The Price of Diabetes Medication Management in Kidney Transplantation: Similar Rates of Readmissions, but More Healthcare Utilization
J. Hardcopf, H. Meadows, N. Pilch, C. Perez, N. Patel, J. Fleming, H. Corbo, T. Harrison, B. O'Brien, D. DuBay, D. Taber.
Medical University of South Carolina, Charleston, SC.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: A228
Keywords: Hyperglycemia, Kidney transplantation, Outcome
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session A: Kidney: Cardiovascular and Metabolic
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, June 2, 2018
Session Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
 Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Presentation Time: 5:30pm-7:30pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Background: The aim of this study was to determine whether changing diabetes (DM) medications during the index admission for kidney transplant (KT) is significantly associated with post-transplant outcomes.
Methods: Retrospective cohort study of adult KT recipients between 7/2015 and 7/2017. Patients that had an admission medication reconciliation at time of transplant verified by a pharmacist and were seen in clinic within 3 days of discharge were included. Outcomes included readmissions, rejection, graft loss and healthcare utilization. Overall utilization definition: composite of clinic visits, length of stay of hospitalizations and ED visits 90 days post-transplant. DM med modifications definition: addition and/or deletion of oral and/or subcutaneous meds.
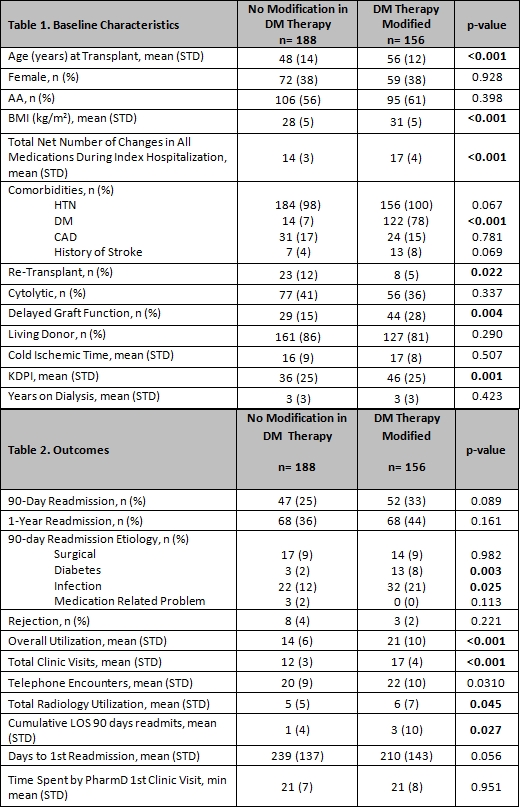
Results: 344 patients were included. A mean of 2 modifications in DM med therapy per patient was observed. Those with DM medication modifications were significantly older, had higher BMIs, more likely to have DM prior to transplant, re-transplant, develop DGF, and have a higher total net number of changes in all medications during index hospitalization. In univariate analysis, the impact of DM med changes on rejection or 90-day and 1-year readmission risk was not significantly different. Readmission etiologies demonstrated that KTs with DM med changes were readmitted predominately more for DM complications and infection. Overall healthcare utilization at 90-days post-transplant, including clinic visits, telephone calls, radiology, and total LOS, was significantly higher in those with DM med changes (Table 2).
Conclusion: KT recipients with DM med changes had similar rates of readmission, but utilized significantly more healthcare resources during first 90-days post-transplant follow-up period to achieve similar outcomes. By increasing resources utilized by these high risk patients, patients with DM medication changes may achieve similar clinical outcomes as those who do not require DM medication changes post transplant. Further studies are needed to confirm these findings.
CITATION INFORMATION: Hardcopf J., Meadows H., Pilch N., Perez C., Patel N., Fleming J., Corbo H., Harrison T., O'Brien B., DuBay D., Taber D. The Price of Diabetes Medication Management in Kidney Transplantation: Similar Rates of Readmissions, but More Healthcare Utilization Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Hardcopf J, Meadows H, Pilch N, Perez C, Patel N, Fleming J, Corbo H, Harrison T, O'Brien B, DuBay D, Taber D. The Price of Diabetes Medication Management in Kidney Transplantation: Similar Rates of Readmissions, but More Healthcare Utilization [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-price-of-diabetes-medication-management-in-kidney-transplantation-similar-rates-of-readmissions-but-more-healthcare-utilization/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress