Safety and Efficacy of Imlifidase in Highly-Sensitized Kidney Transplant Patients: Results from a Phase 2 Study
1Cedars-Sinai Medical Center, Los Angeles, CA, 2Hopital Necker, Paris, France, 3Johns Hopkins University, Baltimore, MD, 4Uppsala University, Uppsala, Sweden, 5Hansa Medical AB, Lund, Sweden, 6NYU Langone Health Transplant Institute, New York, NY, 7University of Oxford, Oxford, United Kingdom
Meeting: 2019 American Transplant Congress
Abstract number: 29
Keywords: Highly-sensitized, Kidney transplantation
Session Information
Session Name: Concurrent Session: Kidney Immunosuppression: Desensitization
Session Type: Concurrent Session
Date: Sunday, June 2, 2019
Session Time: 2:30pm-4:00pm
 Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Presentation Time: 3:06pm-3:18pm
Location: Ballroom A
*Purpose: Many patients eligible for kidney transplantation are sensitized to allo-HLA antigens and face prolonged waiting times and increased mortality. The presence of donor specific antibody (DSA) portends inferior allograft survival. Currently available desensitization strategies have variable effectiveness and side effects. Imlifidase is an enzyme that rapidly cleaves human IgG antibodies and is being evaluated in sensitized patients with a low likelihood of receiving a compatible kidney by any other available modalities.
*Methods: This single arm, 6-month, open label trial assessed imlifidase in abrogating a positive crossmatch (CXM) following drug delivery, enabling renal transplantation. The primary end-point was conversion of a positive to a negative CXM (CDC or Flow Cytometry) to either a living or deceased donor kidney.
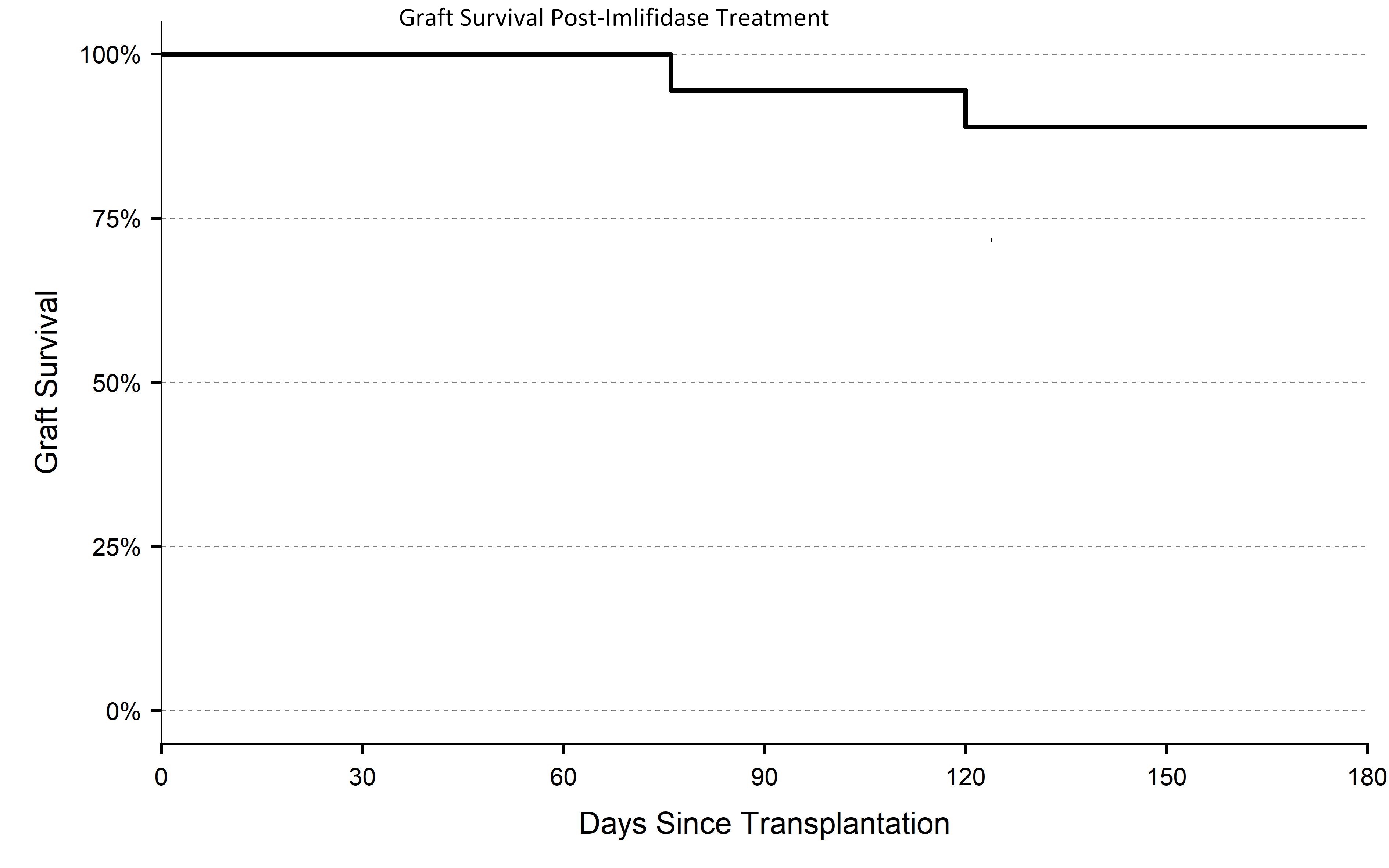
*Results: 18 patients were enrolled with a median calculated PRA of 99.6% and a mean fluorescence intensity [MFI] >2000. All patients had a positive CXM to their donor and half with an immunodominant DSA >12000 MFI. Following imlifidase infusion 17/18 patients converted to a negative CXM; 1 was borderline FCXM positive and virtual CXM negative. At end of study, patient survival was 100%, graft survival was 89% (figure); the median eGFR was 50 (95% CI 36-61). There were 2 graft losses due to primary nonfunction; 25% of patients had biopsy-proven antibody mediated rejection (AMR). All AMRs were effectively treated using standard of care therapy. There were no treatment-related safety concerns.
*Conclusions: Imlifidase, which was well tolerated, enabled all patients to undergo transplantation resulting in good kidney function and graft survival. Frequency of AMR was at a similar level as previously reported for highly sensitized patients undergoing other desensitization protocols. Most AMR episodes were attributable to DSA rebound which generally occurs 7-10 days after imlifidase treatment. Imlifidase is a promising new agent that may enable kidney transplantation for highly sensitized patients, who would otherwise have no hope for a lifesaving transplant.
To cite this abstract in AMA style:
Jordan SC, Legendre C, Desai N, Lorant T, Bengtsson M, Laxmyr L, Lonze B, Vo A, Wood KJ, Kjellman C, Montgomery RA. Safety and Efficacy of Imlifidase in Highly-Sensitized Kidney Transplant Patients: Results from a Phase 2 Study [abstract]. Am J Transplant. 2019; 19 (suppl 3). https://atcmeetingabstracts.com/abstract/safety-and-efficacy-of-imlifidase-in-highly-sensitized-kidney-transplant-patients-results-from-a-phase-2-study/. Accessed March 3, 2026.« Back to 2019 American Transplant Congress