A Pilot Study of Donor: A Smart Phone Application for Identifying Live Kidney and Liver Donors.
1Surgery, Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine, Baltimore, MD
2Epidemiology, Johns Hopkins School of Public Health, Baltimore, MD
3ORGANIZE, New York, NY
4Bond University School of Medicine, Gold Coast, QLD, Australia.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C155
Keywords: Kidney, Kidney/liver transplantation, Liver
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Donor Evaluation and Donor Nephrectomy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Background: With over 100,000 candidates waiting, rates of deceased donation stagnant, and only 17,000 Kidney and liver transplants a year, live donor transplantation may represent the best opportunity to expand the organ supply. We have developed a smartphone application (app), Donor, to help patients share their stories with family and friends to facilitate identification of potential live donors.
Methods: In a pilot study of Donor, 54 patients were enrolled from the adult active kidney and liver waitlists at the Johns Hopkins Hospital to attend study sessions between December 2014 to May 2015. Participants attended two meetings. At the first meeting they learned how to install and use Donor on their phones and at the second meeting they provided feedback. Each participant was matched 3:1 to controls on the waiting list at the beginning of the study, based on age, gender, race, time on wait-list, blood type, PRA, and MELD (for liver participants) using iterative expanding radius matching. Kaplan-Meier curves and Cox proportional hazard models were used to estimate the association between using the app and identifying a potential live donor.
Results: Of the 54 participants, 40.0% were female, 48.1% were African American, 73.1% were kidney transplant candidates and 26.9% were liver transplant candidates. Of the study participants, 57.2% reported Donor to be very easy to use. Compared with matched controls, study participants had a higher number of live donor inquiries (24% versus 7% live donor inquiries within 7 months of app download; HR: 1.33 3.26 7.98, p=0.01)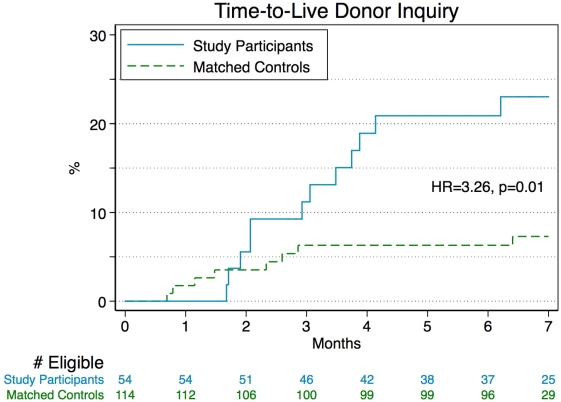
Conclusion: In a cohort of patients who piloted Donor, study participants were more likely to identify a live donor compared to matched controls. Donor is feasible for waitlist candidates to use and an effective tool to help transplant candidates identify live donors using social media.
CITATION INFORMATION: Kumar K, King E, Muzaale A, Konel J, Segal G, Arnold J, Bramstedt K, Segev D, Cameron A. A Pilot Study of Donor: A Smart Phone Application for Identifying Live Kidney and Liver Donors. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Kumar K, King E, Muzaale A, Konel J, Segal G, Arnold J, Bramstedt K, Segev D, Cameron A. A Pilot Study of Donor: A Smart Phone Application for Identifying Live Kidney and Liver Donors. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/a-pilot-study-of-donor-a-smart-phone-application-for-identifying-live-kidney-and-liver-donors/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
