The First 9 Years of KPD through the National Kidney Registry: Characteristics of Donors and Recipients Compared to National Transplant Registries
S. Flechner,1 A. Thomas,2 M. Ronin,3 J. Veale,4 D. Leeser,5 S. Kapur,6 J. Piepert,4 D. Segev,2 G. Hil,3 A. Waterman.4
1Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
2Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD
3National Kidney Registry, Babylon, NY
4UCLA, Los Angeles, CA
5East Carolina, Greenville, NC
6Cornell, New York, NY.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 445
Keywords: Donation, Donors, Kidney transplantation, unrelated
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Paired Exchange
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Tuesday, June 5, 2018
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Presentation Time: 2:30pm-2:42pm
Location: Room 4B
Purpose: The NKR is a voluntary network of 75 transplant centers in 28 States in the USA focused on the facilitation of live donor kidney transplants through kidney paired exchange (KPD), the majority of which are incompatible pairs. This report will describe who is actually transplanted.
Methods: The NKR database was linked and cross validated to the SRTR database using UNOS donor ID, transplant center, date of transplant, donor ABO and gender, recipient ABO and gender. The study population comprised 2,037 consecutive NKR transplants between February 14, 2008 and February 14, 2017, 9 years inclusive. These patients were compared to three distinct control populations from the same time intervals, subtracting the NKR cases.
Control 1: All Live Donor kidney transplants reported to the SRTR; n=49,610
Control 2: All Living Unrelated kidney transplants reported to SRTR; n=23,319
Control 3: All LUR transplants reported to SRTR designated as KPD; n=4,236
Results: The majority of NKR Transplants were between ABO compatible (97.8%) and crossmatch negative (88.3%) pairs. There were 239 recipients intentionally desensitized to facilitate transplant, and 35.8% were pre-emptive. During this time interval the annual rate of unmatched recipients at the end of each year declined from 79% in 2008 to 35% in 2017.
Conclusions: NKR facilitated KPD transplants can be done over a wide geographic area among a demographically and immunologically diverse transplant population with rates and outcomes that equal or exceed national trends. Sharing among NKR centers permits the transplantation of historically difficult to match pairs at rates that exceed those reported by single centers. 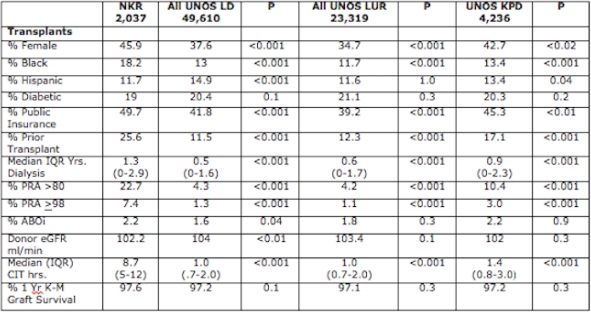
CITATION INFORMATION: Flechner S., Thomas A., Ronin M., Veale J., Leeser D., Kapur S., Piepert J., Segev D., Hil G., Waterman A. The First 9 Years of KPD through the National Kidney Registry: Characteristics of Donors and Recipients Compared to National Transplant Registries Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Flechner S, Thomas A, Ronin M, Veale J, Leeser D, Kapur S, Piepert J, Segev D, Hil G, Waterman A. The First 9 Years of KPD through the National Kidney Registry: Characteristics of Donors and Recipients Compared to National Transplant Registries [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-first-9-years-of-kpd-through-the-national-kidney-registry-characteristics-of-donors-and-recipients-compared-to-national-transplant-registries/. Accessed March 4, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
