The Immigrant Bonus: Non US Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients Have Superior Outcomes versus US Citizen Recipients. A Retrospective Study of 30,092 Subjects Using the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network (OPTN) from 1992-2015
1Transplant Surgery, Crozer Prospect Medical Center-Drexel University, Upland, PA, 2Transplant Surgery, Baylor College of Medicine, Houston, TX
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 213
Keywords: Allocation, Hispanic, Kidney, Multivariate analysis
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Presentation Time: 2:54pm-3:06pm
Location: Ballroom B
*Purpose: In 2017, there were 19,849 kidney transplant recipients, and most of these patients were US Citizens1. There has been however, a significant amount non-US citizen transplant activity in the US. The United Network for Organ Sharing (UNOS) has set as a maximum of 5% of recipients involved in transplant tourism; This policy is now replaced with the 2012 policy that requires all transplant centers to record the citizenship of their patients2. The continued profound organ shortage makes it imperative that this subset of non-US citizen recipients is closely analyzed and critically compared to US recipients.
*Methods: We retrospectively analyzed 30,092 kidney transplant recipients using the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network (OPTN). Using Multivariate Cox Regression and Kaplan-Meier methodology, we evaluated differences in baseline characteristics and outcome in both overall and graft survival between US-Citizen and non-US citizen kidney transplant recipients.
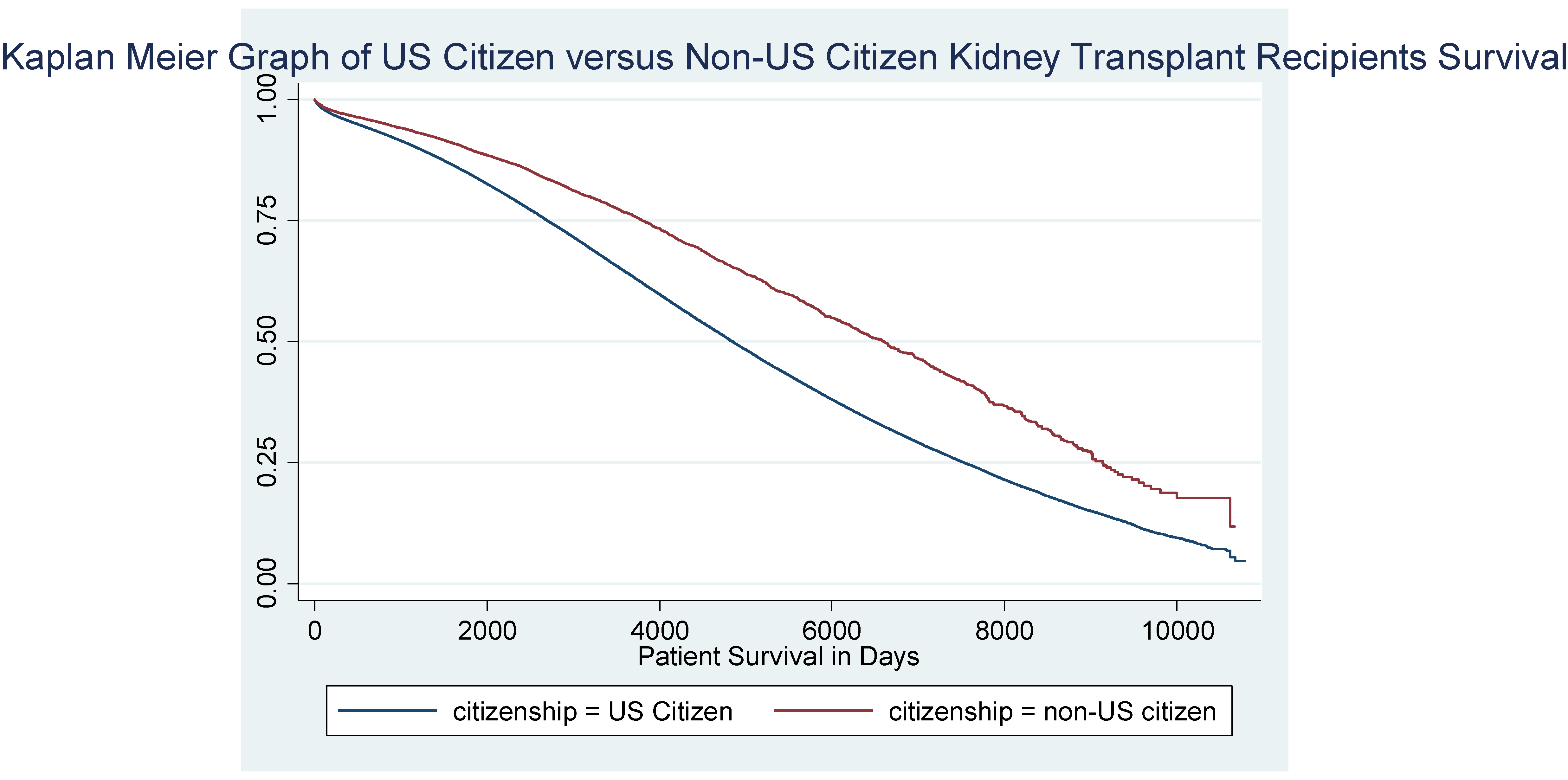
*Results: The US citizens were characteristically similar to the non-US citizens. Non-US citizens have a 10% increase in patient survival when compared to US citizen recipients over time. Most of the non-US recipients were from the country of Mexico (48%). Table 1. Baseline Characteristics of 30,092 Subjects Included in the Organ Procurement Transplant Network Retrospective Analysis Model by Citizenship.
| US Citizens | Non-US Citizens | **p= | |
| Subjects (30,092 total) (n,%) | 29,009 (96%) | 1083 (4%) | |
| Age of Recipient** | 48.7± 17.0 | 44.4±18.5 | <.001 |
| Race (n,%) White | 15,478 (53%) | 160 (15%) | <.001 |
| Black | 9,047 (31%) | 123 (11%) | |
| Other | 1,444 (11%) | 613 (57%) | |
| Hispanic Ethnicity | 3037 (5%) | 187 (17%) | |
| Gender of Recipient (n,%) Male | 18,110 (62%) | 672 (62%) | .80 |
| Female | 10,896 (38%) | 411 (38%) | |
| Blood Type of the Recipient (n,%) O | 13,002 (45%) | 518 (48%) | .01 |
| A | 10,920 (38%) | 356 (33%) | |
| B | 3,635 (13%) | 154 (14%) | |
| AB | 1,449 (15%) | 55 (5%) | |
| Recipient Peripheral Vascular Disease (n,%) | 1,658 (15%) | 52 (5%) | .05 |
| Extended Criteria Donor (n,%) | 5,488 (19%) | 192 (18%) | .33 |
| Functional Status (n,%) No assistance | 11,092 (38%) | 507 (47%) | <.001 |
| Some assistance | 4,284 (15%) | 142 (13%) | |
| Total assistance | 2751 (9%) | 88 (8%) | |
| On hemodialysis prior to transplant (n,%) | 21,997 (76%) | 893 (83%) | <.001 |
| Diabetes (n,%) | 11,473 (40%) | 325 (30%) | <.001 |
| Primary Payment Using Insurance (n,%) | 28,942 (99%) | 1,041 (70%) | <.001 |
| Previous transplant (n,%) | 3,308 (11%) | 70 (7%) | <.001 |
| Delayed Graft Function (n,%) | 8,732 (30%) | 325 (30%) | .53 |
| Age of the Donor* | 37.9±17.4 | 37.4±17.8 | .28 |
| PRA (n,%) 0-20 | 24,763 (85%) | 957 (88%) | .004 |
| 20-80 | 2,777 (10%) | 94 (9%) | |
| 80-100 | 1466 (5%) | 32 (5%) |
Table 2. Cox Survival Regression Model Results from the Organ Procurement Transplant Network from1992-2015 with Covariates of Interest.
| *Hazard Ratio w/ CI | **p= | |
| Non-US Citizenship | .91 (.83-.99) | .03 |
| Male Gender | .99 (.97-1.10) | .07 |
| Age of Recipient | 1.03 (1.03-1.04) | <.001 |
| Blood type ABO (O as Reference) A | 1.00 (.98-1.04) | .75 |
| B | 1.06 (1.02-1.11) | .01 |
| AB | .97 (.91-1.10) | .36 |
| Race (White as Reference) Black | .94 (.91-.97) | <.001 |
| Other | .83 (.78-.88) | <.001 |
| Hispanic Ethnicity | .83 (.78-.87) | <.001 |
| Body Mass Index of Recipient | 1.00 (.99-1.00) | .10 |
| Peripheral Vascular disease in Recipient | 1.04 (1.01-1.06) | .01 |
| Extended Criteria Donor | .97 (.94-1.02) | .29 |
| Functional Status (No Assistance as Reference) Some Assistance | 1.17 (1.12-1.22) | <.001 |
| Total Assistance | 1.84 (1.76-1.93) | <.001 |
| Hemodialysis Prior to Transplant in Recipient | 1.31 (1.27-1.36) | <.001 |
| Diabetes in Recipient | 1.33 (1.29-1.37) | <.001 |
| No Insurance | 1.05 (.80-1.37) | <.001 |
| Previous Transplant | 1.09 (1.03-1.14) | .001 |
| Delayed Graft Function | 1.12 (1.09-1.15) | <.001 |
| Donor Age | 1.00 (1.00-1.00) | .02 |
| Hepaitis C Positivity in Recipient | 1.02 (.99-1.04) | .10 |
| Panel Reactive Antibody (0-20 as Reference) (20-80) | 1.09 (1.04-1.15) | <.001 |
| (80-100) | 1.14 (1.07-1.22) | <.001 |
*Conclusions: Adjusting for gender, age of recipient, blood type, previous transplant, race, ethnicity, BMI of the recipient, peripheral vascular disease of the recipient, ECD donor, functional status, HD and diabetes in the recipient, insurance, delayed graft function, age of donor, hepatitis C positivity in recipient, and PRA, the mostly Mexican Non-US citizen kidney transplant recipients show superior survival when compared to US citizen recipients. These superior outcomes in Non-US citizens justify current UNOS policy of helping these patients.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Butler T, Rana A, Fink S. The Immigrant Bonus: Non US Deceased Donor Kidney Transplant Recipients Have Superior Outcomes versus US Citizen Recipients. A Retrospective Study of 30,092 Subjects Using the Organ Procurement and Transplant Network (OPTN) from 1992-2015 [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-immigrant-bonus-non-us-deceased-donor-kidney-transplant-recipients-have-superior-outcomes-versus-us-citizen-recipients-a-retrospective-study-of-30092-subjects-using-the-organ-procurement-and-tr/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress