Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Living Kidney Donor Nephrectomy.
1Urology, Urological Science Institute, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea
2Transplantation Surgery, Research Institute for Transplantation, Yonsei University College of Medicine, Seoul, Republic of Korea.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C172
Keywords: Kidney transplantation, Renal function
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Donor Evaluation and Donor Nephrectomy
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 13, 2016
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Halls C&D
Introduction: Urinary neutrophil gelatinase-associated lipocalin (uNGAL) is a marker for acute kidney injury. This study was conducted to evaluate the efficacy of perioperative uNGAL in relation to renal function after living donor nephrectomy.
Methods: This prospective study included 76 patients who underwent live donor nephrectomy between September 2013 and November 2014. Donor uNGAL was measured perioperatively until 6 month, and change in perioperative uNGAL was investigated. Changes in uNGAL levels were analyzed for all donors and between subgroups that were dichotomized based on 6 month eGFR values of <60 and ≥60 mL/min/1.73m2. Renal function was estimated with the Modification of Diet in Renal Disease (MDRD) formula.
Results: Before donor nephrectomy mean uNGAL was 5.0 ± 5.2 ng/mL. In the overall group, uNGAL levels increased following donor nephrectomy and stabilized after 3 days. However, neither preoperative uNGAL nor postoperative uNGAL in the period was associated with renal function. The uNGAL was not associated with age, gender, preoperative eGFR, and development of CKD after donation, and multivariate analyses failed to reveal any correctable clinical features associated with perioperative uNGAL changes.
Conclusion: The uNGAL levels may increase following living donor nephrectomy. However, it does not appear to be a useful marker for quantifying the degree of renal injury or predicting postoperative renal function after donation.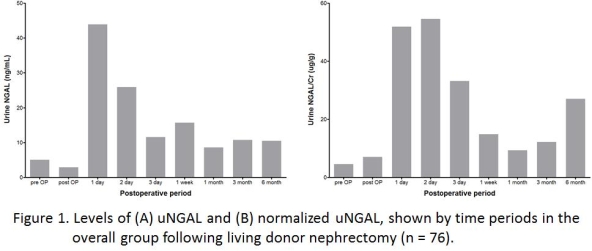
CITATION INFORMATION: Yoon Y, Lee H, Joo D, Huh K, Kim M, Kim S, Kim Y, Han W. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Living Kidney Donor Nephrectomy. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Yoon Y, Lee H, Joo D, Huh K, Kim M, Kim S, Kim Y, Han W. Urinary Neutrophil Gelatinase-Associated Lipocalin in Living Kidney Donor Nephrectomy. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/urinary-neutrophil-gelatinase-associated-lipocalin-in-living-kidney-donor-nephrectomy/. Accessed February 24, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
