Targeted Urine Metabolomics for Monitoring Renal Allograft Injury and Immunosuppression
University of California San Francisco, San Francisco, CA
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 310
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, Rejection, Urinalysis
Session Information
Session Name: Biomarkers, Immune Assessment and Clinical Outcomes III
Session Type: Oral Abstract Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:45pm
 Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Presentation Time: 4:03pm-4:15pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: The purpose of this study was to apply high-throughput metabolomics and machine learning to identify surrogate urine metabolite biomarkers for acute rejection vs. BK virus nephritis (BKVN), and for stable patients on both CNI-based and CNI-free/Belatacept based immunosuppression (IS).
*Methods: Established urine processing and metabolomic assessment protocols using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry (GC-MS) were applied to biopsy matched urine samples from 310 unique kidney transplant recipients, 73 of which received Belatacept/CNI-free IS. Metabolite identification was done using FiehnLIB protocol. Classification models were developed for AR, STA and BKVN using Random Forests, compared using AUC from ROC, and diagnostic accuracy assessed by the DeLong’s test.
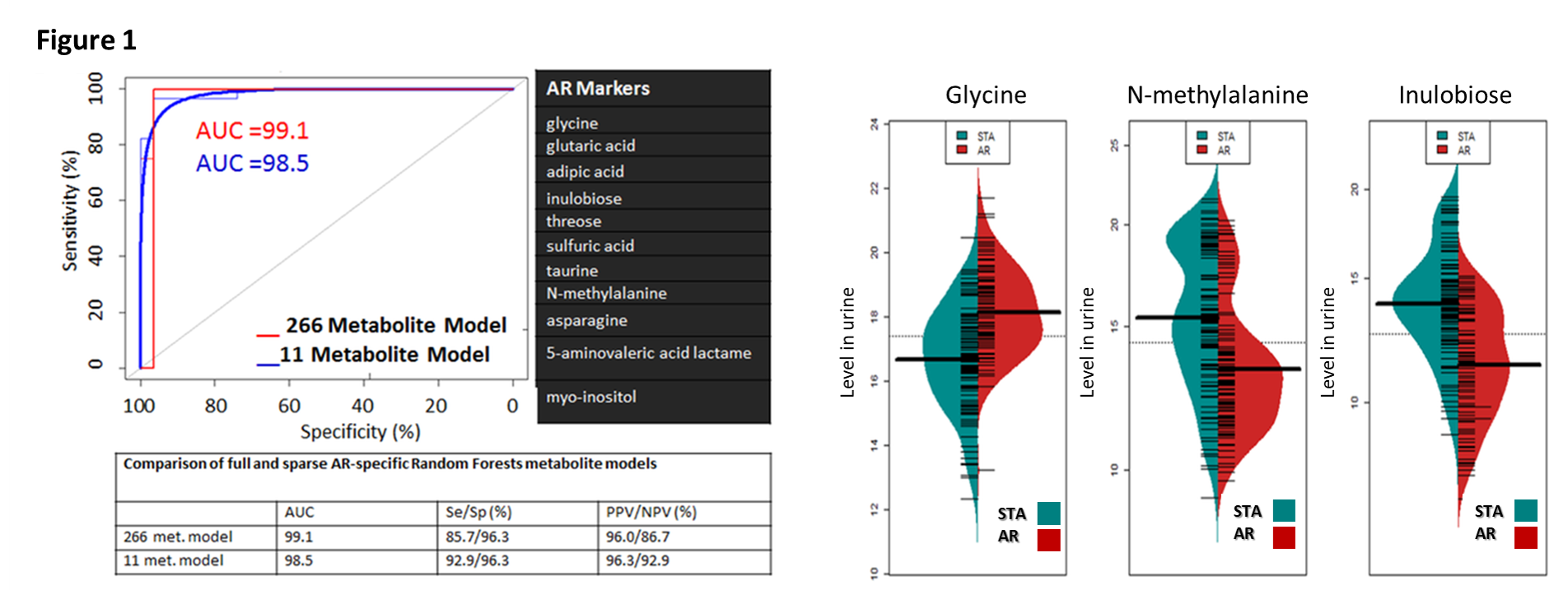
*Results: From a total of 266 urinary metabolites, application of VSURF identified 11 metabolites specific for AR (Fig 1); AUC=0.985, with 92.9% sensitivity and 96.3% specificity (Fig.1). Glycine, N-methylalanine, and inulobiose, were the most significant metabolites in AR (Fig.1, right panel). VSURF identified 5 metabolites specific for BKVN; arabinose, 2-hydroxy-2-methylbutanoic acid, hypoxanthine, benzylalcohol, and N-acetyl-D-mannosamine, with 72.7% sensitivity and 96.2% specificity. Metabolic pathway enrichment identified nitrogen, ascorbate and glucose metabolism as the most enriched pathways in graft rejection. Unique metabolic pathways were noted for Belatacept based IS, involving aminoacyl-tRNA biosynthesis, arginine and proline metabolism.
*Conclusions: Targeted urine metabolomic analyses by GC-MS of biopsy-matched urine samples form kidney transplant patients enables the generation of refined metabolite panels that segregate diagnosis of detect AR and differentiate it from BKVN, which is a clinical unmet need in transplantation. Belatacept based, CNI-free IS drives abundance of tRNAsynthases, which maybe exerting homeostatic control on pathways involved in suppressing inflammation and immunity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Sigdel T, Schroeder A, Yang JY, Sarwal R, Liberto J, Sarwal M. Targeted Urine Metabolomics for Monitoring Renal Allograft Injury and Immunosuppression [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/targeted-urine-metabolomics-for-monitoring-renal-allograft-injury-and-immunosuppression/. Accessed March 14, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress