VO2peak Differentiates Survival Post Kidney Transplant
1Mayo Clinic Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, 2Baylor Scott and White Health, Temple, TX
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 825
Keywords: Allocation, Survival
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Poster Abstract
Session Date & Time: None. Available on demand.
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The OPTN/UNOS utilizes the calculated estimated posttransplant survival (EPTS) score as the measure of post-kidney transplant survival to guide allocation of deceased donor kidney transplantation. This score does not include any metric of functional capacity. Peak oxygen uptake (VO2peak), is an established predictor of survival among both the general and diseased populations.
*Methods: We assessed the association and discriminative capacity of VO2peak and that of EPTS score and all-cause mortality post-kidney transplant. Additionally, we assessed the “mortality risk” lower VO2peak conferred on those patients with low EPTS score
*Results: The study cohort included 293 patients with at least 3 year follow-up. 76.1% were deceased donor transplants. Mean follow-up period was 6.0 years. The mean transplant age was 57.6 years, 61.4% were male, 15.8% with history of coronary artery disease and 48.8% diabetic . The median VO2peak was 15.0 ml/Kg/min. Through last follow-up, the cohort had 38 (13%) deaths. A 1 unit increase in the VO2peak conferred approximately a 10% reduction in mortality [Unadjusted Hazard Ratio (95% Confidence Interval) = 0.90 (0.82-0.98), p = 0.018] and a 10 unit increase in the EPTS score calculated at transplant conferred approximately a 29% increase in mortality [HR (95% CI) = 1.29 (1.13, 1.47), p = 0.001]. In an adjusted survival model (N= 293), Harrell C-Statistic (Standard Deviation) for the model with VO2peak was 0.76 (0.04) indicating good discriminatory ability of VO2peak and all-cause mortality.
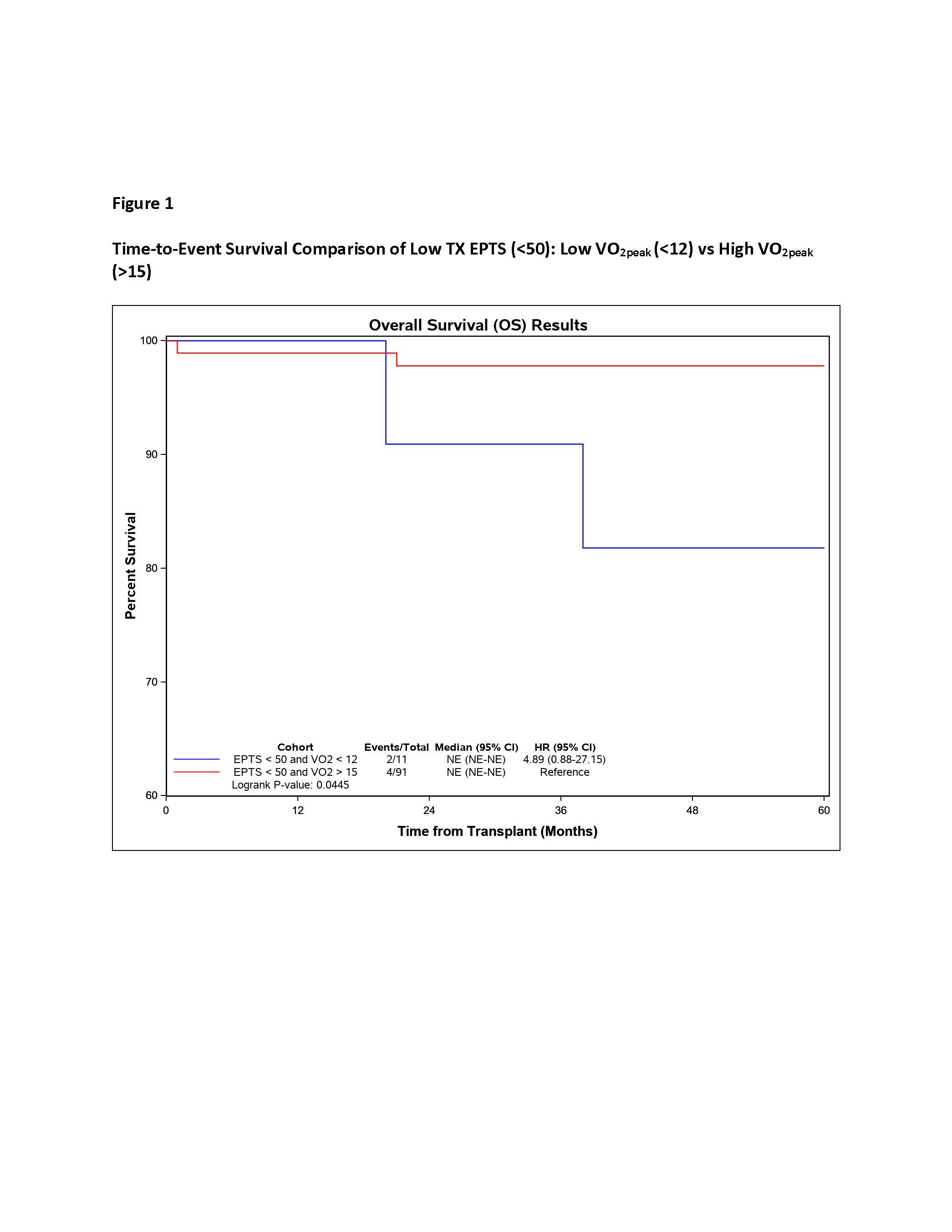
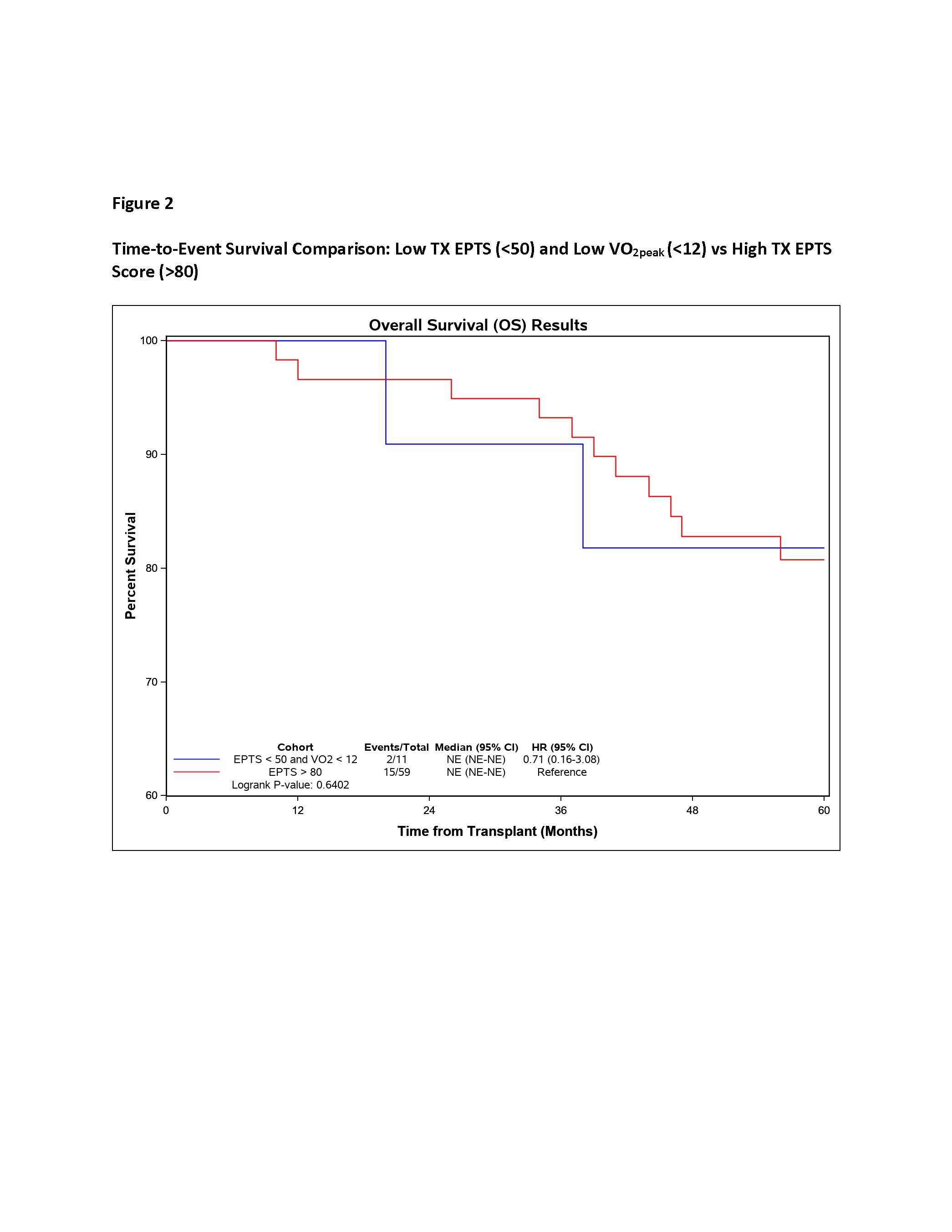
Lower pre-transplant VO2peak and higher EPTS score conferred higher risk of post-transplant mortality. Among the cohort of “low-risk” patients (patients with EPTS score less than 50) those with lower VO2peak had significantly higher risk of mortality (log rank p=0.045)., Figure 1. In fact, the mortality risk among those with low-EPTS (less than 50) and low VO2peak less than12ml/Kg/min was equivalent to those with high EPTS (greater than 80) score., Figure 2.
*Conclusions: We concluded all EPTS is not the same. Functional capacity as defined by VO2peak is an important reflection of post-transplant survival. VO2peak is able to identify those with low EPTS who have similar survival to that of high EPTS phenotype.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Chakkera H, Kaplan B, Budhiraja P, Butterfield R. VO2peak Differentiates Survival Post Kidney Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/vo2peak-differentiates-survival-post-kidney-transplant/. Accessed March 5, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress