Up-Regulation of Circulatory Adiponectin Ameliorates Liver Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Via Inhibiting Macrophage/TNF-α Mediated Inflammatory Response
Organ Transplant Center, the First Affiliated Hospital of Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, China
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C1189
Background: It is still of importance to minimize liver ischemia reperfusion (I/R) injury during liver transplantation. Reducing inflammation reaction is an effective way to achieve this goal. Notably, recently adiponectin (APN) was found to have anti-inflammation action in heart and renal I/R injury. Herein, we investigated the role of APN in liver I/R injury and the related mechanisms.
Methods: Wistar rats were randomized to three groups: (1) sham group; (2) I/R control group; and (3) I/R+APN group. Liver and blood samples were collected after 6h and 24h reperfusion. Liver function and histopathologic changes were assessed. Macrophage and neutrophils infiltration was detected by immunohistochemistry stain, while pro-inflammatory cytokines release in liver were measured using ELISA. Apoptosis was analyzed by TUNEL stain and caspase-3 expression in liver. Downstream molecules of APN were investigated by Western blotting.
Results: Circulatory APN was down-regulated during liver I/R. With exogenous APN treatment, ALT and AST were decreased, accompanying with less hepatocytes necrosis.
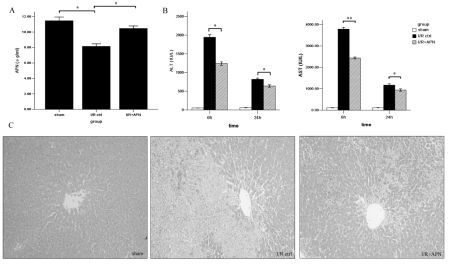
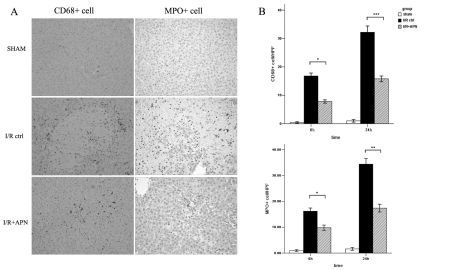
Less inflammatory cell infiltration and pro-inflammatory cytokines release were also observed in I/R+APN group when compared with I/R control group.
Besides, APN treatment reduced hepatocyte apoptosis, evidenced by reduced TUNEL positive cells and less caspase-3 expression in reperfused liver. Finally, molecules of the AMPK pathway was found to be activated by APN.
Conclusion: APN inhibited inflammatory response during liver I/R and prevented hepatocyte apoptosis, probably by activating AMPK. The current study provides a potential pharmacologic treatment target for liver I/R injury.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Guo Z, Wang D, Ju W, Zhang C, He X. Up-Regulation of Circulatory Adiponectin Ameliorates Liver Ischemia Reperfusion Injury Via Inhibiting Macrophage/TNF-α Mediated Inflammatory Response [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/up-regulation-of-circulatory-adiponectin-ameliorates-liver-ischemia-reperfusion-injury-via-inhibiting-macrophagetnf-mediated-inflammatory-response/. Accessed February 28, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
