Share35: Increasing Biliary Complications and Healthcare Resources?
1Pharmacy, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC
2Surgery, Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC
3Surgery, East Carolina University, Greenville, NC
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 138
Keywords: Allocation, Liver transplantation, Post-operative complications, Resource utilization
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver Allocation, Utilization, and Machine Perfusion
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: E451a
Data has shown that major outcomes of liver transplant post-Share35 have been equivalent to pre-Share35, despite organs accumulating longer CIT and traveling further.
The PURPOSE of this study was to evaluate the effect of Share35 on post-transplant biliary complications using the University Healthcare Consortium registry. Secondarily, mean direct transplant costs and length of stay were also assessed.
Methods: This was a retrospective interrupted time study analysis of post-transplant outcomes, comparing the slope of aggregate data pre-Share35 and post-Share35.Data from all adult OLTx at UHC-affiliated centers from 10/2012 to 9/2015 were included.
Results: Seventy-four of 130 (57%) liver transplant programs were included in the UHC database, corresponding to 65% of all adult liver transplants during this time frame. Differences between the cohorts in regards to baseline demographics were in line with the changing population of liver transplant recipients. There was a significant difference in the slope of biliary complications over time since the implementation of Share35 (p=0.023). Additionally, although not statistically significant, the Pre-Share35 decreasing slope in direct costs of transplant and mean length of stay post-transplant were slowed or reversed after the implementation of Share35.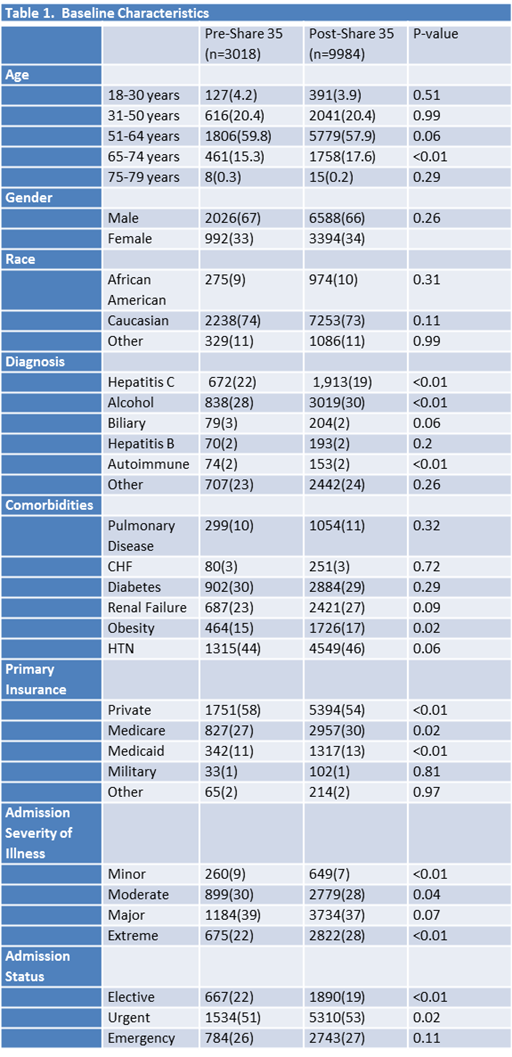
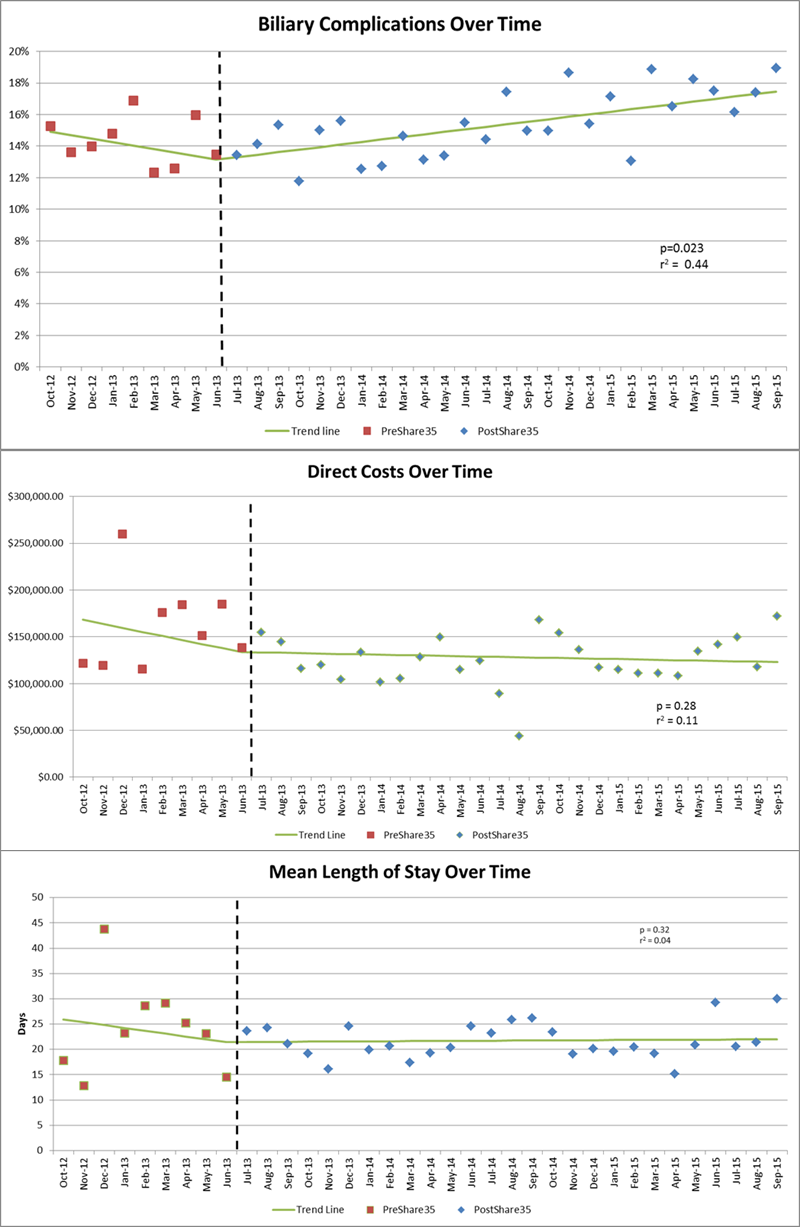 Conclusion: The implementation of Share35 has been associated with an increasing prevalence of biliary complications over time. Additionally, the previous trends of decreasing cost of transplantation and length of stay post-transplant appear to have changed course after the implementation of Share35.
Conclusion: The implementation of Share35 has been associated with an increasing prevalence of biliary complications over time. Additionally, the previous trends of decreasing cost of transplantation and length of stay post-transplant appear to have changed course after the implementation of Share35.
CITATION INFORMATION: Fleming J, Perez C, Sobhanian M, Taber D, Chedister G, Axelrod D, Chavin K. Share35: Increasing Biliary Complications and Healthcare Resources? Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Fleming J, Perez C, Sobhanian M, Taber D, Chedister G, Axelrod D, Chavin K. Share35: Increasing Biliary Complications and Healthcare Resources? [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/share35-increasing-biliary-complications-and-healthcare-resources/. Accessed February 17, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
