Survival with Post-Transplant Diabetes Mellitus is Worse after Heart Transplantation
1Medicine, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 2Pharmacy, Stanford University, Palo Alto, CA, 3Cardiology, University Health Network, Toronto, ON, Canada
Meeting: 2020 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C-271
Keywords: Heart transplant patients, Outcome, Post-transplant diabetes, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Heart and VADs: All Topics
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Saturday, May 30, 2020
Session Time: 3:15pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Presentation Time: 3:30pm-4:00pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: An increasing number of patients undergoing heart transplantation (HTx) have diabetes mellitus (DM). However, there is limited data on clinical outcomes after HTx in this population, particularly in those who develop post-transplant DM (PTDM). In this study, we assessed the relationship between DM status and HTx outcomes.
*Methods: This is a single-center, retrospective study of adult HTx recipients between January 2008 and July 2018. We excluded patients with prior HTx and those who died prior to discharge from index hospitalization for HTx. Patients were defined as having PTDM if an antihyperglycemic medication was prescribed after 45 days post-HTx or if their hemoglobin A1c was at least 6.5% (obtained at least 1-year post-HTx). The primary outcome was overall survival; secondary outcomes included macrovascular complications (composite of stroke, transient ischemic attack, and peripheral artery disease), cardiac allograft vasculopathy (CAV; International Society for Heart and Lung Transplantation grade 1 or higher), moderate or severe acute rejection, infection requiring hospitalization, and need for dialysis. Outcomes were assessed with Kaplan-Meier curves and logrank tests.
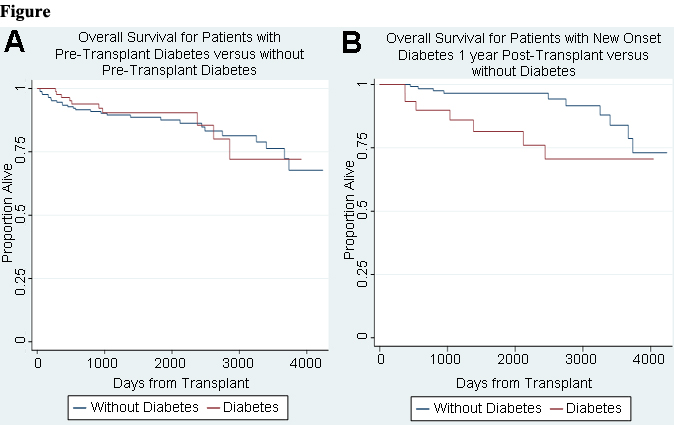
*Results: Of the 253 HTx recipients in the cohort, 85 (33.6%) had pre-transplant DM and, of the 168 who did not have pre-transplant DM, 79 (47.0%) developed PTDM. Compared with patients with pre-transplant DM, those without did not have a significant difference in survival (p=0.82; Figure Panel A). However, compared with patients who had PTDM at 1-year, those who never developed any form of DM had improved survival (p=0.03; Figure Panel B). There were no significant differences in post-HTx macrovascular complications (p=0.13), development of CAV (p=0.88), moderate or severe acute rejection (p=0.14), or need for dialysis (p=0.43) between patients with pre-transplant DM and those without. However, patients with pre-transplant DM, compared to those without, had worse infection requiring hospitalization-free survival (p=0.007).
*Conclusions: HTx recipients who develop PTDM may have worse survival compared to those who do not develop DM. Further investigation with longer follow-up time is necessary to clarify the relationship between DM and HTx outcomes.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Feng KY, Henricksen E, Moayedi Y, Lee R, Han J, Purewal S, Puing A, Basina M, Teuteberg JJ, Khush KK. Survival with Post-Transplant Diabetes Mellitus is Worse after Heart Transplantation [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2020; 20 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/survival-with-post-transplant-diabetes-mellitus-is-worse-after-heart-transplantation/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2020 American Transplant Congress