Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type 2 Expression on Regulatory T Cells Predicts Acute Kidney Injury after Kidney Transplantation
Multi-Organ Transplant Program, McGill University Health Centre, Montreal, QC, Canada
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: B1137
Background: Acute kidney injury (AKI) leads to worse graft outcomes after kidney transplantation. Tumor necrosis factor (TNF) is classically a mediator of AKI. Recent evidence, however, suggests that interaction between TNF and TNF receptor type 2 (TNFR2) expressed on AKI-protective regulatory T cells (Tregs) increases their survival and immune suppressive function. We investigated whether pre-transplant TNFR2 expression on peripheral Tregs was reduced in kidney transplant recipients suffering from AKI and had any predictive value.
Methods: 53 consecutive deceased donor kidney transplant recipients were divided into AKI (n=37) and immediate graft function (IGF, n=16) groups based on post-transplant dialysis and 24-hour serum creatinine. Donor, organ procurement, and recipient characteristics were similar between both groups except for donor age and cold ischemic time (CIT). Pre-transplant recipient peripheral blood TNFR2 expression was quantified by flow cytometry, gating on CD4+CD127- Treg. Treg suppressive function was measured by in vitro suppression of autologous CD4+CD25- CFSE-labeled effector T cell proliferation by CD4+CD25+ Treg.
Results: Pre-transplant TNFR2 expression on Tregs correlated with Treg suppressive function (r=0.38, p=0.02), and was decreased in AKI compared to IGF recipients (p<0.05; Fig. 1A). It also accurately predicted AKI in ROC curve analysis (AUC=0.71, p<0.02; Fig. 1B) with a sensitivity of 97.3% and a specificity of 56.3% at a cut-off value of 91.6%. This cut-off value remained a significant predictor of AKI in multivariate logistic regression (OR=119, p<0.01) adjusting for dissimilar variables between our groups (donor age, CIT). Combining TNFR2 expression on Tregs with donor age and CIT to form a logistic regression model improved the predictive accuracy for AKI (AUC=0.95, p<0.01; Fig. 1C).
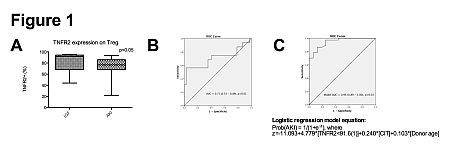
Conclusion: TNFR2 expression on Tregs is a rapid surrogate marker of Treg suppressive function, and predicts AKI pre-transplant independent of or in combination with donor age and CIT. Its measurement could further guide organ allocation to prevent AKI.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Nguyen M, Fryml E, Sahakian S, Liu S, Tchervenkov J, Paraskevas S. Tumor Necrosis Factor Receptor Type 2 Expression on Regulatory T Cells Predicts Acute Kidney Injury after Kidney Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tumor-necrosis-factor-receptor-type-2-expression-on-regulatory-t-cells-predicts-acute-kidney-injury-after-kidney-transplantation/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
