Simultaneous or Sequential Heart-Liver Transplantation Confer Superior Survival in Patients with Listed for Heart-Liver Transplantation: A National Analysis.
1Duke School of Medicine, Durham, NC
2Dept of Surgery, Duke University Medical Center, Durham, NC
Meeting: 2017 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 39
Keywords: Heart failure, Liver failure, Survival
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Heart Waitlist and Allocation: Working to Get It Right
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, April 30, 2017
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Presentation Time: 3:42pm-3:54pm
Location: E267
Background: Simultaneous heart-liver transplantation (TXP), for patients with combined heart and liver failure, confers survival benefit over remaining on the waitlist. Whether heart TXP followed by sequential liver TXP can match the benefit of simultaneous TXP is unknown. Our objective was to determine if simultaneous heart-liver TXP conferred a survival advantage to sequential heart-liver TXP.
Methods: The OPTN/UNOS STAR file was queried for adult recipients waitlisted for simultaneous heart and liver TXP. The UNOS thoracic and liver databases were linked and univariate survival analysis was used to determine overall survival.
Results: 237 patients met inclusion criteria; 200 (84%) underwent simultaneous TXP (SHL), 7 (3%) sequentially underwent liver TXP (LAH), and 30 (13%) did not go on to liver TXP (HnoL). There was no significant difference in recipient demographics including age, gender, ethnicity, BMI, diabetic status, diabetic status, and dialysis requirement between all three groups (p's>0.05). Donor SHL patients were more likely to have required inotropic support at procurement (39%, HnoL 38%, LAH 14% p=0.04). Initial MELD, albumin, rates of encephalopathy, serum Cr, initial ascites, and initial Na+ were similar between matched groups. HnoL candidates had higher INR (1.6, LAH 1.1, SHL 1.3, p<0.001) but lower bilirubin (0.7, LAH 1.2, SHL1.0, p=0.005). SHL patients were less likely to experience rejection in the first year (2.5%, LAH 14.3%, and HnoL 13.8%, p=0.007). LAH conferred a significant 10-year survival advantage (53.6%) compared to SHL (52.1%), and HnoL (27.5%) (log rank =0.003).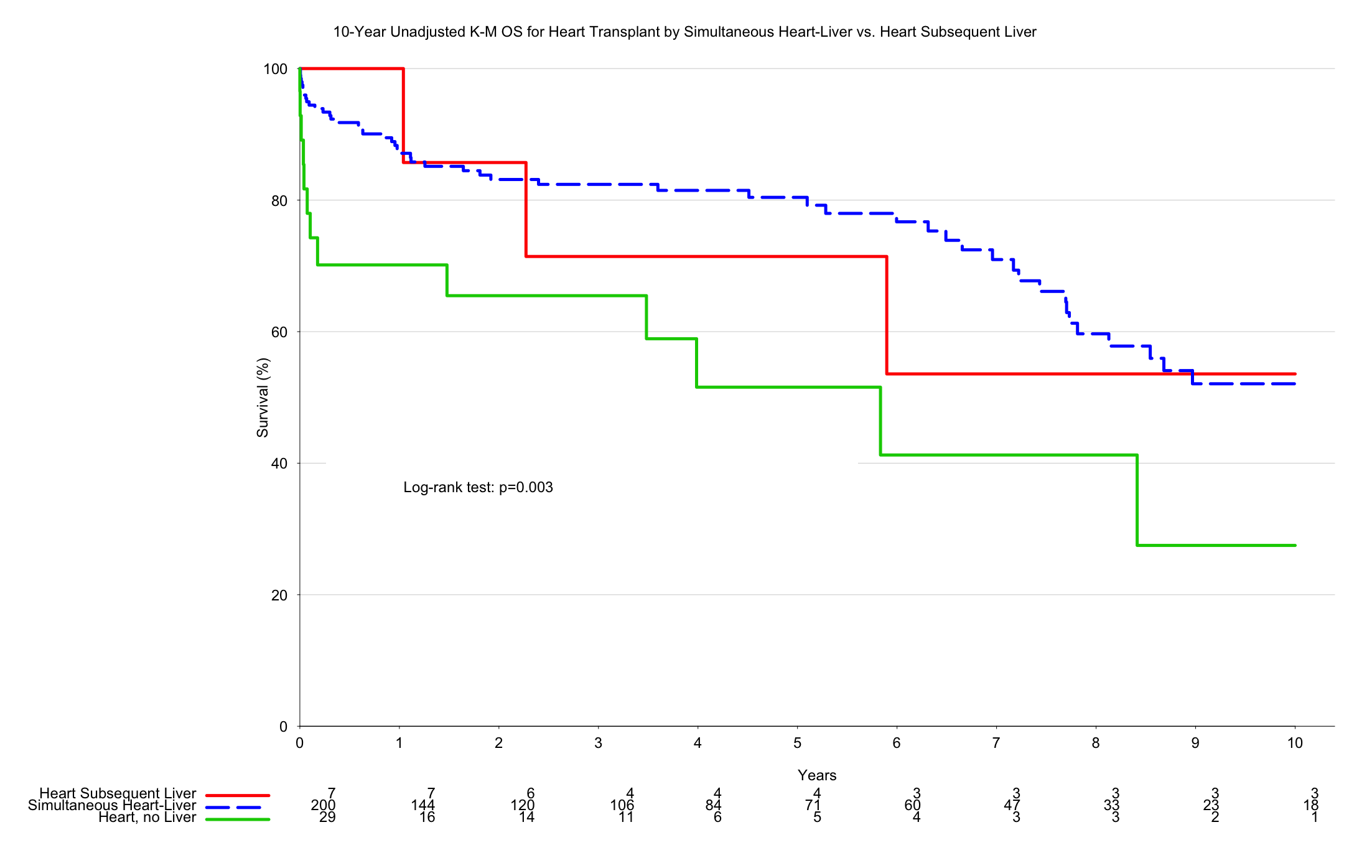 Conclusions: Combined heart-liver TXP confers survival advantage to heart transplant alone in patients listed for heart-liver TXP. TXP in a simultaneous or sequential fashion yields equivalent outcomes. In patients with combined heart and liver failure with a projected need for two allografts, simultaneous TXP maximizes the utility of the scarce cardiac allograft.
Conclusions: Combined heart-liver TXP confers survival advantage to heart transplant alone in patients listed for heart-liver TXP. TXP in a simultaneous or sequential fashion yields equivalent outcomes. In patients with combined heart and liver failure with a projected need for two allografts, simultaneous TXP maximizes the utility of the scarce cardiac allograft.
CITATION INFORMATION: Anderson K, Mulvihill M, Yerokun B, Barbas A, Hartwig M. Simultaneous or Sequential Heart-Liver Transplantation Confer Superior Survival in Patients with Listed for Heart-Liver Transplantation: A National Analysis. Am J Transplant. 2017;17 (suppl 3).
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Anderson K, Mulvihill M, Yerokun B, Barbas A, Hartwig M. Simultaneous or Sequential Heart-Liver Transplantation Confer Superior Survival in Patients with Listed for Heart-Liver Transplantation: A National Analysis. [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2017; 17 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/simultaneous-or-sequential-heart-liver-transplantation-confer-superior-survival-in-patients-with-listed-for-heart-liver-transplantation-a-national-analysis/. Accessed March 13, 2026.« Back to 2017 American Transplant Congress
