Use of Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA Assay to Monitor Treatment Response to Allograft Rejection in Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients
1Comprehensive Transplant Center, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, West Hollywood, CA, 2Pediatric Nephrology, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, West Hollywood, CA, 3HLA Laboratory, Cedars-Sinai Med Center, West Hollywood, CA, 4Pathology, Cedars Sinai Medical Center, West Hollywood, CA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B-319
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Acute rejection (AR) accounts for 13%-21% of graft failure in pediatrics (peds), with the number, severity, and response to treatment being a major determinant of long-term survival. With 10-year graft failure as high as 45.8%, early detection and optimizing treatment are essential. The detection of donor-derived cell-free DNA (dd-cfDNA, Allosure) has been shown to reliably identify allograft rejection in adult kidney transplant patients (pts). Here we evaluate the utility of dd-cfDNA for monitoring treatment response amongst peds renal transplant (tx) pts suffering rejection.
*Methods: 58 peds tx pts were enrolled between 4/2018 and 9/2019 and underwent initial testing with dd-cfDNA to monitor for AR. Allograft biopsy was performed for dd-cfDNA >1.0% and pts found to have AR on biopsy formed the study cohort. Treatment for AR consisted of IV pulse steroids with or without IVIg and rituximab. Dd-cfDNA, serum creatinine (SCr), histology, treatment and outcomes were evaluated.
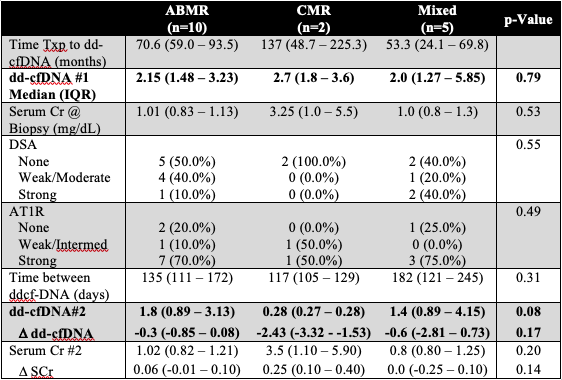
*Results: 18/58(31%) patients had dd-cfDNA score >1.0%, of which 17 (94.4%) had rejection on histology. Median time from transplant to dd-cfDNA testing was 67 months (interquartile range, IQR 51-79). Median dd-cfDNA score was 2% (IQR 1.47-3.25). 10 pts (58.8%) had antibody ABMR, 2 pts(11.8%) had TCMR, and 5 pts (29.4%) had mixed ABMR and TCMR. SCr at time of biopsy was normal at 1.00 mg/dL (IQR 0.87-1.15 mg/dL), showed minimal change post treatment and did not correlate with dd-cfDNA (p=0.65). Following treatment, dd-cfDNA decreased for all types of rejection but remained >1.0% in both ABMR (median 1.8, IQR 0.89-3.13) and Mixed (1.4, 0.89-4.15) groups. Dd-cfDNA was lower for pts with TCMR (0.28, 0.27-0.28). Table 1 shows change in dd-cfDNA, DSA, AT1R testing between the 3 subgroups.
*Conclusions: dd-cfDNA represents a potential non-invasive method for early detection (despite stable creatinine) of rejection in the peds renal tx pts Pts with TCMR may be reliably followed by ddcf-DNA; however, it remains unclear whether persistently elevated dd-cfDNA in pts with ABMR is a reflection of ongoing subclinical rejection or an inherent limitation of the assay.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Steggerda J, Pizzo HPhan, Garrison J, Zhang X, Haas M, Kim I, Jordan S, Puliyanda D. Use of Donor-Derived Cell-Free DNA Assay to Monitor Treatment Response to Allograft Rejection in Pediatric Renal Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/use-of-donor-derived-cell-free-dna-assay-to-monitor-treatment-response-to-allograft-rejection-in-pediatric-renal-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress