Screening Recipients of Increased Risk Donor Organs: A Multicenter Study
1Infectious Diseases, The Ohio State University, Columbus, OH
2Infectious Disease, Cleveland Clinic, Cleveland, OH
3Infectious Diseases/Organ Transplantation, Northwestern University, Chicago, IL.
Meeting: 2015 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 20
Keywords: Hepatitis C, HIV virus, Infection, Screening
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Donor-Derived Infection/Lifestyle/Tourism/Vaccines
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, May 3, 2015
Session Time: 2:15pm-3:45pm
 Presentation Time: 2:15pm-2:27pm
Presentation Time: 2:15pm-2:27pm
Location: Room 115- AB
Purpose:
Policy mandates post-transplant (tx) evaluation of recipients of increased risk donor organs (ROIRDO). PHS guidelines recommend that screening include HIV & hepatitis C virus (HCV) nucleic acid testing (NAT) between 1 and 3 months post-tx and testing for hepatitis B virus (HBV) between 1 and 3 months and at 12 months post-tx. Follow-up testing of ROIRDO is not routinely conducted and tracked. The purpose of our study was to evaluate the current post-tx screening algorithms and their results.
Methods:
After IRB approval, all medical records of ROIRDO transplanted from 2008 – 2012 at 3 transplant centers were abstracted. Descriptive statistics were used.
Results:
308 organ recipients from 193 distinct increased risk donors were evaluated. Recipient and donor demographics are shown in Table 1. The identified donor risk factors are shown in Figure 1.
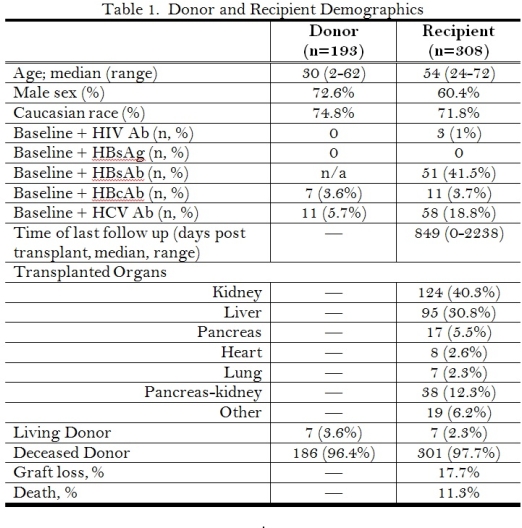
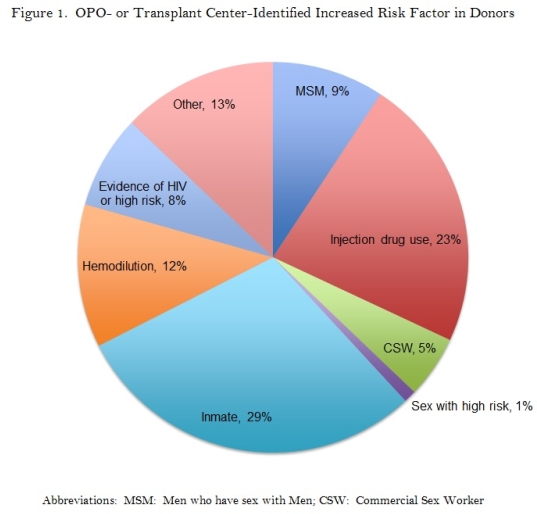
Post-tx screening at 1 month (median 36 days) was performed in 136 (44.2%), at 3 months (median 102 days) in 93 (30.2%) and at 1 year (median 353 days) in 26 (8.4%). At the first screening time point the following tests were used for HIV: 114 (83.8%) HIV Ab and 89 (65.4%) HIV NAT; HBV: 126 (92.6%) HBsAg, 25 (18.4%) HBcAb, 91 (66.9%) HBV NAT; HCV: 119 (87.5%) HCV Ab, 100 (73.5%) HCV NAT. There were no documented HIV, HBV or HCV transmissions.
Conclusions:
Adherence to post-transplant screening of ROIRDO was poor and declined substantially at 3 and 12 months. Further, use of serology without NAT, which has been demonstrated to result in missed recognition of transmitted infection, was also documented in 16-22% of episodes of screening. These data underscore an opportunity to improve screening of ROIRDO and detection of rare transmission events.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Theodoropoulos N, Brizendine K, Ison M. Screening Recipients of Increased Risk Donor Organs: A Multicenter Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2015; 15 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/screening-recipients-of-increased-risk-donor-organs-a-multicenter-study/. Accessed February 23, 2026.« Back to 2015 American Transplant Congress
