Urinary Cell Cycle Arrest Biomarkers as Early Predictors of Acute Kidney Injury Following Advanced Cardiac Replacement Therapies
Baylor University Medical Center, Dallas, TX.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B40
Keywords: Heart assist devices, Heart transplant patients
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session B: Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Sunday, June 3, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: Current strategies to detect acute kidney injury (AKI) after cardiothoracic surgery rely on elevations in serum creatinine and diminished urine output, which are insensitive and late manifestations of AKI. The early-phase renal biomarkers insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 7 (IGFBP7) and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases-2 (TIMP-2) have been validated as sensitive predictors of AKI within 12 h of measurement. Here we study the efficacy of these biomarkers for predicting AKI following ventricular assist device (VAD) implantation and cardiac transplantation.
Methods: This was a prospective study of 73 consecutive patients undergoing VAD implantation (N=37) or heart transplant (N=36) from 2016-2017 at our center. TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 were measured with the NephroCheckTM Test on urine samples at baseline (pre-surgery) and 1-6 h after surgery. A NephroCheck score >0.3 mg/dL was assessed as predictor of moderate/severe AKI (KDIGO 2/3). Creatinine levels and urine output within 48 h of surgery were collected to assess AKI.
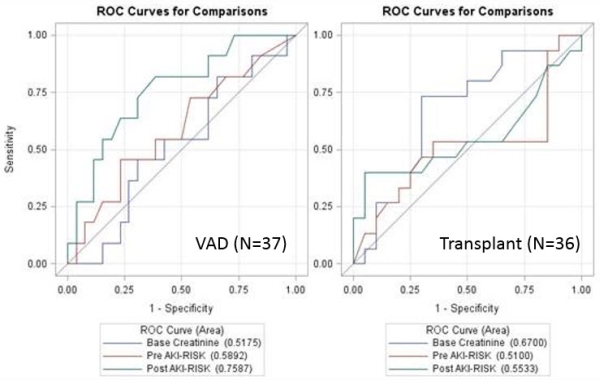
Results: The 2 group (VAD and transplant) were similar in gender, age, body weight, and baseline creatinine (P>0.28), but the VAD group contained more non-Caucasian patients (P=0.001). Eleven (30%) VAD patients and 16 (44%) transplant patients developed moderate/severe AKI. Overall, AKI was associated with post-surgery NephroCheck (OR=21, 95%CI=1.4-322) but not with baseline NephroCheck (P=0.9). When analyzed separately for each group, this effect remained in the VAD group (OR=177, 95%CI=1.4-1000) but not in the transplant group (P=0.15). ROC analysis showed post-surgery NephroCheck to be superior to baseline creatinine in the VAD group (P=0.046; Fig 1).
Conclusion: Assessment of TIMP-2 and IGFBP7 within a few hours post-surgery appeared effective at predicting AKI in the group of VAD recipients, but not in the transplant group; and performed better than baseline creatinine. Larger studies are needed to assess this test's sensitivity.
CITATION INFORMATION: Joseph S., Medel-Martinez H., Bottiglieri T., Wasek B., Yeramaneni S., Felius J., Bonilla C., Sido O., Gottlich C., Lima B., Hall S. Urinary Cell Cycle Arrest Biomarkers as Early Predictors of Acute Kidney Injury Following Advanced Cardiac Replacement Therapies Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Joseph S, Medel-Martinez H, Bottiglieri T, Wasek B, Yeramaneni S, Felius J, Bonilla C, Sido O, Gottlich C, Lima B, Hall S. Urinary Cell Cycle Arrest Biomarkers as Early Predictors of Acute Kidney Injury Following Advanced Cardiac Replacement Therapies [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/urinary-cell-cycle-arrest-biomarkers-as-early-predictors-of-acute-kidney-injury-following-advanced-cardiac-replacement-therapies/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress