Utilization and Characteristics of Kidney Donors in the US by OPTN-Defined Increased Risk Donor Status
1Infectious Diseases, Northwestern University, Chicago
2Organ Transplantation, Northwestern University, Chicago.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C45
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: ECD/DCD/high KDPI
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, May 4, 2015
Session Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-6:30pm
Location: Exhibit Hall E
Background: The number of candidates in need of kidney transplantation is far larger than the number of organ donors. To expand the organ pool, there has been increased use of OPTN-defined increased risk (IR) donors (D). The utilization and epidemiology of the infectious disease marker positivity of these IR kidney donors has not been previously described.
Methods: We obtained data from the US OPTN to perform a blinded assessment of kidney transplant center-specific utilization of OPTN-defined increased risk donors. We evaluated the epidemiology of infectious disease marker positivity of kidney IRDs and non-IRDs from July 2004 – December 2014. Student's T-test was used to compare groups.
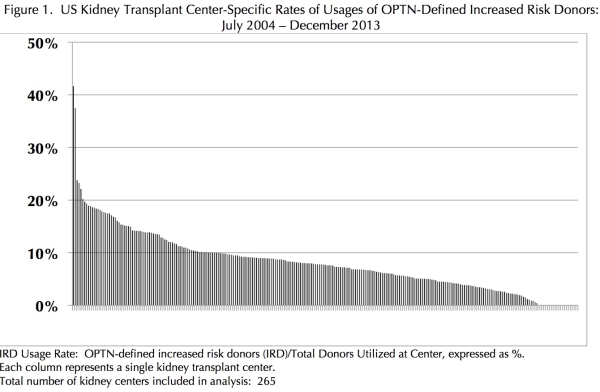
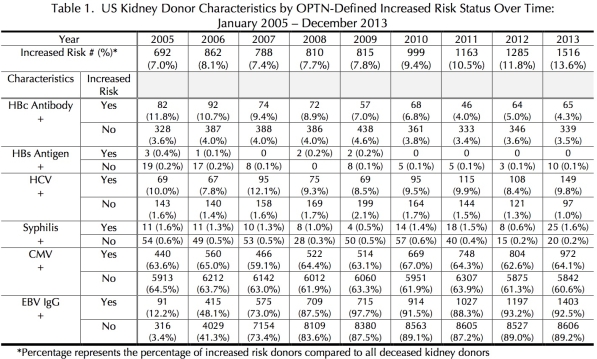
Results: IRDs accounted for 7.0 – 13.6% of kidney donors during the study period (see Table 1) and there was a trend towards increased utilization of IRDs over time. Of the 265 US kidney transplant centers, 84 (31.7%) had ≥ 10% utilization of IRDs while 21 (7.9%) did not utilize any OPTN-defined IRDs during the 8.5 years study period (See Figure 1). IR kidney donors were more likely to be seropositive for HBsAg (p = 0.005), HBcAb (p = 0.0035) and HCV (p = 0.014) and have a reactive syphilis screening test (p = 0.0004).
Conclusions: There is significant variability in the use of OPTN-defined IRDs by US kidney transplant centers. The OPTN-defined kidney IRDs were more likely to have positive HBsAg, HBcAb, HCV and syphilis screening, yet an increasing number of centers use those organs in the setting of organ shortage. Further analysis is ongoing to assess the outcomes of both groups.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Ison M, Ho B, Leventhal J, Ladner D. Utilization and Characteristics of Kidney Donors in the US by OPTN-Defined Increased Risk Donor Status [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/utilization-and-characteristics-of-kidney-donors-in-the-us-by-optn-defined-increased-risk-donor-status/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
