TBX21 Polymorphism Influence BK Virus Viremia in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients (SOT)
University Hospital, Lausanne, Switzerland
University Hospital, Zürich, Switzerland
Cantonal Hospital, St Gallen, Switzerland
Clinica Luganese, Lugano, Switzerland
University Hospital, Basel, Switzerland
University Hospital, Geneva, Switzerland
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 432
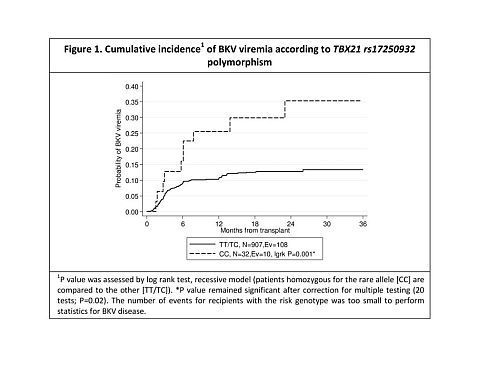
Background Human polyomavirus BK (BKV) viremia is an important cause of nephropathy among SOT after kidney transplantation. Single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in immune genes have been previously associated with susceptibility to viral infection, but few studies explored the role of such polymorphisms on BK viremia and/or disease. Methods The STCS is a large, well documented prospective cohort of SOT recipients followed at 6 hospital centers in Switzerland. DNAs from patients were genotyped using a custom-made Illumina® Golden Gate assay. We analyzed the association between 20 SNPs from 12 genes previously associated with viral phenotypes (IL28B, CCR2, CCR5, CD209, CLEC4M, CXCL12, TLR8, TLR9, TLR2, TBX21, TRAF6, RAG1) and BK reactivation or disease, by using cumulative incidence charts and multivariate Cox regression models. Results The study included 1099 Caucasian SOT patients (670 kidneys, 187 liver, 148 lungs, 79 hearts, 60 other/mixed). BKV viremia occurred in 136 recipients (including 121 kidney transplant) and was associated with SNP in TBX21 (rs17250932; Figure 1). The associations remained significant after adjustment for relevant covariates (Table 1), including treatment with tacrolimus. Conclusion A SNP in IFN-Γ transcription factor gene TBX21 may promote BKV viremia in SOT recipients. This observation may have implication for preventive strategies.
| Variable | HR | 95% CI | P |
| TBX21 rs17250932 (CC vs TT/TC) | 2.70 | (1.41-5.17) | 0.003 |
| Tacrolimus | 1.62 | (1.05-2.48) | 0.03 |
| Recipient age (per year) | 0.99 | (0.98-1.00) | 0.18 |
| Donor age (per year) | 1.00 | (0.99-1.01) | 0.93 |
| Recipient sex | 1.37 | (0.90-2.08) | 0.14 |
| Donor sex | 1.00 | (1.00-1.00) | 0.15 |
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Wójtowicz A, Bibert S, Manuel O, Golshayan D, Berger C, Boggian K, Garzoni C, Weisser M, Delden CVan, Mueller N, Meylan P, Pascual M, Hirsch H, Bochud P. TBX21 Polymorphism Influence BK Virus Viremia in Solid Organ Transplant Recipients (SOT) [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tbx21-polymorphism-influence-bk-virus-viremia-in-solid-organ-transplant-recipients-sot/. Accessed March 12, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
