Upregulation of Innate Immune Pathways is Associated with Increased Rejection in HIV-Infected Kidney Transplant Recipients
1UC San Francisco, San Francisco, CA, 2CA
Meeting: 2022 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 369
Keywords: HIV virus, Kidney transplantation, Rejection
Topic: Basic Science » Basic Science » 02 - Acute Rejection
Session Information
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:40pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-5:40pm
Location: Hynes Room 309
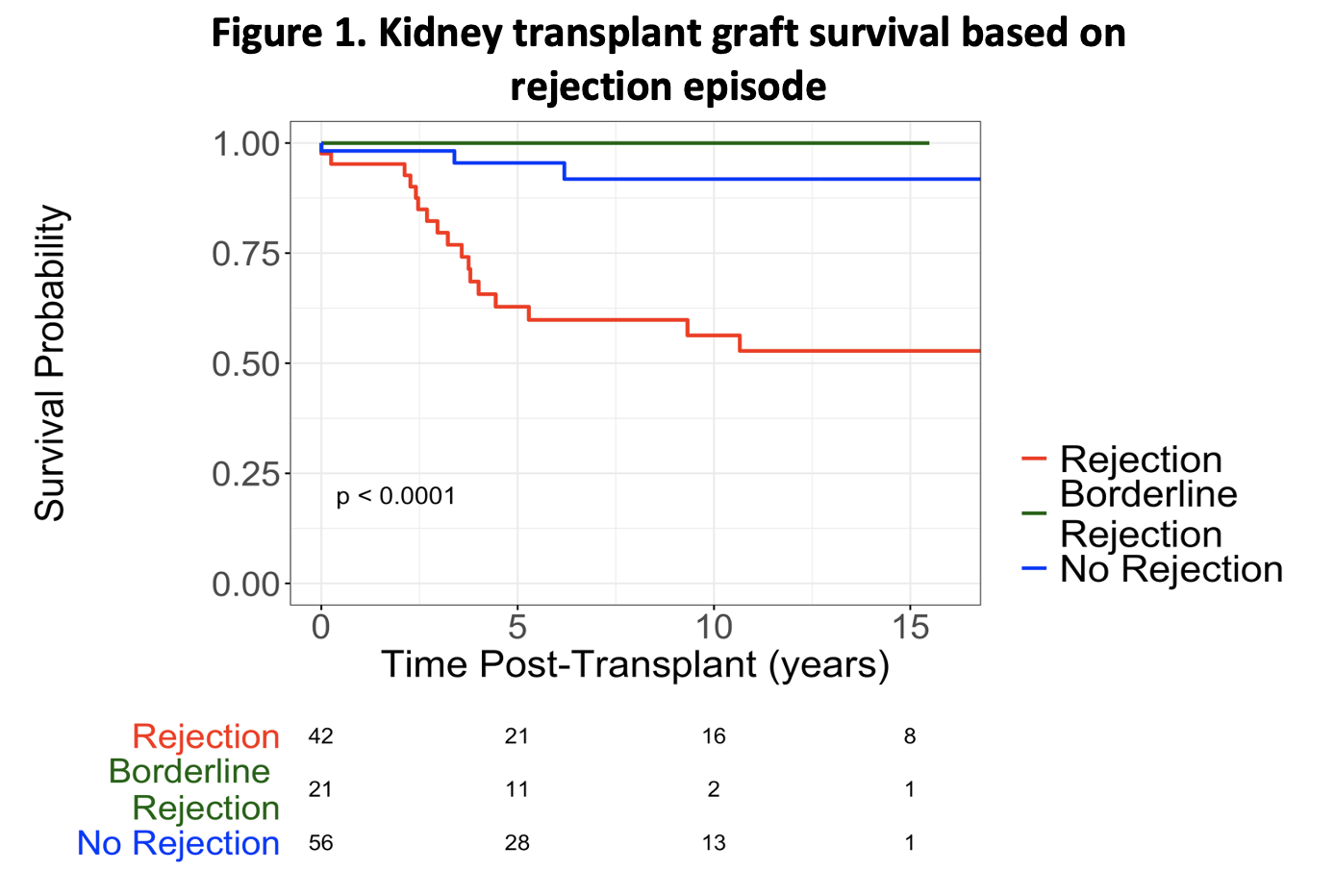
*Purpose: Although kidney transplantation (KT) has become the standard of care for HIV+ patients with renal failure, early experiences revealed high acute rejection (AR) rates. Data from our center’s results have showed that an episode of AR is associated with significantly reduced graft survival in HIV+ KT recipients (Figure 1). We sought to further assess the etiology of increased AR in HIV+ patients by performing a transcriptomic analysis of biopsy specimens, comparing HIV+ to HIV- patients.
*Methods: We studied 68 (34 HIV+, 34 HIV-) formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded (FFPE) renal biopsies from KT patients with acute cellular rejection (ACR), borderline rejection (BL), and normal findings. RNA from FFPE sections was isolated, and gene expression measured using the NanoString platform. We performed differential gene expression (DE) and pathway analysis (PA) using the Reactome database, comparing DE of HIV+ to HIV- patients. Here we show our analysis in ACR biopsies.
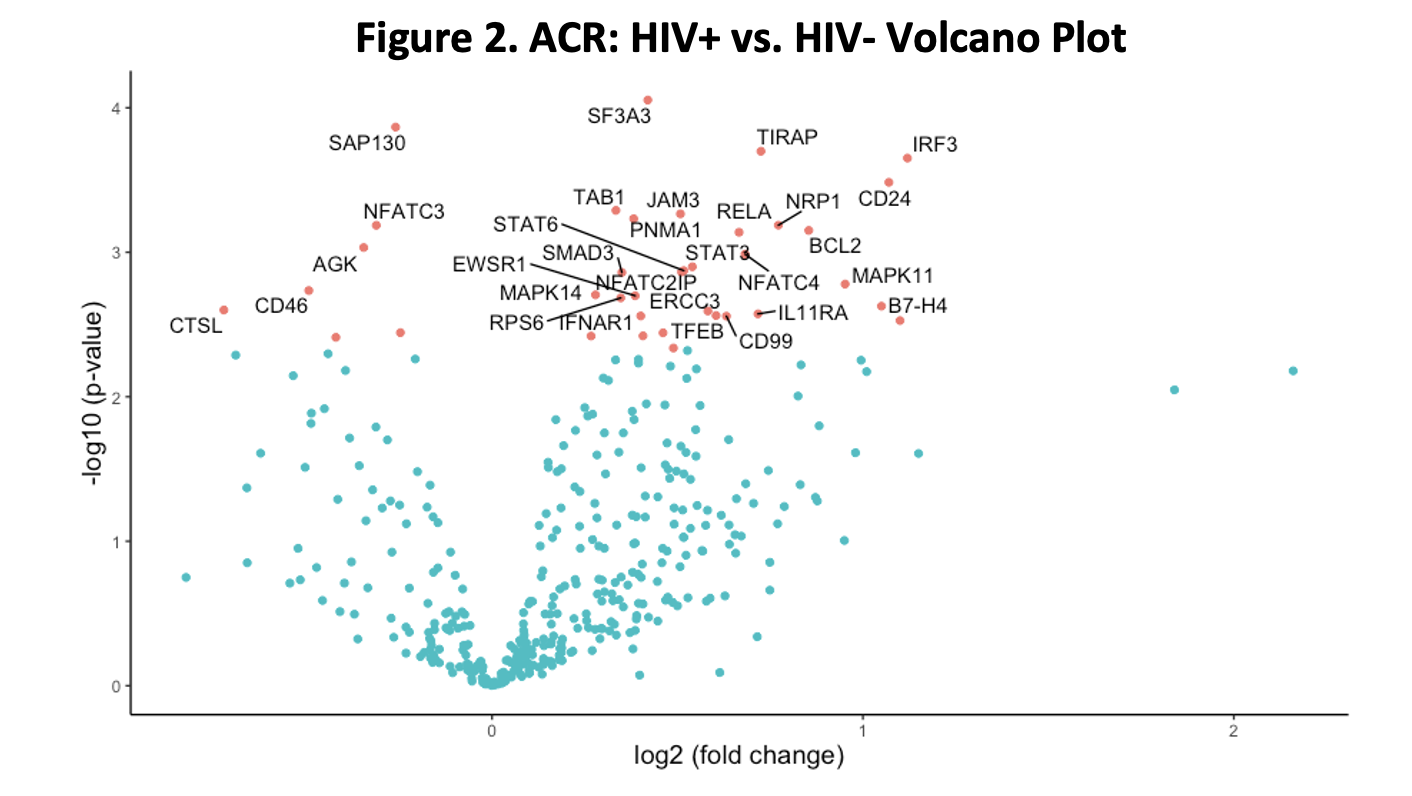
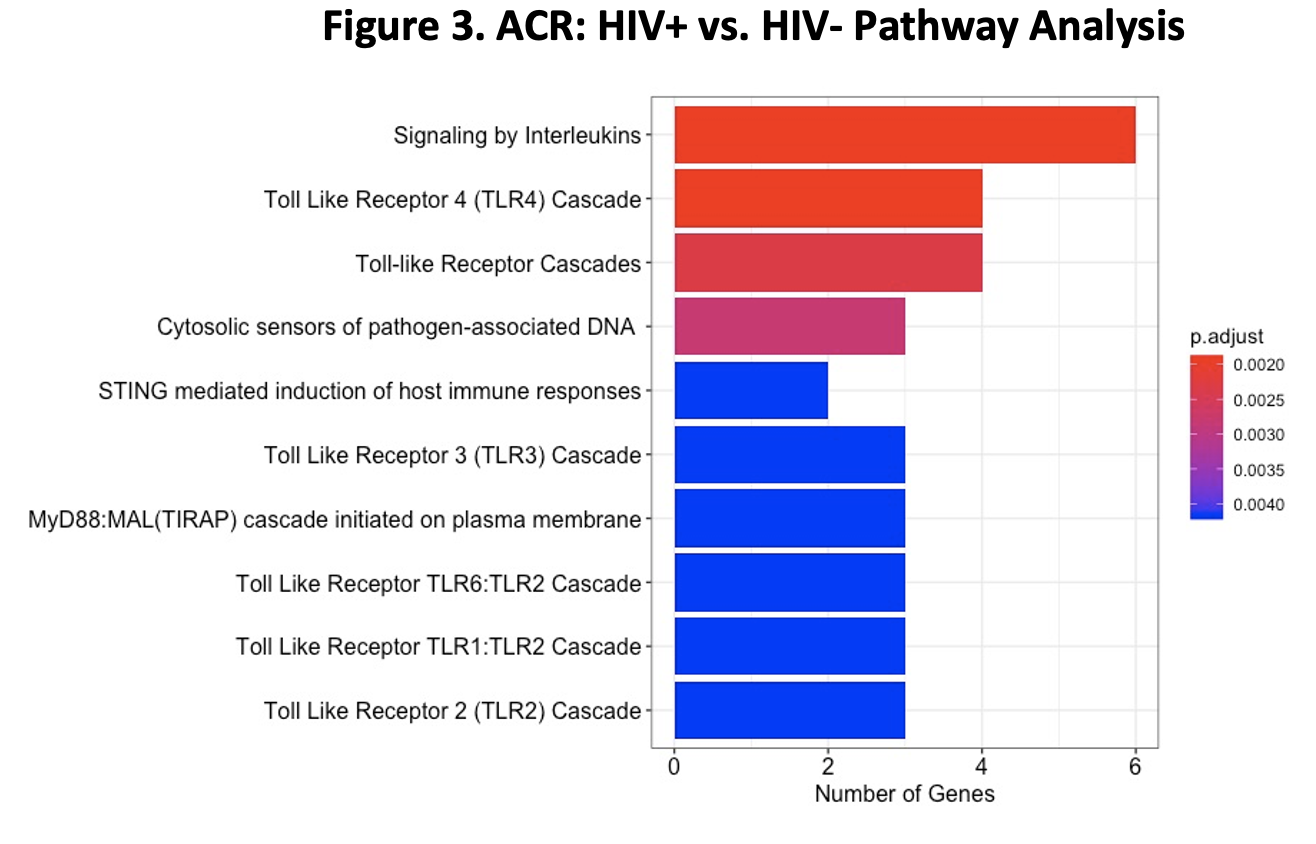
*Results: DE analysis revealed multiple genes with significantly increased expression in the HIV+ patients relative to the HIV- patients in ACR (Figure 2). PA of these genes showed enrichment of various inflammatory pathways, particularly innate immune pathways associated with Toll-like receptors (Figure 3).
*Conclusions: Upregulation of the innate immune pathways in the biopsies of HIV+ patients with ACR is suggestive of a unique immune response that may stem from immune dysregulation caused by HIV infection. These findings suggest that these unique HIV-driven pathways may in part be contributory to the increased incidence of allograft rejection seen in HIV+ KT.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Zarinsefat A, Kelly Y, Dobi D, Szabo G, Laszik Z, Stock P, Braun H. Upregulation of Innate Immune Pathways is Associated with Increased Rejection in HIV-Infected Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2022; 22 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/upregulation-of-innate-immune-pathways-is-associated-with-increased-rejection-in-hiv-infected-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2022 American Transplant Congress