When Living Donor Liver Allografts Fail: Exploring the Pitfalls of Retransplantation Using Deceased Donor Organs.
T. Bittermann,1 A. Shaked,2 K. Lloyd,2 D. Goldberg.1
1Gastroenterology and Hepatology, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA
2Transplant Surgery, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, PA.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 331
Keywords: Allocation, Living-related liver donors, Outcome, Retransplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Liver Transplantation Peri-Operative Considerations
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:42pm-5:54pm
Presentation Time: 5:42pm-5:54pm
Location: Room 311
Background: In the US, living donor liver transplantation (LDLT) is associated with increased long-term graft and patient survival compared to deceased donor liver transplantation (DDLT). However, patients undergoing LDLT have a higher risk of surgical complications leading to retransplantation (reLT) than those undergoing DDLT. To date, reLT outcomes after failed initial LDLT are not known.
Methods: We identified 276 patients in the UNOS database who underwent reLT with a deceased-donor allograft after initial LDLT from 2002-2013. Multivariable logistic models were used to evaluate the association between pre-LT characteristics and 1-year mortality.
Results: ReLT occurred within 14 days of LDLT in 29% of recipients, of which 78.8% were in the intensive care unit (ICU) at the time of reLT. Overall unadjusted 1-year mortality after reLT was 32.3%. In univariable analysis, only donor age and patient location at the time of reLT were significantly associated with 1-year mortality. As a category, timing between LDLT and reLT was not significantly associated with the risk of death at 1-year (p=0.09), however in pairwise comparisons there was an increased risk of death at 1-year if reLT occurred 15-90 (OR 1.89; 95% CI 0.88-4.06), 91-365 (OR 2.96; 95% CI 1.22-7.19) or >365 days (OR 2.39; 95% CI 1.02-5.58) from initial LDLT using reLT ≤ 14 days as a reference. Using multivariable logistic regression modeling with donor age, patient location at reLT and time category of reLT as covariates, demonstrated a 1-year predicted mortality of 31%, 45.5%, 52.7% and 50.8% for reLT recipients in the ICU at ≤ 14, 15-90, 91-365 and >365 days from initial LDLT, respectively 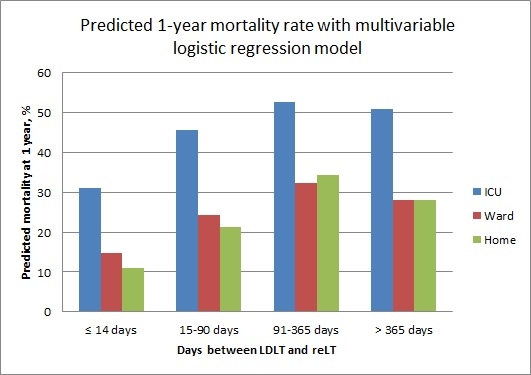 .
.
Conclusion: A significant proportion of reLTs occur soon after LDLT and in critically ill recipients with significantly lower survival than after initial LDLT, though outcomes appear best if reLT is needed emergently.
CITATION INFORMATION: Bittermann T, Shaked A, Lloyd K, Goldberg D. When Living Donor Liver Allografts Fail: Exploring the Pitfalls of Retransplantation Using Deceased Donor Organs. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Bittermann T, Shaked A, Lloyd K, Goldberg D. When Living Donor Liver Allografts Fail: Exploring the Pitfalls of Retransplantation Using Deceased Donor Organs. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/when-living-donor-liver-allografts-fail-exploring-the-pitfalls-of-retransplantation-using-deceased-donor-organs/. Accessed March 7, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
