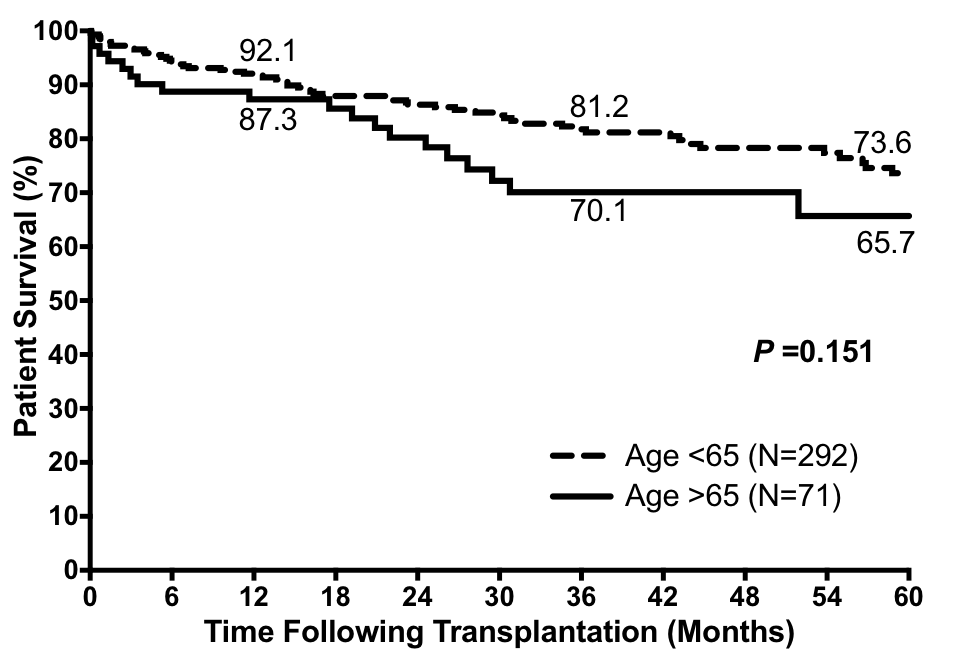
Of 363 LTs, 71 (19.6%) were in AAP. Medical acuity (Table) and survival were similar in AAP compared to younger pts (YP, age<65, p=ns, Figure). AAP were more likely than YP to have HCC (p=0.02), coronary artery disease (CAD, p<0.01), valvular disease (p=0.03), hypertension (p<0.01), and renal insufficiency (CRI, p=0.04). Among cardiac risk factors, AAP were more likely to have undergone CABG or PCI (p=0.05), and had decreased cardiac output (p<0.001), elevated pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR, p<0.01), and decreased stroke volume (p=0.02) (Table). Multivariate predictors of mortality in AAP included CRI (HR 4.4, CI 1.7-11.3, p<0.01) and CAD (HR 3.7, CI 1.0=13.3, p=0.04) but not medical acuity. Mortality in AAP most commonly resulted from sepsis (30%, 6/20) or cardiac disease (25%, 5/20).
| Age <65 (n=292) | Age >65 (n=71) | p-value | |
| Age (yrs) | 55.4 (22-64.8) | 67.2 (65-77) | <0.01 |
| HCC | 111 (38%) | 37 (52%) | 0.02 |
| MELD >35 | 87 (30%) | 20 (28%) | ns |
| ICU | 102 (35%) | 21 (30%) | ns |
| Ventilation | 64 (22%) | 18 (25%) | ns |
| HTN | 134 (46%) | 47 (66%) | <0.01 |
| CAD | 40 (14%) | 22 (31%) | <0.01 |
| CRI | 51 (18%) | 20 (28%) | 0.04 |
| CVD | 182 (62%) | 53 (75%) | 0.03 |
| PCI/CABG | 9 (3%) | 6 (9%) | 0.05 |
| CO | 8.2 (3-24.7) | 6.8 (2.2-13.3) | <0.01 |
| PVR | 159 (27-529) | 213 (80-388) | <0.01 |
| SV | 111 (41-211) | 94 (48-149) | 0.02 |
Despite high acuity, survival following LT in AAP is similar to that seen YP; however, AAP demonstrate increased comorbidities. Attention to CRI and CAD is warranted when considering AAP for LT, given the impact on survival.
CITATION INFORMATION: Balogh J, Lunsford K, Nguyen D, Gravis E, Saharia A, Mobley C, Gordon Burroughs S, Cercio O, Victor D, Monsour H, Gaber A, Ghobrial R. Optimizing Survival Outcomes for Advanced Age Patients Undergoing Liver Transplant. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Balogh J, Lunsford K, Nguyen D, Gravis E, Saharia A, Mobley C, Burroughs SGordon, Cercio O, Victor D, Monsour H, Gaber A, Ghobrial R. Optimizing Survival Outcomes for Advanced Age Patients Undergoing Liver Transplant. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/optimizing-survival-outcomes-for-advanced-age-patients-undergoing-liver-transplant/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress