Single versus Bilateral Simultaneous Nephrectomy during Kidney Transplantation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease
1Department of Surgery, Seoul National University College of Medicine, Seoul, Korea
2Department of Surgery, Myongji Hospital, Goyang-si, Gyeonggi-Do, Korea.
Meeting: 2018 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: C180
Keywords: Hypertension, Kidney transplantation, Nephrectomy, Polycystic kidney disease
Session Information
Session Name: Poster Session C: Kidney Technical
Session Type: Poster Session
Date: Monday, June 4, 2018
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Presentation Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
Location: Hall 4EF
Purpose
Although there are some controversies about nephrectomy in patient with autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD), simultaneous nephrectomy has done selectively. There are few report about comparisons between single nephrectomy (SN) and bilateral nephrectomy (BN).
Methods
From 2003 to April, 2017, 46 of ADPKD recipients received simultaneous nephrectomy with their kidney transplantation.
Results
There were 31 SN and 15 SN in ADPKD recipients. Recipient age was 51.9±9.3 in SN and 41.7±17.2 in BN (p=0.012). Indications for nephrectomy were follows: to secure space for kidney graft; uncontrollable hematuria; flank pain; cyst infection. Deceased donors were 12 in SN and 1 in BN (p=0.035). Mean length of resected ADPKD kidney was 21.8±4.5 cm in SN and 25.1±5.1 cm in BN (p=0.036). Operation time was 341.1±66.1 min in SN and 413.7±104.2 min in BN (p=0.006). Estimated blood loss was 1518.0±5296.5 ml in SN and 702.7±515.4 ml in BN (p=0.557). While GFR was higher in BN than in SN during most period 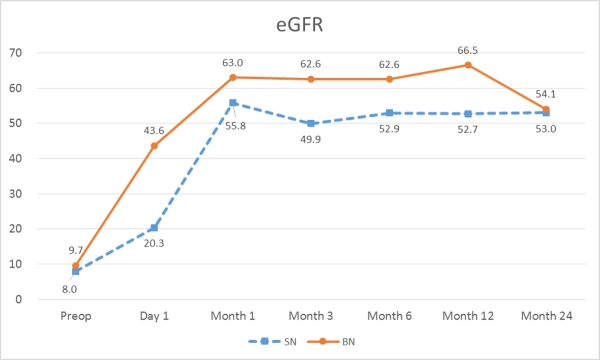 (p=0.015), hemoglobin and mean blood pressure
(p=0.015), hemoglobin and mean blood pressure  were no significant difference between SN and BN. Total follow-up duration was 58.5 months in SN and 85.9 months in BN. One graft failure was in SN due to acute T cell mediated rejection, and two recipient mortalities were in SN by pneumonia and recurrent peritonitis.
were no significant difference between SN and BN. Total follow-up duration was 58.5 months in SN and 85.9 months in BN. One graft failure was in SN due to acute T cell mediated rejection, and two recipient mortalities were in SN by pneumonia and recurrent peritonitis.
Conclusions
In kidney transplantation with younger recipients or living donors, bigger native ADPKD kidney, simultaneous BN was preferred. Postoperative GFR was better in BN. However, operation time was shorter in SN and postoperative control of blood pressure was good in SN as well as in BN.
CITATION INFORMATION: Choi C., Cho S., Cho M-.J., Cho W., Ahn S., Min S-.I., Min S-.K., Kim S., Ha J. Single versus Bilateral Simultaneous Nephrectomy during Kidney Transplantation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Choi C, Cho S, Cho M-J, Cho W, Ahn S, Min S-I, Min S-K, Kim S, Ha J. Single versus Bilateral Simultaneous Nephrectomy during Kidney Transplantation in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease [abstract]. https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/single-versus-bilateral-simultaneous-nephrectomy-during-kidney-transplantation-in-autosomal-dominant-polycystic-kidney-disease/. Accessed February 26, 2026.« Back to 2018 American Transplant Congress
