Uromodulin and Toll-Like Receptor 4 Levels Predict Susceptibility to Bacterial Urinary Tract Infection After Renal Transplantation.
1Internal Medicine, Nephrology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
2Pathology, Hannover Medical School, Hannover, Germany
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B94
Keywords: Infection, Kidney transplantation, Urinalysis
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Bacteria, Fungi, Parasites
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall D1
Background: Urinary tract infection (UTI) remains the most common bacterial infection after kidney transplantation (kTx) and is associated with reduced allograft function as well as allograft and patient survival. The reasons for susceptibility for UTI after kTx are only partly understood. Lately, molecules of the innate immune system might play a pathogenic role have been linked to UTI. This study focuses on uromodulin (UMOD) and Toll-like-receptor-4 (TLR4).
Methods: UMOD and TLR4 concentrations were measured in spot urine samples from kTx patients with UTI (n=132) and compared to patients without UTI obtained within the first 6 months after transplantation (n=39) using previous established ELISA methods.
Results: Urinary UMOD and TLR4 concentration were significantly lower in the UTI group compared to kTx patients without UTIs. (medians with the 25% and 75% interquartiles are: for UMOD 6.11ug/ml (3.59;10.83ug/ml) vs. 16.99ug/ml (10.96;20) (p<0.0001), TLR4 (102.8pg/ml (55.86;160.6) vs. 389.2pg/ml (136.6;565pg/ml) (p<0.0001)) 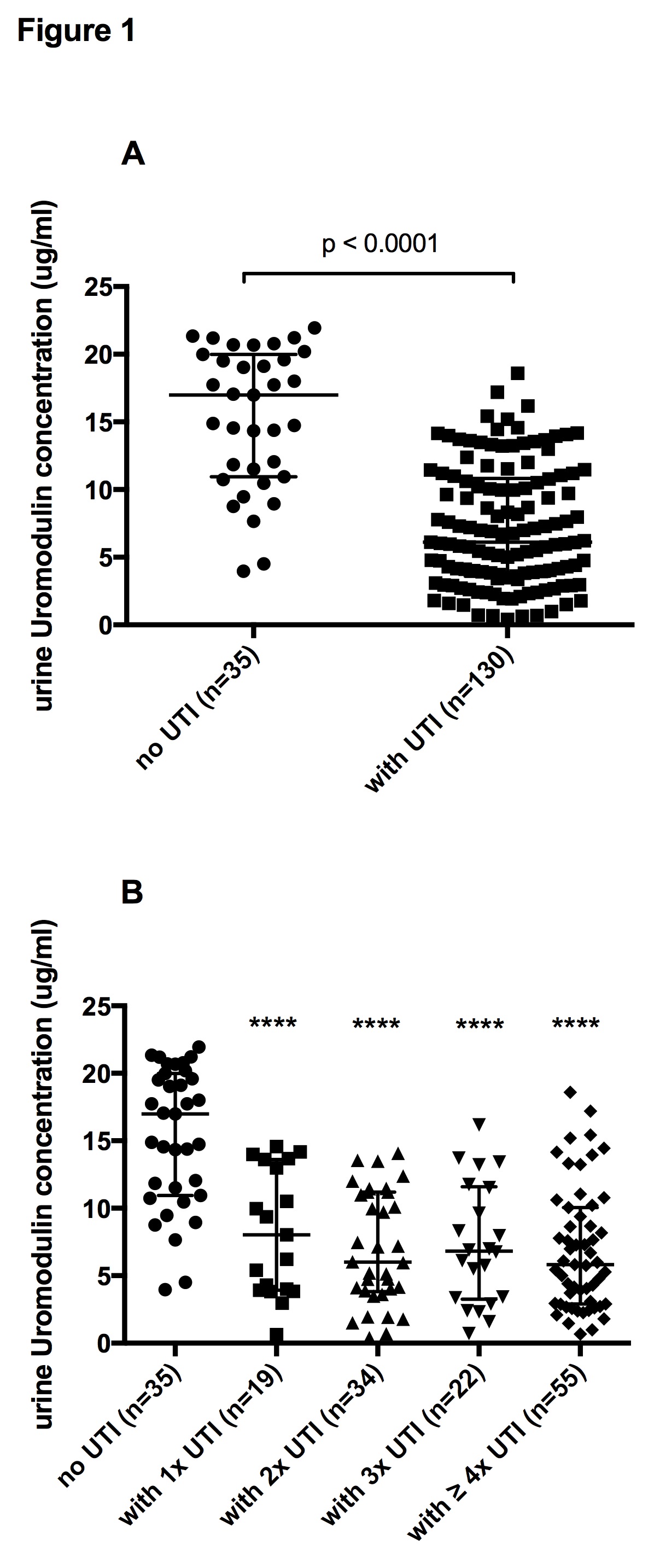 and
and 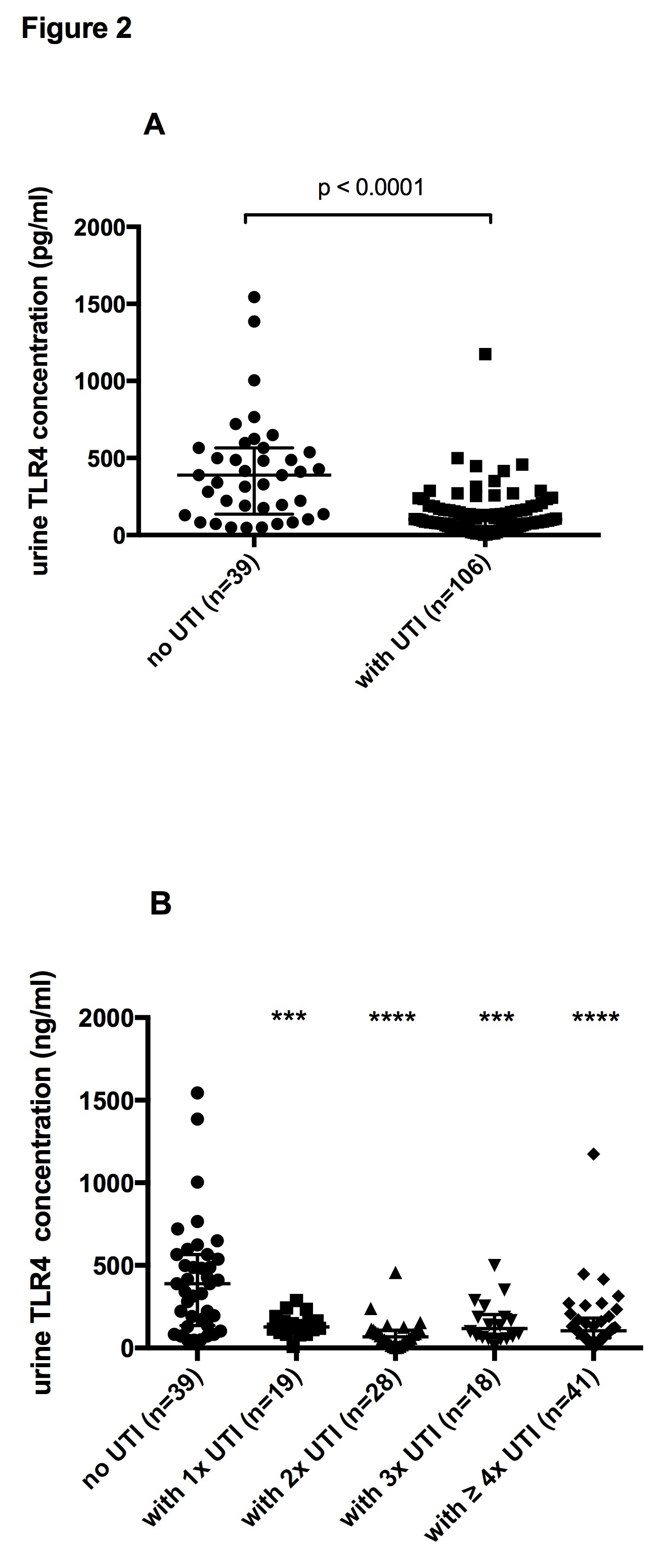 This finding was consistent in all studied subcohorts (patients with one, two, three, four and more UTIs within the first 6 months post-transplant). ROC curve analysis showed a good level of discrimination using UMOD and TLR4 urine concentrations as predictor of UTI areas under the ROC curve of 0.876 for UMOD and 0.803 for TLR4.
This finding was consistent in all studied subcohorts (patients with one, two, three, four and more UTIs within the first 6 months post-transplant). ROC curve analysis showed a good level of discrimination using UMOD and TLR4 urine concentrations as predictor of UTI areas under the ROC curve of 0.876 for UMOD and 0.803 for TLR4.
Conclusions: Our data indicate that UMOD and TLR4 are markers for UTI after kTx and might be important protective factors for UTIs in kTx patients. Thus urine levels of UMOD and TLR4 could be useful tools to identify patients at risk for UTI that would benefit from a prophylactic antibiotic therapy after renal transplantation.
CITATION INFORMATION: Stahl K, Lührs H, Schmitz J, Scheffner I, Gwinner W, Bräsen J, Haller H, Schiffer M. Uromodulin and Toll-Like Receptor 4 Levels Predict Susceptibility to Bacterial Urinary Tract Infection After Renal Transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Stahl K, Lührs H, Schmitz J, Scheffner I, Gwinner W, Bräsen J, Haller H, Schiffer M. Uromodulin and Toll-Like Receptor 4 Levels Predict Susceptibility to Bacterial Urinary Tract Infection After Renal Transplantation. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/uromodulin-and-toll-like-receptor-4-levels-predict-susceptibility-to-bacterial-urinary-tract-infection-after-renal-transplantation/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
