Time within Therapeutic Range: A Comparison of Three Tacrolimus Formulations within Ninety Days of Renal Transplant
University of Illinois Hospital and Health Sciences System, Chicago, IL
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A239
Keywords: African-American, FK506, Kidney transplantation, Obesity
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 1, 2019
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall C & D
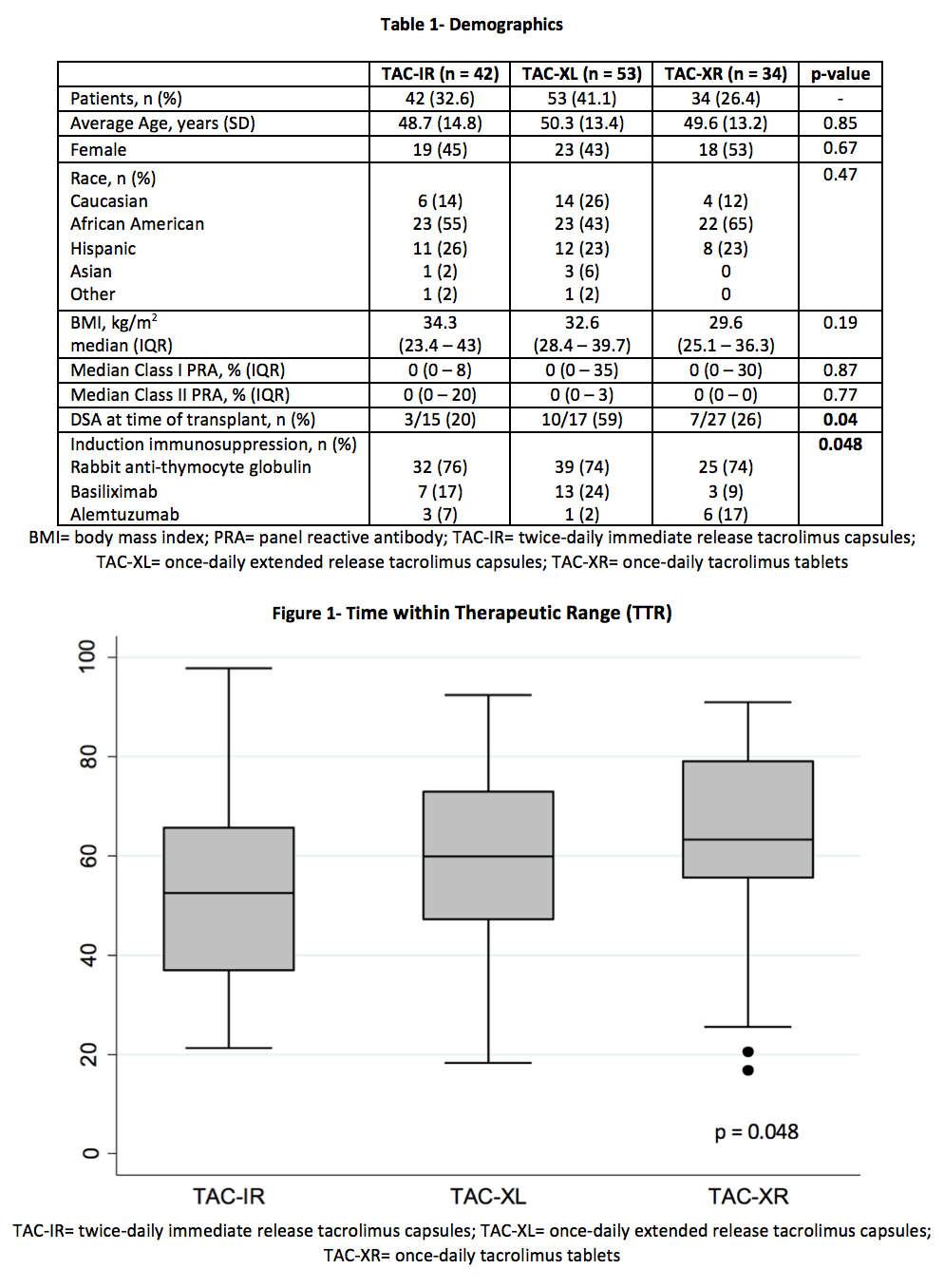
*Purpose: Optimizing tacrolimus (TAC) time within therapeutic range (TTR) has been shown to improve outcomes post-transplant. To date, there are no studies assessing differences in TTR among the 3 TAC formulations (immediate-release [TAC-IR]; extended-release capsules [TAC-XL]; extended-release tablets [TAC-XR]). The controlled release of TAC-XR is associated with a unique pharmacokinetic profile that includes lower peak concentrations and less intra-day fluctuation which may lead to improved TTR. The aim of this study is to compare differences in TTR among the 3 TAC formulations.
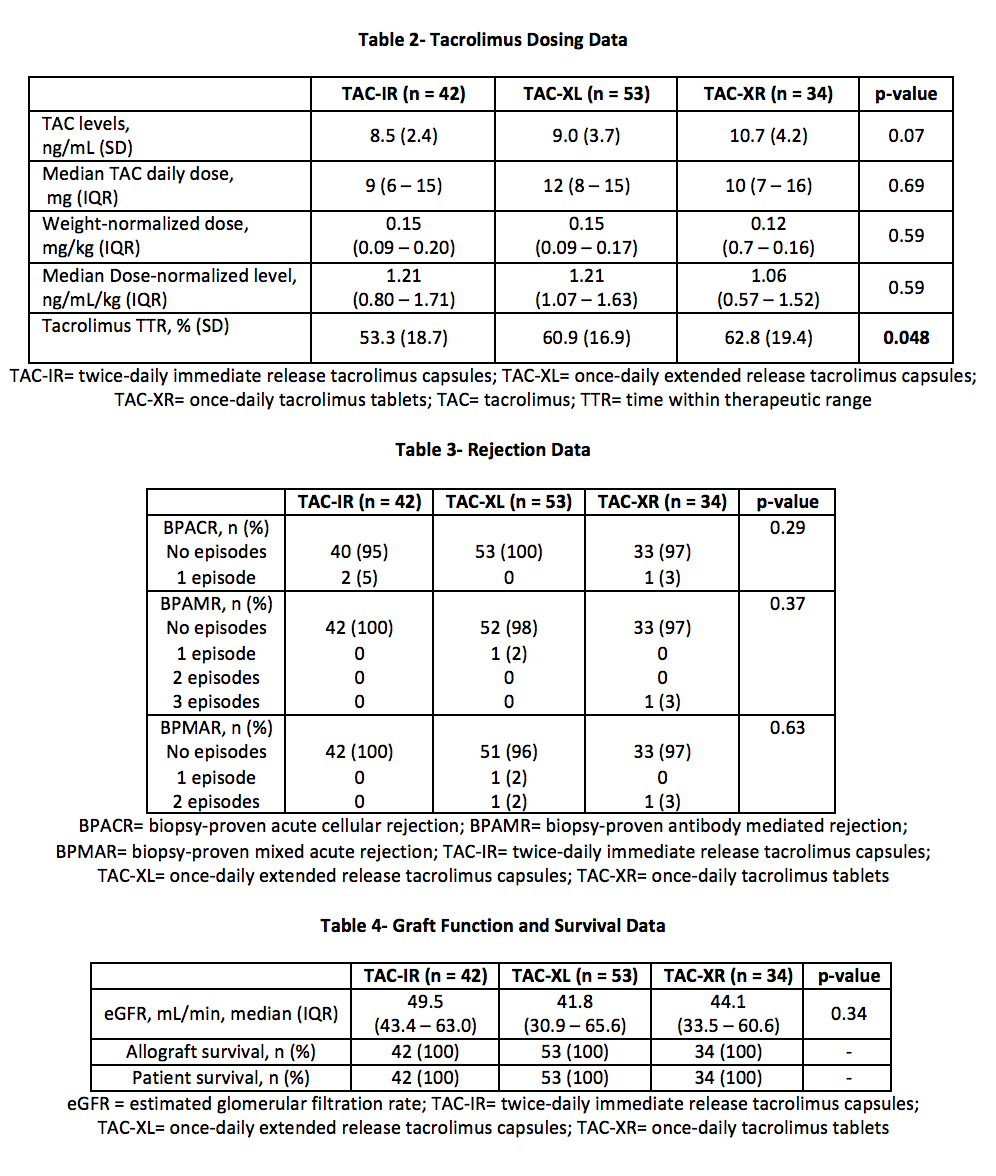
*Methods: A total of 187 renal transplant recipients were retrospectively identified for analysis from 01/01/2013 to 10/01/2017. Exclusion criteria included: deviation from standard TAC protocol, formulation changes, multi-organ, or en-bloc transplant. The primary outcome compared percent TTR (%TTR) among 3 TAC formulations over the first 90 days post-transplant. TTR was calculated using the Rosendaal method. Secondary outcomes included: TAC levels, TAC dose, eGFR, rejection, patient and graft survival. Comparisons were made with chi-square comparisons, the Kruskal-Wallis test, and one-way ANOVAs as appropriate.
*Results: A total of 129 patients were analyzed. The average patient was 50 years old, male, and of African American decent with median BMI 30-34 kg/m2 (Table 1). TAC-XR demonstrated a significantly favorable %TTR compared to TAC-IR and TAC-XL (62.8% vs 53.3% vs. 60.9%, p = 0.048) (Figure 2, Table 2). In post-hoc analysis, TAC-XR had a higher %TTR compared to TAC-IR (p = 0.065), which approached statistical significance. Average TAC levels, weight-normalized TAC doses, median dose-normalized TAC levels, rejection rates, eGFR, and graft or patient survival were similar among groups (Tables 3 and 4).
*Conclusions: In the early transplant period, TTR was significantly different among the groups. TAC-XR demonstrated numerically superior time within therapeutic range. Longer duration of follow-up and investigation into impact on post-transplant outcomes is warranted.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Patel S, Khalil K, Lichvar A, Benedetti E, West-Thielke P. Time within Therapeutic Range: A Comparison of Three Tacrolimus Formulations within Ninety Days of Renal Transplant [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/time-within-therapeutic-range-a-comparison-of-three-tacrolimus-formulations-within-ninety-days-of-renal-transplant/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress