Successful ABO Incompatible (ABOi) Kidney Transplantation with Rapid Steroid Withdrawal
Nephrology, Columbia University, New York
Surgery, Columbia University, New York
Meeting: 2013 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 231
INTRO: ABOi transplantation is thought to be of high immunologic risk. However, chronic steroid use has been associated with long term complications. Little data are available about outcomes of rapid steroid discontinuation in ABOi patients AIM: We compare a cohort of patients who underwent rapid steroid withdrawal to a historical group maintained on chronic steroids.
METHODS/RESULTS: Since 2004, we have performed 40 ABOi transplants with pre-transplant plasmapheresis(PP) supplemented with IVIG (100mg/kg) to an isohemagluttinin titer ≤1:16 and 2 post-txp PP/IVIG treatments. Maintenance immunosuppression with tacrolimus, mycophenolate is begun pretransplant, and all patients receive intraoperative rituximab (375m/m2). Prior to 2008, patients received induction with IL-2 receptor blocker daclizumab and IV methylprednisone, tapered to 20 mg at day 4, to 5 mg by 6 months. After 2008, induction included Thymoglobulin® (6 mg/kg in 4 divided doses) and steroid withdrawal (IV methylprednisolone 500 mg intraoperatively, 250 mg day 1, 125 mg day 2, 80 mg day 3, then discontinued).
| daclizumab+steroids | thymo+steroid withdrawal | p value | |
| n | 30 | 10 | |
| Male | 30% | 50% | 0.813 |
| AMR | 40% | 30% | 0.56 |
| All rejections | 73.3% | 50% | 0.246 |
| 1 yr creatinine | 1.8±1.2 | 1.6±0.9 | 0.6 |
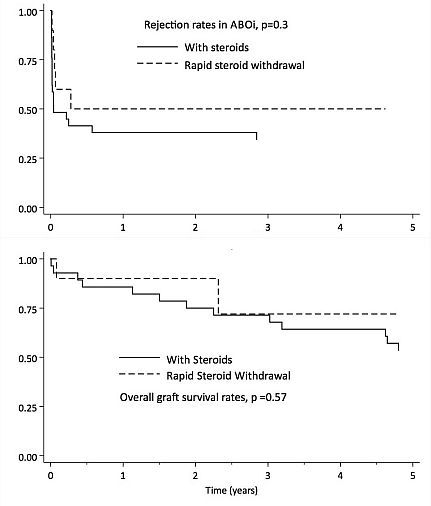
CONCLUSION: Our results demonstrate successful withdrawal of steroids in patients with ABOi renal transplants, leading to similar rejection rates and allograft survival to a historical control group. Rapid steroid discontinuation should be considered in ABOi transplantation and may be beneficial in reducing long term morbidity.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Crew R, Patel S, Mohan S, Dube G, Ratner L. Successful ABO Incompatible (ABOi) Kidney Transplantation with Rapid Steroid Withdrawal [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2013; 13 (suppl 5). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/successful-abo-incompatible-aboi-kidney-transplantation-with-rapid-steroid-withdrawal/. Accessed March 9, 2026.« Back to 2013 American Transplant Congress
