Vo2peak Superior to Current Established Measure of Post Kidney Transplant Survival Score (EPTS Score)
H. Chakkera1, R. Butterfield1, M. Buras1, B. Kaplan2
1Mayo Clinic Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, 2Baylor Scott and White, Dallas, TX
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 536
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Kidney/pancreas transplantation, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic III
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 4, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Presentation Time: 4:30pm-4:42pm
Location: Ballroom C
*Purpose: The Scientific Registry of Transplant Recipients (SRTR) utilizes the calculated estimated posttransplant survival (EPTS) score as the measure of post kidney transplant survival to guide allocation of deceased donor kidney transplantation. This score does not include any metric of functional capacity. Peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak), is an established marker of functional capacity and predictor of survival among both the general and diseased populations.
*Methods: We compared the association, predictive ability and discriminative capacity of VO2peak measured prior to transplant vs. the EPTS score and all-cause mortality post kidney transplant.
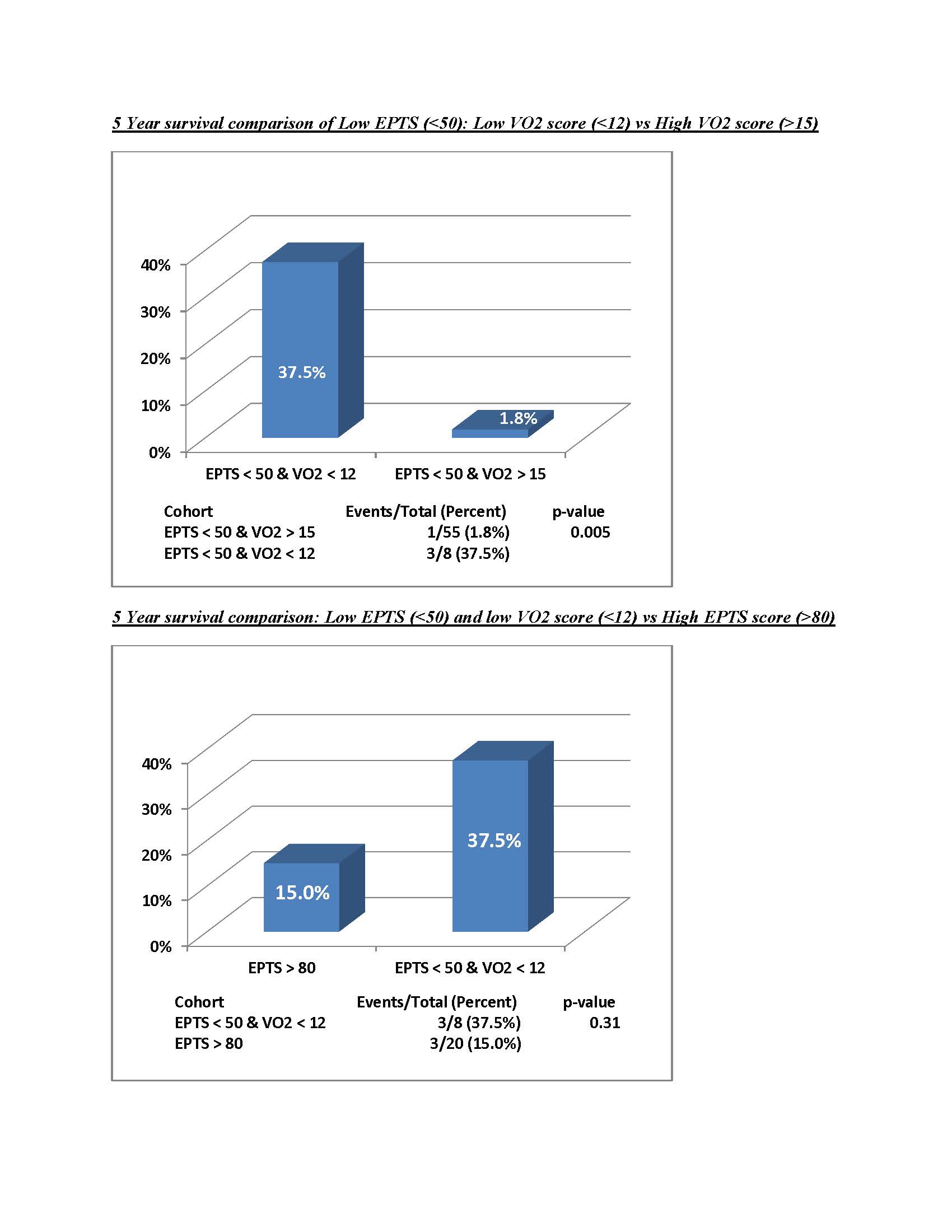
*Results: Among a cohort of 158 transplant recipients (65% deceased donor) with at least 3 years post-transplant follow-up, the median VO2peak was 14.9 ml/Kg/min. 1 unit increase in the pre-transplant VO2peak conferred approximately a 20% reduction in mortality (Hazard ratio (HR), adjusted for age, diabetes and coronary heart disease = 0.81, Confidence Interval (CI) = (0.644 – 1.007), p=(0.058) and 10 unit increase in the EPTS score conferred approximately a 5% increase in mortality, albeit not statistically significant (Hazard ratio (HR), adjusted for gender and coronary heart disease = 1.055, Confidence Interval (CI) = (0.825-1.349), p=(0.668). The discriminatory capacity for the model with EPTS was lower than VO2peak (C-statistic of 0.685 vs. 0.781). We also observed among the cohort of “low risk” patients (defined as patients with EPTS score <50) those with lower VO2peak had significantly higher risk of mortality. This increased mortality risk in the low-EPTS and low VO2peak cohort was equivalent to those with high EPTS score cohort.
*Conclusions: VO2peak demonstrated improved association and discriminatory capacity of patient survival than EPTS score. Thus, in our single center study cohort functional capacity as defined as VO2peak was an important reflection of post-transplant survival. Among “low risk” patients with EPTS <50, EPTS alone without VO2peak did not accurately capture true patient survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chakkera H, Butterfield R, Buras M, Kaplan B. Vo2peak Superior to Current Established Measure of Post Kidney Transplant Survival Score (EPTS Score) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/vo2peak-superior-to-current-established-measure-of-post-kidney-transplant-survival-score-epts-score/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress