Validation of a Simplified Cost-Effective Clinical Risk Stratification That Predicts Myocardial Ischemic Events in Kidney Transplant Candidates.
1Bhumirajanagarindra Kidney Institute, Bangkok, Thailand
2Division of Nephrology, Department of Medicine, Brigham and Women's Hospital and Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center, Harvard Medical School, Boston, MA
3Division of Nephrology, Chulalongkorn University, Bangkok, Thailand.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 6
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Cardiovascular Complications in Kidney Transplantation
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 12, 2016
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: Room 304
Background: Diagnosis of coronary artery disease before kidney transplantation is crucial in decreasing morbidity and mortality & avoiding the need for angiography in kidney transplant recipients(KTR).
Methods: We examined the predictive value of non-invasive cardiac testing for KTR and developed an algorithm classifying patients into low, intermediate & high risk groups for cardiovascular events(CVe) post transplant according to degree of association between clinical risk factors & CVe. The proposed algorithm was validated using a separate KTR population & compared with the 2012 American Heart Association(AHA) recommendations. A CVe was defined as post-transplant unstable angina, myocardial infarction, cardiac arrest,or the need for pre-transplant coronary intervention.
Results: A total of 517 KTR in 2 cohorts were retrospectively analyzed. Non-invasive tests had a sensitivity & specificity of 40% & 91%, respectively, in predicting a CVe. Of the 254 KTR in the risk stratification population,(Oct.2007-Dec.2011),198 KTR had non-invasive cardiac testing prior to transplantation. Sixteen patients(6.3%) experienced a CVe. Using clinical risk stratification, 30 high, 172 intermediate,& 52 low-risk KTR were identified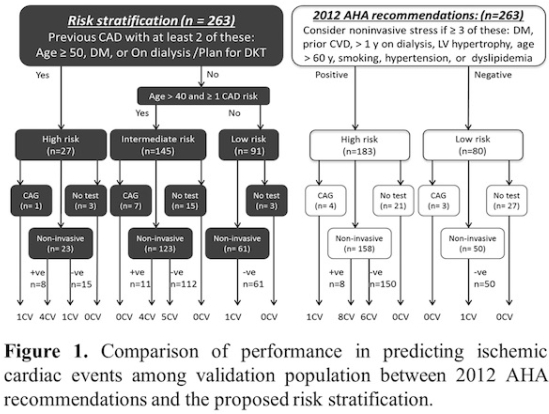 . Stratification into the high-risk group predicted a CVe with 44% sensitivity & 90% specificity. In the validation population,263 KTR(Jan.2012-Jun.2014),sensitivity & specificity were very similar,35.2% &91.5%, respectively.
. Stratification into the high-risk group predicted a CVe with 44% sensitivity & 90% specificity. In the validation population,263 KTR(Jan.2012-Jun.2014),sensitivity & specificity were very similar,35.2% &91.5%, respectively.
Conclusion: AHA guidelines stratify patients into low (30%) & high risk (70%) groups. Our proposed stratification would reclassify patients into a low risk group (35%) who do not need further testing, a high-risk group (10%) who need pre-transplant testing (angiography or non-invasive). For the intermediate-risk KTR non-invasive cardiac testing may be appropriate. Our stratification is simpler but more discriminatory than the AHA recommendations.
CITATION INFORMATION: Jiamjariyapon T, Townamchai N, Garg N, Pavlakis M, Chandraker A. Validation of a Simplified Cost-Effective Clinical Risk Stratification That Predicts Myocardial Ischemic Events in Kidney Transplant Candidates. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jiamjariyapon T, Townamchai N, Garg N, Pavlakis M, Chandraker A. Validation of a Simplified Cost-Effective Clinical Risk Stratification That Predicts Myocardial Ischemic Events in Kidney Transplant Candidates. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/validation-of-a-simplified-cost-effective-clinical-risk-stratification-that-predicts-myocardial-ischemic-events-in-kidney-transplant-candidates/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
