Three-Year Graft Loss Risk in Kidney Transplants: Dynamic Patient Level Data Improve Predictive Efficacy.
MUSC, Charleston, SC.
Meeting: 2016 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 1
Keywords: Outcome, Prediction models, Risk factors, Survival
Session Information
Session Time: 8:30am-9:45am
 Presentation Time: 8:30am-8:45am
Presentation Time: 8:30am-8:45am
Location: Veterans Auditorium
Background: Predictive models in kidney transplantation using national data (UNOS, SRTR) lack longitudinal patient level data, limiting accuracy. Adding patient level data capturing dynamic clinical evolution post-tx, may improve predictive accuracy for graft loss (GL) risk.
Methods: In a quality initiative, we built GL risk prediction models, using baseline and follow up data (0- 90-days post-tx; structured & unstructured) on adult solitary kidney transplant recipients transplanted 2007-15. Structured data were directly applied from electronic medical records (EHR,Txp database (Velos) and UNOS.Natural Language Processing (IBM Watson) was applied to unstructured text to extract Banff scores and vitals. We built 4 models: Model 1) UNOS data; Model 2) UNOS & Velos (caregiver) data; Model 3) UNOS, Velos & EHR data (comorbidity); Model 4) UNOS, Velos, EHR & Post-tx trajectory data. We used IBM SPSS Modeler and Essentials for R in analyses. We used Backward Selection at the 20% level to select variables; statistical significance was determined at the 5% level.
Results: We included 890 patients in the GL model, with a 10% 3-yr GL rate. Model 1: KDRI significantly associated with increased 3-year GL (AUC ,0.66 ;95% CI: 0.60, 0.72). Model 2: With addition of Velos data we saw a favorable association on 3-year GL of the patient having a Primary Care Giver at Tx (AUC, 0.68 ;95% CI: 0.61, 0.74). Model 3 EHR data (Cardiac Arrhythmia) added significant positive association with 3-year GL(AUC,0.72;95% CI: 0.66, 0.77). Model 4 : Several post-transplant trajectory variables through year 1 post-tx added to model accuracy: Pulse Pressure Standard Deviation, Hemoglobin Slope (day7-365), Std Deviation of eGFR, Days from Tx to 1st Maximum eGFR, Acute MI, Cardiac or Vascular Events, and 1st year Acute Banff lesion scores (AUC ,0.84, 95% CI: 0.79, 0.89).
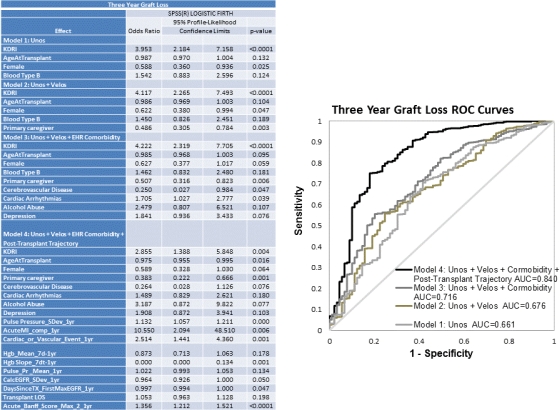
Conclusion: A Big Data approach to curating diverse data sources significantly adds accuracy to 3 year graft loss prediction models, capturing complexity and longitudinal evolution across several clinically mutable domains. This solution is executable daily through EHR workflows to optimize outcomes.
CITATION INFORMATION: Srinivas T, Zhang J, Su Z, Taber D, Marsden J, Reilly K, Northrup D, Long J, Lenert L, Moran W, Mauldin P. Three-Year Graft Loss Risk in Kidney Transplants: Dynamic Patient Level Data Improve Predictive Efficacy. Am J Transplant. 2016;16 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Srinivas T, Zhang J, Su Z, Taber D, Marsden J, Reilly K, Northrup D, Long J, Lenert L, Moran W, Mauldin P. Three-Year Graft Loss Risk in Kidney Transplants: Dynamic Patient Level Data Improve Predictive Efficacy. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2016; 16 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/three-year-graft-loss-risk-in-kidney-transplants-dynamic-patient-level-data-improve-predictive-efficacy/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2016 American Transplant Congress
