Treatment of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Infections after Solid Organ Transplant
Comprehensive Transplant Center, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C350
Keywords: Bacterial infection, Infection, Length of stay, Mortality
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Transplant Infectious Diseases
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Introduction: Infections with multi-drug resistant (MDR) gram-negative bacilli are associated with significant morbidity and mortality after solid organ transplant. This study characterized patient outcomes related to antimicrobial therapy used to treat MDR gram negative infections in the post solid organ transplant population.
Methods: A single center retrospective chart review identified all solid organ transplant recipients between January 1, 2007 and July 1, 2017. All patients with cultures containing an extended-spectrum beta-lactamase (ESBL) or carbapenamase producing organism were included.
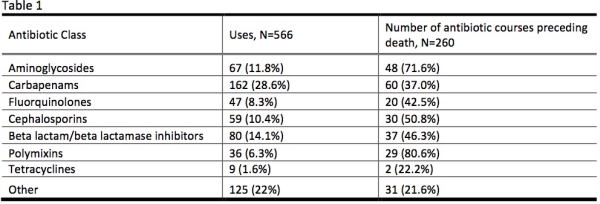
Outcomes: 504 cultures were obtained from 187 patients. 405/504 (80.3%) cultures were treated with one or more antibiotics. Among treated cultures, 159 (39.2%) were urine cultures, 94 (23.2%) were respiratory cultures (23.2%) and 78 (19.3%) were blood cultures. 566 antibiotic courses were given as either empiric or organism-specific therapy. Eighty (14.1%) of antibiotic courses were associated with subsequent need for renal replacement therapy. Treated cultures were associated with 216 hospitalizations and 120 ICU admissions. Thirty-six (6.3%) of antimicrobial courses were associated with possible neurotoxicity. Three allergic reactions were observed. At the end of the study's follow-up, 65/153 treated patients (42.5%) were deceased. Table 1 shows the frequency of use of each antibiotic class as well as the frequency of death following antibiotic use.
Conclusions: Antibiotic therapy is initiated for the majority of positive cultures among solid organ transplant patients. Urine is the most common source of infection, though colonization, rather than true infection, of the urine is common. Carbapenams are the most commonly used class of antibiotics, and aminoglycosides and polymixins are used in one-fifth of cases. A sizeable minority of patients require renal replacement therapy after the initiation of antibiotics. Death is common following treatment with aminoglycosides and polymixins. Further investigation is needed to determine relationship between specific classes of antibiotics and outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Heldman M., Nelson B., Babu T., Ison M. Treatment of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Infections after Solid Organ Transplant Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Heldman M, Nelson B, Babu T, Ison M. Treatment of Multi-Drug Resistant Gram Negative Infections after Solid Organ Transplant [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/treatment-of-multi-drug-resistant-gram-negative-infections-after-solid-organ-transplant/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress