Tacrolimus Concentrations Are Associated with Measures of Body Composition in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients
1Department of Surgery, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI, 2Morphomic Analysis Group, University of Michigan, Ann Arbor, MI
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-122
Keywords: Immunosuppression, Kidney transplantation, N/A, Prediction models
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Immunosuppression: Novel Regimens and Drug Minimization
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: Tacrolimus (Tacro) is essential for kidney transplant immunosuppression but has a narrow therapeutic window. Tacro dosing preventing rejection must be balanced with potential delayed graft function, nephrotoxicity, hypertension, electrolyte imbalances, and hyperglycemia. Unfortunately, traditional variables are poor predictors of optimal dose, while methods such as gene mapping are impractical. As such, initial dose is based on patient weight and optimal dose is determined by trial and error. Analytic morphomics may provide objective, accessible and novel means to assess body composition and predict optimal Tacro dosing. We investigate the association of analytic morphomics with Tacro trough concentrations in the early post-transplant period.
*Methods: Retrospective data from kidney transplant recipients from June 2004 – September 2015 who underwent CT scan within 18 months prior to transplant were analyzed. Target Tacro trough levels were 8-12 ng/mL, and mean Tacro trough (MTT) levels over the first three days post-transplant were calculated. Morphomic measures of psoas muscle area (PMA), dorsal muscle group area (DMA), subcutaneous fat area (SFA), visceral fat area (VFA), belly fat (BeF), and back fat (BaF) were included. PMA was measured at the L4 vertebral level, DMA at each level from T11 to L3, while other measures were taken at each level from T11 to L4. Principal component analysis was performed on measures with multiple vertebral levels. PMA and the first principal component of each of DMA, SFA, VFA, BeF and BaF were linearly regressed against MTT. Multiple linear regression was performed to control for potential confounding patient characteristics.
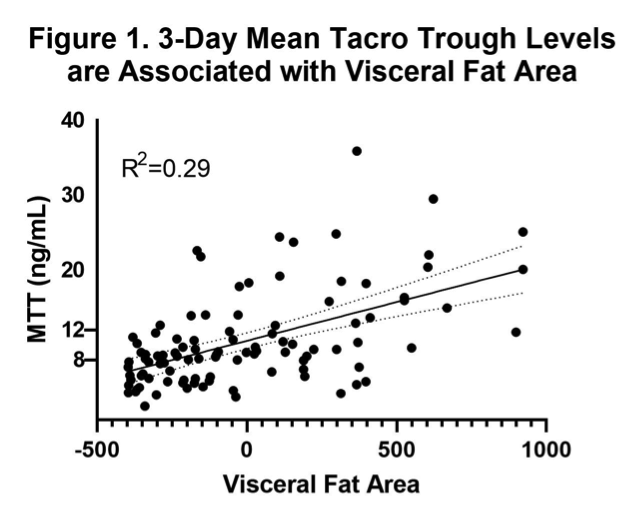
*Results: A total of 101 patients were included in the analysis. The mean MTT was 10.57 ng/mL, and 54 patients had sub-therapeutic MTT levels < 8 ng/mL while 32 patients were supra-therapeutic with MTTs > 12ng/mL. SFA, VFA, and BaF were each significantly associated with MTT, however VFA was most strongly associated with MTT (Figure 1, P < 0.0001, R2= 0.29). VFA remained significant in a linear model controlling for sex, age, weight, height, albumin, hematocrit, and diagnoses of hypertension or diabetes (P < 0.001).
*Conclusions: Analytic morphomic measures such as visceral adiposity offer promise in determining optimal dosing for Tacrolimus. Additional studies which further refine a predictive model would help to avoid complications related to under and over-dosing.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Parker KS, Derstine B, Sullivan J, Wang S, Mazurek A, Cron D, Waits S. Tacrolimus Concentrations Are Associated with Measures of Body Composition in Adult Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/tacrolimus-concentrations-are-associated-with-measures-of-body-composition-in-adult-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress