Standardizing Blood Pressure Measurement across 17 Pediatric Transplant Centers: The Improving Renal Outcomes Collaborative
1University of Alabama, Birmingham, AL, 2Emory University, Atlanta, GA, 3Phoenix Children's Hospital, Phoenix, AZ, 4Saint Louis University, St. Louis, MO, 5Stanford University, Stanford, CA, 6Children's Hospital Colorado, Aurora, CO, 7Michigan Medicine, Ann Arbor, MI, 8Lurie Children's Hospital, Chicago, IL, 9University of Iowa, Iowa City, IA, 10Riley Hospital For Children, Indianapolis, IN, 11Children's Hospital of Pittsburgh of UPMC, Pittsburgh, PA, 12UCLA Mattel Children’s Hospital, Los Angeles, CA, 13Seattle Children's Hospital, Seattle, WA, 14Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, 15Cohen Children's Medical Center, New Hyde Park, NY, 16University of Minnesota, Minneapolis, MN, 17Children's Mercy Kansas City, Kansas City, MO, 18Cincinnati Children's Hospital Medical Center, Cincinnati, OH
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 346
Keywords: Hypertension, Kidney transplantation, Outcome, Pediatric
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney: Pediatrics II
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Monday, June 3, 2019
Session Time: 4:30pm-6:00pm
 Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Presentation Time: 4:54pm-5:06pm
Location: Room 304
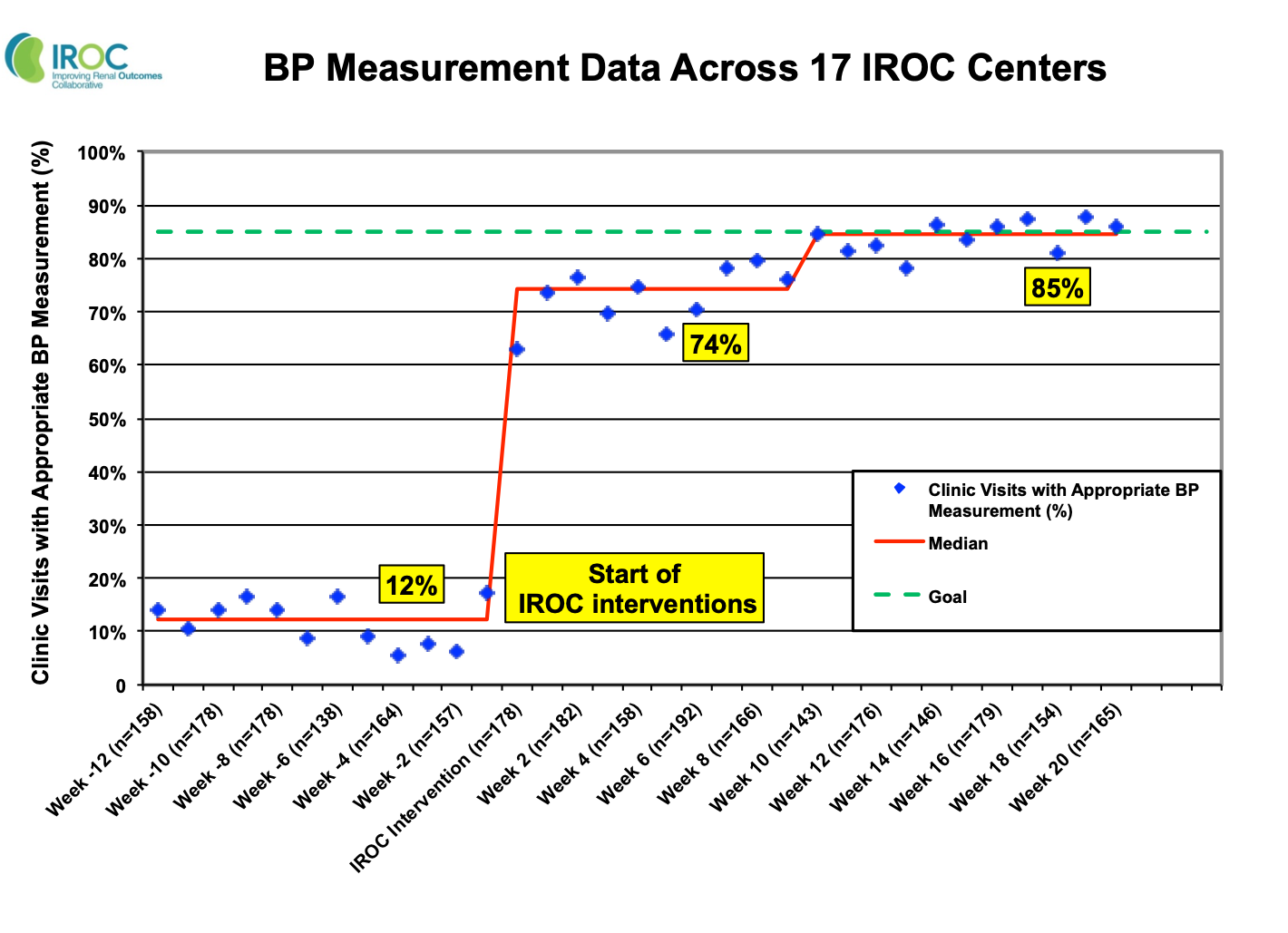
*Purpose: We report efforts from the Improving Renal Outcomes Collaborative (IROC) to standardize appropriate BP measurement across 17 pediatric kidney transplant centers.
*Methods: 17 centers participated in quality improvement (QI) activities facilitated by the IROC QI fundamentals seminar. QI activities included interventions that addressed center-specific barriers to appropriate BP measurement. We prospectively collected BP data from August 2016 to July 2018 and calculated the proportion of clinic visits with appropriate BP measurement according to published guidelines. Data were analyzed over a 12-week baseline pre-intervention period and a 20-week post-intervention period. We used run charts to quantify improvements in appropriate BP measurement across the IROC network.
*Results: We analyzed data from 5,392 transplant clinic visits. Prior to IROC interventions, BP was measured appropriately at just 12% of visits. Common reasons for improper BP measurement included not measuring arm circumference and not allowing 5 minutes of rest. Center-specific interventions included education of clinic staff, creation of BP tracking tools, and regular team meetings. Within 10 weeks post-intervention, BP was measured appropriately at 85% of visits. This improvement was sustained for at least 10 weeks.
*Conclusions: We standardized appropriate BP measurement across 17 pediatric transplant centers using the infrastructure of the IROC learning health system. Accurate BP assessment will allow further interventions to improve patient and graft survival.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Seifert ME, Garro R, George RP, Barletta G, Belsha CW, Chaudhuri A, Goebel JW, Wickman L, Matossian D, Misurac J, Nailescu C, Nguyen CR, Pearl M, Pollack A, Pruette CS, Singer P, Verghese PS, Warady BA, Dahale DS, Hooper DK. Standardizing Blood Pressure Measurement across 17 Pediatric Transplant Centers: The Improving Renal Outcomes Collaborative [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/standardizing-blood-pressure-measurement-across-17-pediatric-transplant-centers-the-improving-renal-outcomes-collaborative/. Accessed March 2, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress