Substance Abuse in Acute Liver Failure: Time to Talk About Opiates.
M. Jesse, N. Rebhan, A. Yoshida, D. Moonka, A. Eshelman, M. Abouljoud, M. Rizzari.
Transplant Institute, Henry Ford Health System, Detroit
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 95
Keywords: Liver failure, Outcome, Psychiatric comorbidity, Psychosocial
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Psychosocial and Mediation Adherence Concerns
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Location: E271b
Purpose: Prescription opiate utilization is on the rise. Research on acute liver failure (ALF) has focused on acetaminophen (APAP) overdose or other medical etiologies but has not examined the influence of chronic opiate use or abuse.
Methods: Retrospective chart review of opiate and other substance abuse histories (from routine psychiatric evaluations) in patients presenting in ALF at a single center from 1/1/04-12/31/12.
Results: 105 ALF patients, etiology; 40 overdose, 65 medical/other. Patients in ALF overdose were significantly more likely to have active issues with opiates compared to other etiologies of ALF (Table 1). However, several ALF due to medical/other had histories or current issues with opiates. Further, alcohol abuse was less frequently reported in the overall sample and there were not significant differences between groups. There were various combinations of active and in remission abuse of other substances (e.g., marijuana, benzodiazepines) present in both groups. For example, 9 patients current marijuana abuse (5 OD, 4 med/other), 3 current cocaine abuse (1 OD, 2 med/other).
Conclusions: Chronic opiate use and dependence were highly prevalent in ALF and the most frequent substance use concern for liver transplantation. It is imperative to distinguish between chronic use, abuse, and dependency, although this distinction adds additional complexity in the evaluation and treatment of these patients. Overall, substance abuse concerns were prevalent in both groups, but greater in the overdose patients.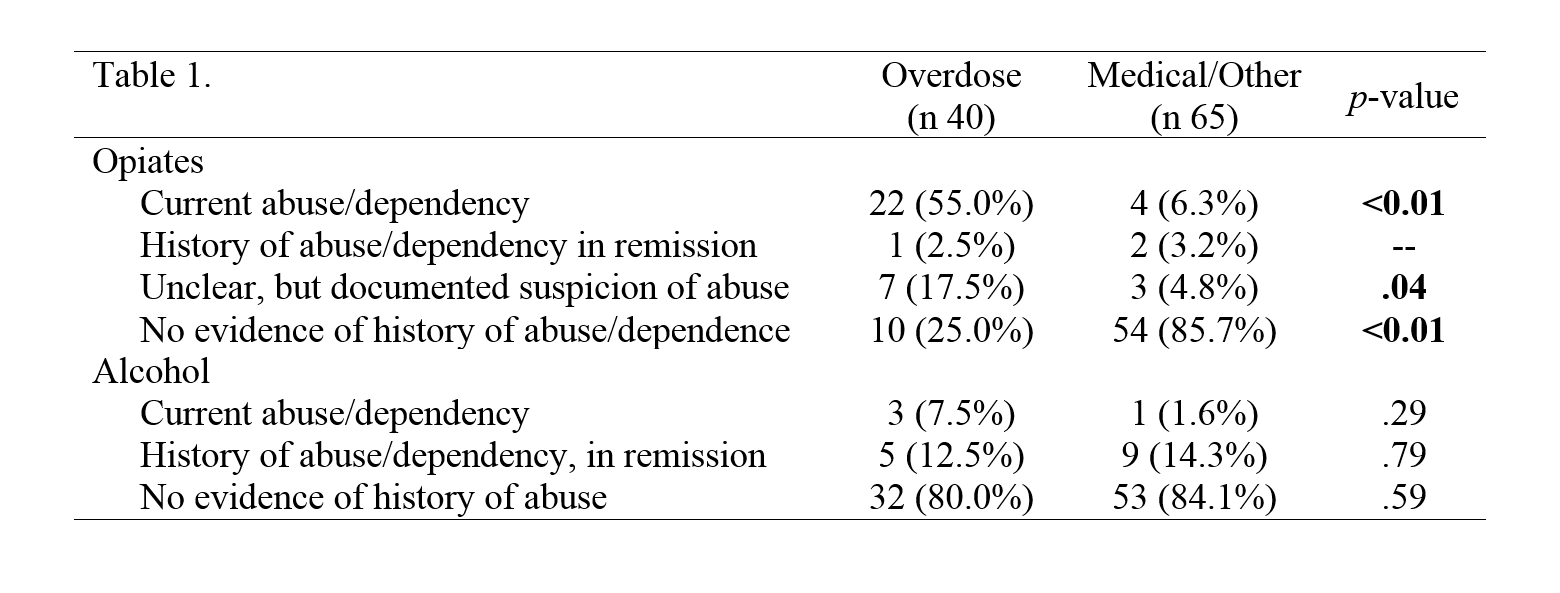 .
.
CITATION INFORMATION: Jesse M, Rebhan N, Yoshida A, Moonka D, Eshelman A, Abouljoud M, Rizzari M. Substance Abuse in Acute Liver Failure: Time to Talk About Opiates. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jesse M, Rebhan N, Yoshida A, Moonka D, Eshelman A, Abouljoud M, Rizzari M. Substance Abuse in Acute Liver Failure: Time to Talk About Opiates. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/substance-abuse-in-acute-liver-failure-time-to-talk-about-opiates/. Accessed March 11, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
