Multicenter Validation of a Clinicopathologic Risk Score to Predict Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Following Liver Transplantation: Analysis of 4984 Patients from the US Multicenter HCC Transplant Consortium.
UCLA, LA
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 21
Keywords: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Liver transplantation, Recurrence, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Clinical Science: Liver - Hepatocellular Carcinoma
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Location: E451b
Objective: Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) following liver transplantation (LT) negatively impacts survival. Existing risk prediction models either lack external validation or limit their scope to patients within the Milan criteria. We sought to develop and validate a risk assessment tool for individualized prediction of post-LT HCC recurrence generalizable for all HCC patients and across all UNOS regions.
Methods: A novel clinicopathologic risk score predicting post-LT HCC recurrence was developed from a multivariate competing-risk Cox regression analysis in 4984 consecutive patients from 20 US centers spanning 10 of the 11 UNOS regions (2002-2013).
Results: At a median follow-up of 46.5 months, overall patient and recurrence-free survivals were 90%, 79%, 70% and 87%, 75%, 67% at 1-, 3-, and 5-years, with a cumulative incidence of HCC recurrence of 4.7%, 10%, 12.5%, respectively. 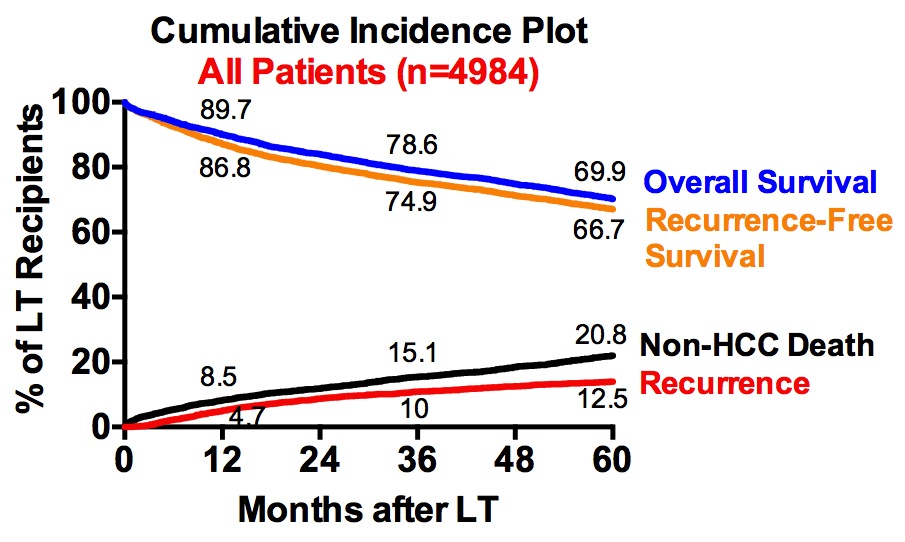 Multivariate predictors of survival included pathologic maximum tumor diameter, vascular invasion, tumor differentiation, and pre-LT maximum alphafetoprotein and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, with a model C-statistic of 0.78 in the training set (n=3262) and 0.76 in the independent validation group (n=1722). A risk score model based on the multivariate predictors was developed to allow for individualized prediction of post-LT HCC recurrence risk.
Multivariate predictors of survival included pathologic maximum tumor diameter, vascular invasion, tumor differentiation, and pre-LT maximum alphafetoprotein and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio, with a model C-statistic of 0.78 in the training set (n=3262) and 0.76 in the independent validation group (n=1722). A risk score model based on the multivariate predictors was developed to allow for individualized prediction of post-LT HCC recurrence risk. 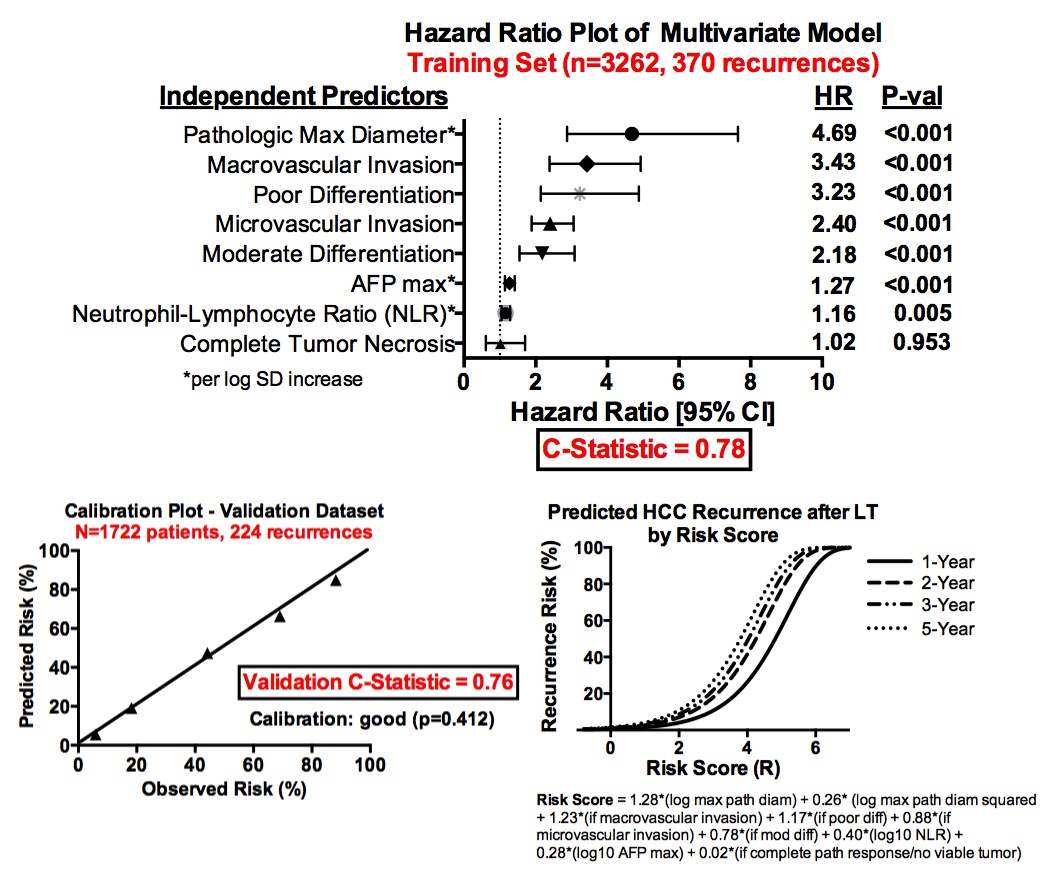 Conclusions: We report outcomes from the largest multicenter experience of LT for HCC, and develop and validate a simple, risk score calculator for individualized prediction of post-LT HCC recurrence risk that is 1) generalizable to all HCC patients across the United States and 2) may be used to guide frequency of post-LT surveillance and selection of high-risk patients who may benefit from developing adjuvant therapies.
Conclusions: We report outcomes from the largest multicenter experience of LT for HCC, and develop and validate a simple, risk score calculator for individualized prediction of post-LT HCC recurrence risk that is 1) generalizable to all HCC patients across the United States and 2) may be used to guide frequency of post-LT surveillance and selection of high-risk patients who may benefit from developing adjuvant therapies.
CITATION INFORMATION: Agopian V, On Behalf of the US Multicenter HCC Transplant Consortium Multicenter Validation of a Clinicopathologic Risk Score to Predict Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Following Liver Transplantation: Analysis of 4984 Patients from the US Multicenter HCC Transplant Consortium. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Agopian V. Multicenter Validation of a Clinicopathologic Risk Score to Predict Hepatocellular Carcinoma Recurrence Following Liver Transplantation: Analysis of 4984 Patients from the US Multicenter HCC Transplant Consortium. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/multicenter-validation-of-a-clinicopathologic-risk-score-to-predict-hepatocellular-carcinoma-recurrence-following-liver-transplantation-analysis-of-4984-patients-from-the-us-multicenter-hcc-transplan/. Accessed February 18, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
