SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response After Induction Therapy in Kidney Transplant Recipients
M. Lubetzky1, S. Sultan2, Z. Zhao3, M. Cushing3, Z. Kapur1, S. Albakry1, N. Hauser1, J. Marku-Podvorica1, R. Craig-Schapiro2, J. Lee1, T. Salinas1, M. Aull2, S. Kapur2, M. Suthanthiran1, D. Dadhania1
1Nephrology, Weill Cornell-NYPresbyterian, New York, NY, 2Transplant Surgery, Weill Cornell-NYPresbyterian, New York, NY, 3Pathology, Weill Cornell-NYPresbyterian, New York, NY
Meeting: 2021 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 61
Keywords: Antibodies, Infection, Kidney transplantation
Topic: Clinical Science » Infectious Disease » Kidney Infectious Non-Polyoma & Non-Viral Hepatitis
Session Information
Session Name: COVID-19 in Kidney Recipients
Session Type: Rapid Fire Oral Abstract
Date: Saturday, June 5, 2021
Session Time: 6:00pm-7:00pm
 Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:15pm
Presentation Time: 6:10pm-6:15pm
Location: Virtual
*Purpose: SARS-CoV-2 antibody prevalence in kidney transplant recipients is beginning to be reported, although little is known about the humoral immune response in the immediate post-transplant period when immunosuppressive therapy burden is highest and graft recipients are least likely to mount a robust immune response.
*Methods: Patients transplanted from May 28, 2020 until October 1, 2020 (n=78) were followed prospectively. SARS-CoV-2 antibody testing was performed at the time of transplant. Semi-quantitative IgM and IgG data was collected on a subset of patients and followed both before and after transplant.
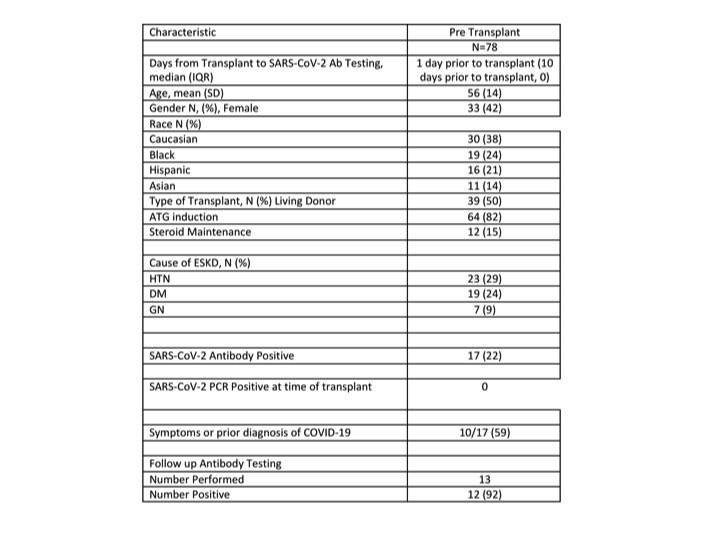
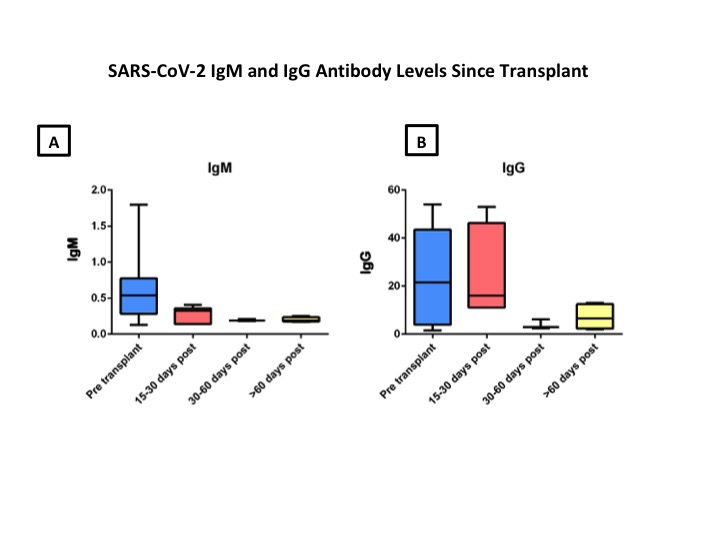
*Results: At the time of kidney transplantation, SARS-CoV-2 antibody prevalence was 22%. Patient demographics are shown in Table 1. Of the patients with a positive antibody (n=17), 10 either had symptoms consistent with COVID-19 infection or had documented SARS-CoV-2 PCR positive testing prior to transplant. A total of 13 patients had follow-up antibody testing between 30 and 60 days post transplantation and 12 (92%) had persistent antibodies at the time of follow up. Figures 1A and B demonstrate box and whisker plots of the median and the 25th and 75th percentile values (bottom and top of each box, respectively), levels of IgM and IgG from the pre- and post-transplant period. Both SARS-CoV-2 IgM and IgG antibody levels declined in the post transplantation period but remained above the threshold for positivity (an index value of 1) despite induction therapy with ATG and the initiation of maintenance immunosuppression with CNI and MMF. To date, none of the 78 patients transplanted has manifested new or recurrent SARS-CoV-2 infection.
*Conclusions: SARS-CoV-2 antibodies remain positive despite the high dose immunosuppression in the early post transplant period. Our data provide a framework for future prospective studies on the kinetics and isotype of SARS-CoV-2 antibody response and as an essential reference to gauge immune response following vaccination.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Lubetzky M, Sultan S, Zhao Z, Cushing M, Kapur Z, Albakry S, Hauser N, Marku-Podvorica J, Craig-Schapiro R, Lee J, Salinas T, Aull M, Kapur S, Suthanthiran M, Dadhania D. SARS-CoV-2 Antibody Response After Induction Therapy in Kidney Transplant Recipients [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2021; 21 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/sars-cov-2-antibody-response-after-induction-therapy-in-kidney-transplant-recipients/. Accessed February 27, 2026.« Back to 2021 American Transplant Congress