The Association Between Environmental Determinants and High KDRI Organ Offer Acceptance Ratios
United Network for Organ Sharing, Henrico, VA
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 30
Keywords: Donors, marginal, Kidney, Multivariate analysis, Public policy
Topic: Clinical Science » Kidney » Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Information
Session Name: Kidney Deceased Donor Allocation
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 5, 2021
Session Time: 4:30pm-5:30pm
 Presentation Time: 4:45pm-4:50pm
Presentation Time: 4:45pm-4:50pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Increasing the number of transplants could be realized by increasing high KDRI organ utilization. While the impact of transplant center (TXC) aggressiveness and competition on kidney offer acceptance is known, little is known about how changes in the donor pool affects acceptance rates (O to E ratio). Resource Dependence Theory posits that increased munificence (donor pool) could induce deceases in high KDRI acceptance ratios. Our questions are how stable are acceptance ratios for high KDRI kidneys over time, and do changes in donor volume affect acceptance patterns of high KDRI organs?
*Methods: We collected kidney PTR data from 2015 to 2019. Replicating SRTR risk-adjusted offer acceptance models, we calculated O to E ratios for each KDRI strata each year. We calculated TXC volumes, number of kidneys recovered per DSA, and the HHI Index per DSA (a measure of competition) for each year from the OPTN STAR file. Examining the high KDRI strata, we examined the Spearman correlation between 2015 O to E ratios and 2019 O to E ratios; in addition, we leveraged the panel analysis methods of first difference estimators and robust clustered errors to control for omitted variables and autocorrelation. The dependent variable was the logarithmic transformation of acceptance ratio. Independent variables were the log of the number of donors, log of transplant volume, log of prior year’s acceptance ratio, and HHI.
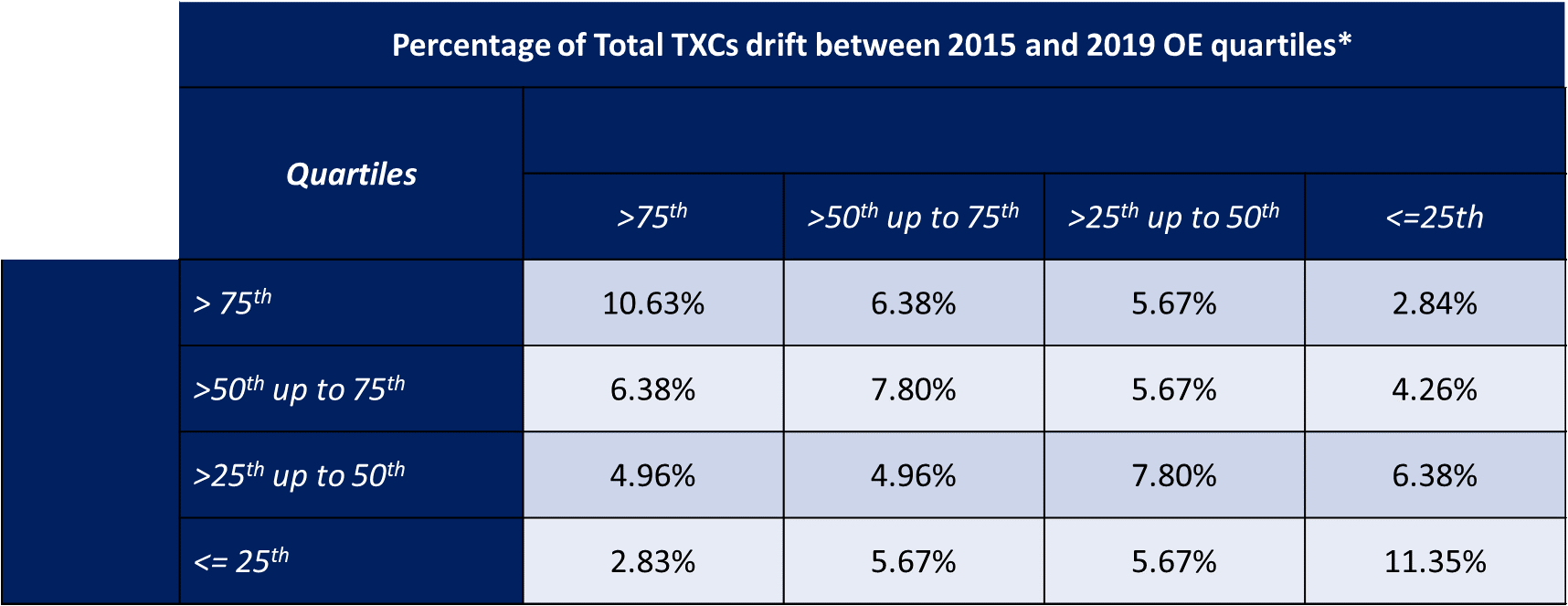
*Results: The Spearman correlation between 2015 acceptance ratios and 2019 acceptance ratios was .46. Regression analysis indicates that increases in donor volume was negatively (-.54) and near significant (p=.0975). Increases in transplant volume were positive (.77) and statistically significant (p<.0001). Previous year’s O to E ratio was negative (-.301) and statistically significant (p <.0001). Adjusted R squared was .1867.
*Conclusions: Results indicate the previous year’s performance, in terms to O to E ratios, may reflect either a regression to the mean effect or strategic decisions by TXCs. Since the dependent variable was log transformed and centered around zero, it could also reflect general changes in the national benchmark. That said, the Spearman correlation indicates that rank ordering does change over time as exhibited in Table 1. While our hypothesis about the number of recovered kidneys was near significant, directionally a 1% increase in donor volume is associated with .53% decrease in high KDRI offer acceptance. Future research should examine whether increases or decreases in the donor pool interact with PSR ratings from the prior year.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Placona AM, Martinez C, Stuart M. The Association Between Environmental Determinants and High KDRI Organ Offer Acceptance Ratios [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/the-association-between-environmental-determinants-and-high-kdri-organ-offer-acceptance-ratios/. Accessed February 19, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress